
Repository
What Will I Learn?
- You will learn the Heritage.
- You will learn the Visibility.
- You will learn Overriding and Polymorphism.
Requirements
- You need to have Ruby installed on your computer
Difficulty
- Basic
Tutorial Contents
1- Heritage
Heritage is one concept in all programming languages. It is derived from real life, where the child inherits from his father the qualities and actions and everything that is specific to him. From this concept the heritage was applied to programming languages.
Assuming that people are a classes, when a son inherits from his father is the same thing when the class inherits from another class, it will take all the variables and functions and the constructors of the father.
We will give a simple example, we have a class Human and we want to create a class professor where the professor is also a human , what can we understand? Since the professor is also a human , he has a name, age and sex and some of the functions he performs. Moreover, the professor has other things such as the salary.
class Professor < Human # Heritage
def initialize(name, sex, age, salary) # creation of constructor
super(name, sex, age) // call to the super method for the super constuctor
@salary=salary // add the salary to the salary variable
endWhen creating an object from a human class, we create the name, the sex and the age of the person, since the professor class is also a human. When we create it we do not add another constructor, but we call the function super and only add information about the professor.
The constructor of the human class contains the " name, age and sex ", when we create the professor we need to add just the " salary " and for that we don't need to create new constructor with all these parameters but we will add just the salary to the super constructor of " Human ".
I want to give you three functions that we will use :
a- is_a(class) Function
This function will test if the object is an object from the class passed as parameter or not, it return a boolean value.
b- instance_of?(class) Function
This function also will test if the object is an instance of the class passed as parameter or not, so if we have an object from the human class " h1 " and we want to see if this object is from human or not we will call this function and see the result ( True/False).
c- kind_of?(class) Function
This function also the same concept of the other functions , will test the relation of the class passed as parameter and the object, it returns a boolean value.
Let's apply these functions and see the result of the heritage
h1=Human.new("Alex", "m", 20) #creation of object from Human class
puts "h1 is an instance of human" if h1.instance_of?(Human) #an Object of the Human class
puts h1.class #Human
prof1=Professor.new("Alex", "m", 20, 2000)
puts "prof1 is an instance of Professor class" if prof1.instance_of?(Professor)
puts prof1.class #Professor
puts h1.is_a?(Human) #is h1 a human ?
puts h1.is_a?(Professor) # is h1 an professor ?
puts prof1.is_a?(Professor) # is prof1 an professor?
puts prof1.is_a?(Human) # is prof1 a human ?
puts prof1.instance_of?(Human)We've created two objects " h1 " from " human" and " prof1 " from " professor ". I have applied the functions
is_a :
I have tested if h1 is a human or not and if prof1 is professor or not.
instance_of :
I have tested if the prof1 is an instance of human or not.
This is the output, the functions has returned " true and false " you can understand from the output how to use these functions :
h1 is an instance of human
Human
prof1 is an instance of Professor class
Professor
true
false
true
true
false Let's now create a complete example with the human, professor and university classes
class Human
@@NUMBER_OF_HUMANS=0
#The Constructor
def initialize(name, sex, age)
@name =name
@sex =sex
@age=age
@legs=2
@eyes=2
@@NUMBER_OF_HUMANS += 1
end
attr_accessor :name, :age
attr_reader :sex
def move()
#moving code
end
def sleep()
#sleeping code
end
def drink()
#drinking code
end
def Human.numberOfHumans
return @@NUMBER_OF_HUMANS
end
end
class Professor < Human
attr_accessor :salary
def initialize(name, sex, age, salary)
super(name, sex, age)
@salary=salary
@state=""
end
def work
#working code
end
def getHired(salary)
@salary=salary
@state="hired"
end
def getFired
@salary=0
@state="fired"
end
def profInfo
s="Name: " << @name
s << ", State: " << @state
s << ", Salary: " << @salary.to_s
return s
end
end
class University
def initialize(university_name, administrator)
@university_name=university_name
@administrator=administrator
@profs=[]
end
def raiseProfessor(prof, raise)
prof.salary += raise
puts @administrator + ": " + prof.name + " is raised!\n"
end
def hire(prof, salary)
prof.getHired(salary)
@profs.push(prof)
puts @administrator + ": " + prof.name + " is hired.\n"
end
def fire(prof)
prof.getFired
@profs.delete(prof)
puts @administrator + prof.name + ": " + "is fired.\n"
end
def profsList
return @profs
end
end
#demo
university=University.new("Oxford", "Alex Harry")
$Alex=Professor.new("Alex", "m", 20, 2000)
$Tina =Professor.new("Christina", "f", 35, 4000)
$Sordin = Professor.new("Sordin", "m", 32, 3000)
def profsInfo
puts "----------------"
lst=[$Alex, $tina, $Sordin]
for prof in lst
puts prof.profInfo
end
puts "----------------"
end
puts "Hiring..."
university.hire($Alex, 2500)
university.hire($Tina, 2500)
university.hire($Sordin, 3000)
$Alex.profInfo
$Tina.profInfo
$Sordin.profInfo
puts "Firing Sordin..."
university.fire($Sordin)
profsInfo
university.raiseProfessor($Alex, 1000)
profsInfo
puts "--------------"
puts "The list of professors: "
for prof in university.profsList
puts prof.name
endHuman Class :
In the human class I have created the constructor with 3 variables " name, sex and age", and inside I have added some constants variables " eyes and legs ", and also when the constructor has been executed the number of humans will be +1
And I have created also 4 functions " move, sleep, drink and the number of humans that return the number of humans created ".
Professor Class :
In the professor class I have added another variable which is " salary ", as we mentioned because the professor is also a human so he will take the " name,sex and age", I have added the salary to the constructor and I have used the " super " method.
I have created 4 functions for the professor " work, getHired that changes the state to " hired ", getFired that changes the state to "fired " and sets the salary to 0 and finally profInfo that combine between the informations of the user and returns them in a variable called " s ".
University Class :
In the university class we have other variables so we have a new constructor with the ' university_name and administrator ' as parameters to the constructor and an array " profs " .
I have created 4 functions for the university " raiseProfessor to raise the salary of the professor by the value passed as parameter, hire to add the professor to the list of professors and to call getHired, fire to delete a professor from the list of professors and to call getFired, and finally profsList to return the list of professors ".
Alex Harry: Alex is hired.
Alex Harry: Christina is hired.
Alex Harry: Sordin is hired.
---------------
Name: Alex, State: hired, Salary: 2500
Name: Christina, State: hired, Salary: 2500
Name: Sordin, State: hired, Salary: 3000
--------------
Firing Sordin...
Alex Harry Sordin: is fired.
---------------
Name: Alex, State: hired, Salary: 2500
Name: Christina, State: hired, Salary: 2500
Name: Sordin, State: fired, Salary: 0
---------------
Alex Harry: Alex is raised!
---------------
Name: Alex, State: hired, Salary: 3500
Name: Christina, State: hired, Salary: 2500
Name: Sordin, State: fired, Salary: 0
---------------------------
The list of professors:
Alex
ChristinaI have created a university object from University class and 3 profs " Alex,Tina and Sordin", I have created a list of these professors and I have called the function " profInfo " to get the informations about each professor.
I have called the function " Hire " with 3 different names " Alex,Christina and Sordin", I have called " Fire " for Sordin so its salary is now 0, when we call " profsInfo " it will return the professors and Sordin with a salary 0, Than I have raised the professor Alex with 1000$ , finally I have printed the professors with and without Sordin after deleting him from the list.
This is the output of this code :
2-Public/Private/Protected
When we say " public, private and protected " you will think directly to the accessibility, these indicators will protect your variables, classes and functions ..etc.
Public :
It's accessible by all, it's in the public without any obstructions and protection.
Private :
When the visibility is " private " means that the variables , functions ..etc accessible just in the class.
Protected :
It's like the "private", but it's accessible only through the class or from the classes that derived from it or let's say its children.
Let's now create an example to see the difference between these indicators.
class Human
def move
end
def sleep
end
def drink
end
end
class Professor < Human
endSo I have created two classes " Human and Professor " as the previous example, the Human class contains 3 public methods " move, sleep and drink", and the class Professor which inherits from Human.
Let's create two object, the first from Human and the second from Professor.
h1=Human.new()
prof1=Professor.new()We can simply call the methods in the Human class because they are " public ", we know in many languages that we use " private and protected " to protect the accessibility, in Ruby "private = protected" it means they have the same effect.
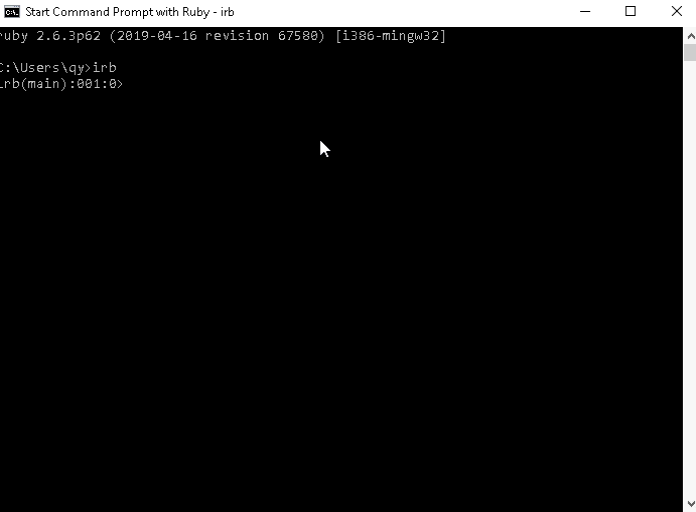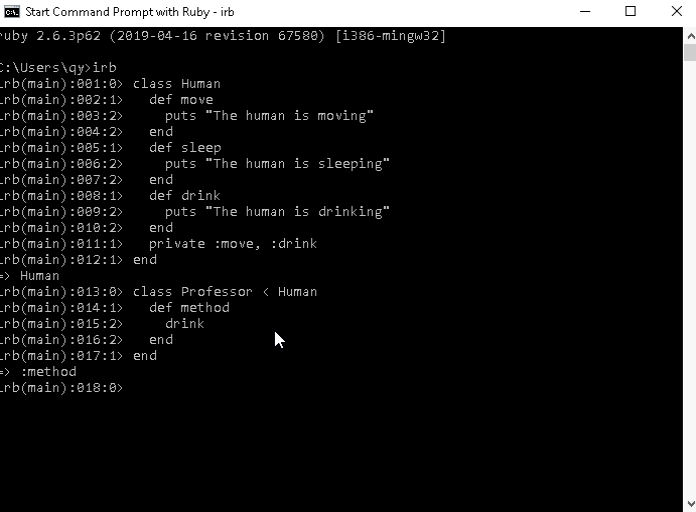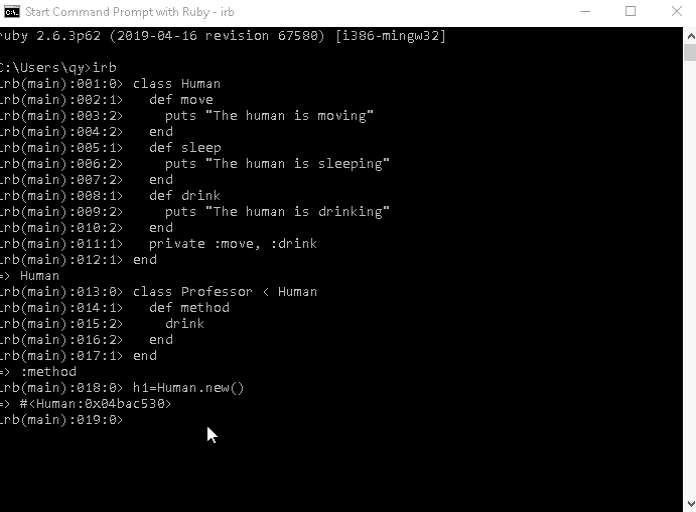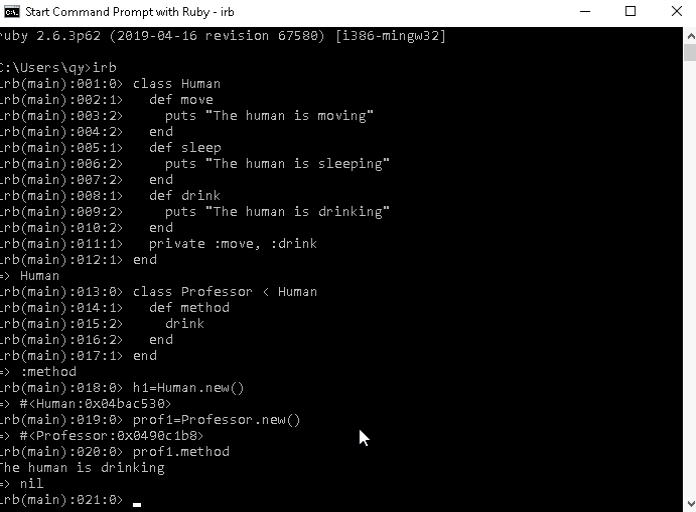
class Human
def move
puts "The Human is moving"
end
def sleep
puts "The human is sleeping"
end
def drink
puts "The human is drinking"
end
private :move, :drink
end
class Professor < Human
def method
drink
end
endLet's create two object, the first from Human and the second from Professor and I will call the method of the professor object.
h1=Human.new()
prof1=Professor.new()
prof1.methodWe can see that the object "prof1" can access to the function " drink " although its a private function.
3- Overriding and Polymorphism
a- Overriding
The redefinition of a method exists in the parent or in the original class to be defined in the child class in a different way compatible with the work of the class.
class A
def method1
puts "A's method1 is called"
end
def method2
puts "A's method2 calling method3.."
method3
end
def method3
puts "A's method3 is called"
end
private :method1, :method3
end
class B < A
def method2 #override the protected method
puts "B's method2 is called"
end
def method4
puts "Calling method1..."
method1
end
endWe have two classes A and B, the class A contains 3 methods " method1, method2 and method3" two of them are privates, the class B extends from A so it can call any method in the parent class " A ", in the class B I have created " method2 " or in other words I have copied the method and change in it and this action called " Overriding ".
a=A.new()
#Calling the parent's method2
a.method2
b=B.new()
#Calling the overriden method2 in the child b.method2I have created two object a from A and b from B, I have called method2 by " a and b ", if I call method3 for example by " b " we will get " A's method3 is called ", but we have used " overriding " so the method called by " b" will be the method in the class "B", and this is the result :
output =>
A's method2 calling method3..
A's method3 is called
B's method2 is called b- Polymorphism
The polymorphism is very known in programming, it means one method with many different forms, for example in Java the polymorphism is a method duplicated but with different parameters or types of parameters, in Ruby is the same thing a method duplicated but with different content.
class A
def method1
puts "A's method1 is called.."
end
end
class B
def method1
puts "B's method2 is called.."
end
endWe have two classes A and B, each one contains a method called " method1 ", the content of method1 in class A is not the same content of the method in the class B, " A's method1 is called.. " and " B's method2 is called.. ".
a=A.new()
b=B.new()I have created two objects " a from A " and " b from B ", I can simply call the methods using these objects and I want to give you two different ways to call the methods:
a.method1
b.method1
# or
objects=[a, b]
for obj in objects
obj.method1
endThe first way is the simple way so we can directly call the method using the object.
The second way is to create an array [a,b], to use a " for " loop and call the method1 by each object.
This is the result :
#output =>
#A's method1 is called..
#B's method2 is called..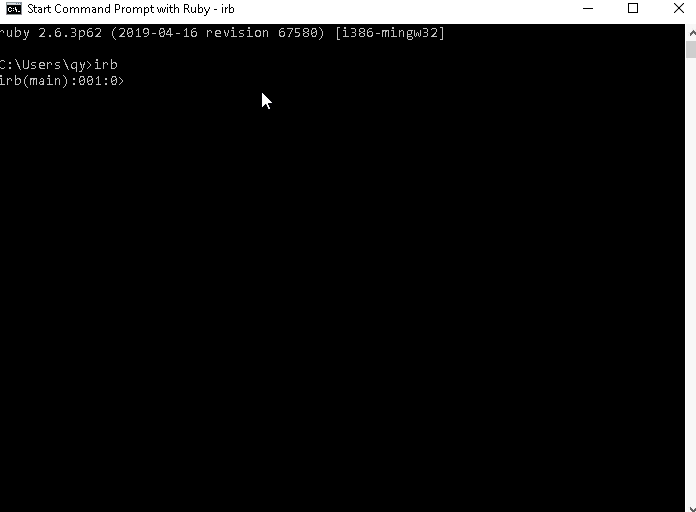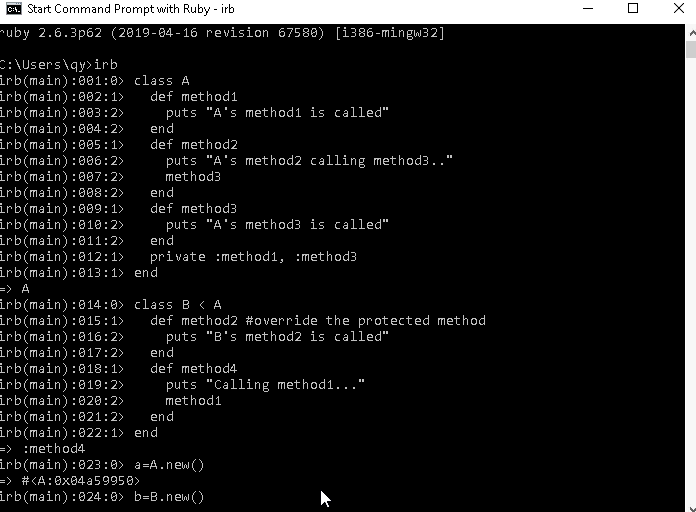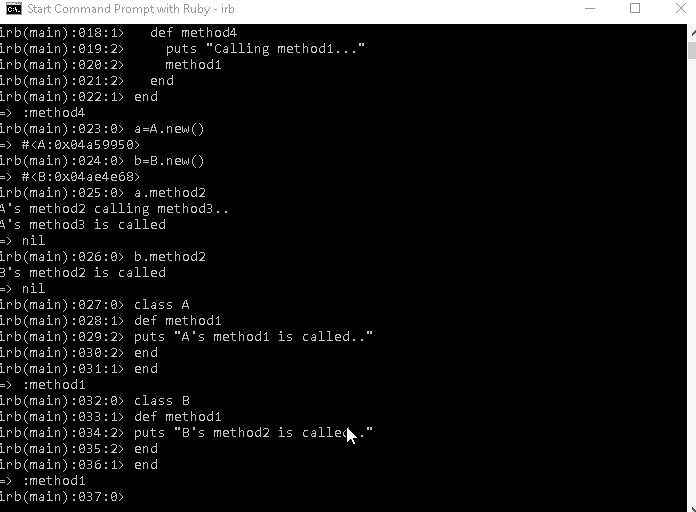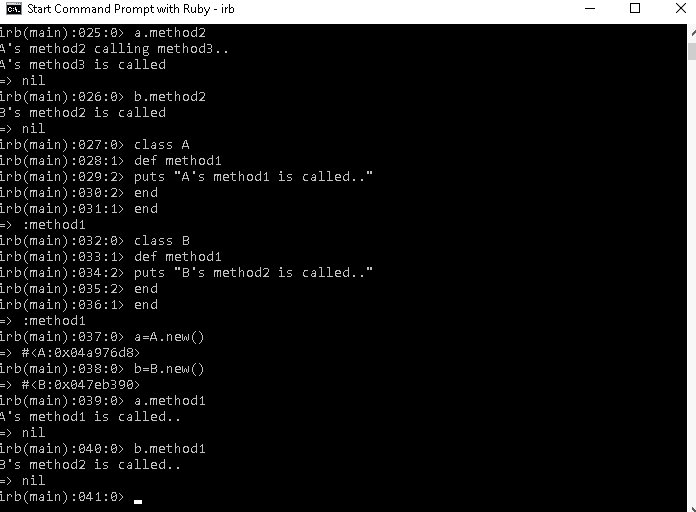
Curriculum
Proof of Work Done
https://github.com/alex-harry/rubyTutorial/blob/master/ruby2.rb
Thank you for your contribution @alex-harry.
After reviewing your contribution, we suggest you following points:
Using the first person in the tutorials makes it difficult to understand the tutorials. We suggest using the third person in your text.
Nice work on the explanations of your code, although adding a bit more comments to the code can be helpful as well.
Using GIFs to show results is definitely better than standard still images.
In your next tutorial try to improve the structure of the contribution.
Thanks for following some of our suggestions from your previous tutorial.
Looking forward to your upcoming tutorials.
Your contribution has been evaluated according to Utopian policies and guidelines, as well as a predefined set of questions pertaining to the category.
To view those questions and the relevant answers related to your post, click here.
Need help? Chat with us on Discord.
[utopian-moderator]
Thank you for your review, @portugalcoin! Keep up the good work!
Hi @alex-harry!
Your post was upvoted by @steem-ua, new Steem dApp, using UserAuthority for algorithmic post curation!
Your post is eligible for our upvote, thanks to our collaboration with @utopian-io!
Feel free to join our @steem-ua Discord server
Congratulations @alex-harry! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Hey, @alex-harry!
Thanks for contributing on Utopian.
We’re already looking forward to your next contribution!
Get higher incentives and support Utopian.io!
Simply set @utopian.pay as a 5% (or higher) payout beneficiary on your contribution post (via SteemPlus or Steeditor).
Want to chat? Join us on Discord https://discord.gg/h52nFrV.
Vote for Utopian Witness!