In the last little tutorial you might‘ve asked yourself where we got the IP-Addresses from when we typed the arpspoof command:

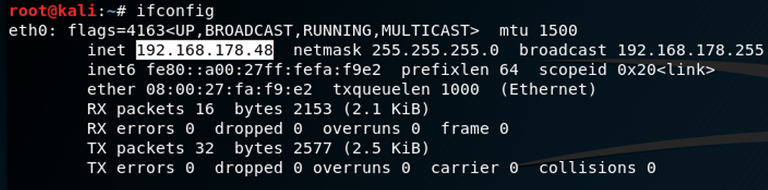
First you find out what your IP-Address is by typing:
ifconfig
or
ip a
which will give you the following output
Nmap:
Nmap is a so called portscanner which means you can use this tool to see which ports are open on a given server or on a computer in your network. Nmap is in the reposetories of most Linux distributions and can be installed via your packet manager.
It can also be used to evaluate the machines on a local area network which we are going to do now.
We‘ll now run the following command.
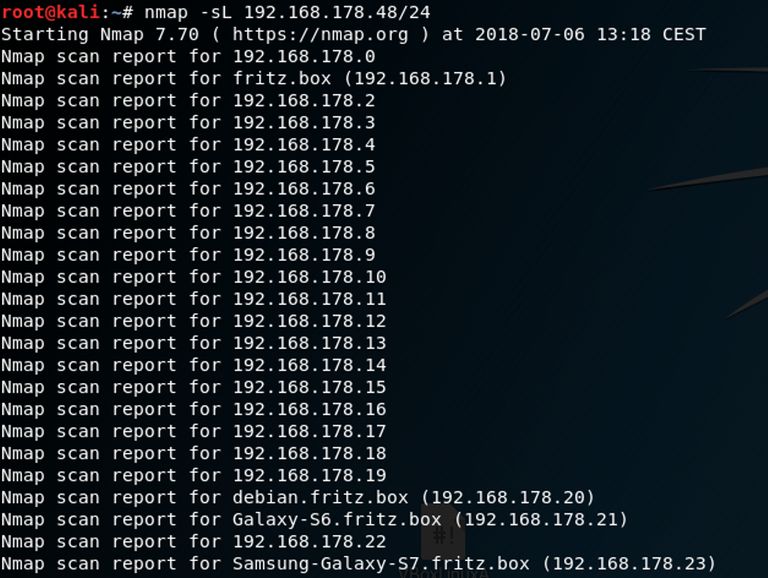
where nmap is the name of the program we‘re using
-sL: is the list-scan which evaluates all given hosts on a network
192.168.178.46/24: is our IP-Address and the bits(the /24) for the given subnet. If you don‘t know what a subnet is, you can read about it here.
The problem with this scan is that we now know about all the hosts in the network but not which hosts are actually up.
Therefore we‘ll use another option to scan the network.
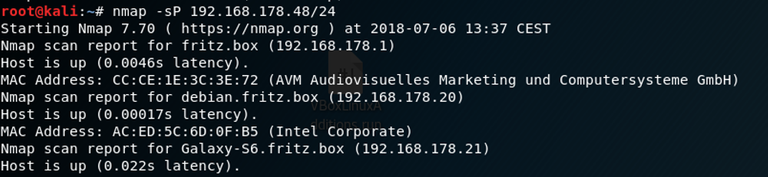
You can see that the command is almost the same as before instead of the -sP we are using, which is the Ping-Scan. This type of scan pings all given hosts to see which one is up and responding.
So that‘s it for today. If you want to know more about Nmap and its options you can always type
nmap -h
which will give you all the available options for scanning. Maybe we‘ll have a deeper look at it in the future because there are a lot more scenarios of how to utilize nmap.
Stay safe as you sail the ocean of information out there!!
@toalsty you were flagged by a worthless gang of trolls, so, I gave you an upvote to counteract it! Enjoy!!