In this post, I would like to introduce a topic that is part of my research.
In wireless networks [1, 3], computers communicate with each other through a non-physical medium, using radio waves. A wireless network can be configured to function in either Basic Service Set (BSS) or Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS) mode [3]. In BSS mode or infrastructure mode, mobile devices communicate with each other through a non-mobile Base Station (BS) as access point. IBSS or ad hoc mode, allow wireless devices point-to-point communication, i.e., no access point nor fixed infrastructure is needed.
An ad hoc network consists of wireless devices that may be mobile and can communicate without the need of a fixed infrastructure. In a Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET), the network topology may change dynamically since nodes can move in an unpredictable manner [2, 1]. Nodes are free to move at any speed in any direction and join or leave the network at any time. Nodes with heterogeneous capabilities (e.g., transmission range) can coexist. In [1], Agrawal and Zeng formally define a MANET as an autonomous system of nodes or Mobile Stations (MSs) connected by a wireless medium. This network may be modeled in the form of an arbitrary communication graph.
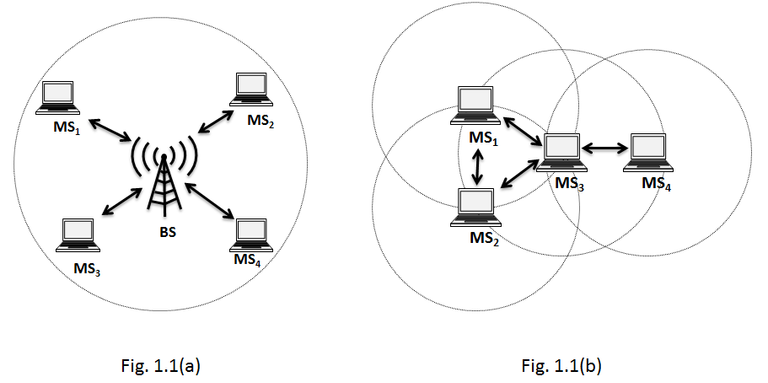
In a MANET, every node is able to communicate directly with other nodes within its range. Nodes with direct communication are called neighbors. Any pair of nodes not directly connected, can communicate through a path formed by other nodes. MANETs are basically peer-to-peer, multihop wireless networks [1]. The established links can be either symmetric (i.e., links with the same characteristics in both directions) or asymmetric (i.e., links with different characteristics in each direction). Information packets are transmitted in a store-and-forward manner by intermediate nodes, i.e., every node acts as arouter. In a MANET, every node configures its network address and can resolve the way to reach any destination. There is no need for an address communication server, e.g., DHCP server. Fig. 1.1(a), presents an example of a wireless network. Every pair of MSs has to commnicate throug the BS.Fig. 1.1(b), shows an example of a network in ad hoc mode. MSs within the same range can establish direct communication.
Characteristics of MANETs
The decentralized nature of MANETs provides additional robustness against the single point of failure in centralized approaches, e.g., BS or access point. MANETs can be deployed in scenarios where it is almost impossible to set up and maintain a wired network (e.g., a disaster area or a battlefield). MANETs have particular characteristics and restrictions [1]:
- Dynamic topologies: Nodes are free to move arbitrarily at different speeds. It is difficult to predict a node’s movement and its trajectory. Therefore, the network topology may change randomly and unpredictably.
2.Limited bandwidth: Wireless links have lower capacity than wired networks. Nowadays however, some standards offer better data rates comparable to those of Ethernet (e.g., WiMAX). Additionally, the throughput in wireless communication is affected by the conditions of the environment, fading, noise or interference. - Energy-constrained: In a MANET, nodes may rely on limited batteries as source of energy. Nodes do not have enough transmitting power to reach all nodes in the network. This restricts the nodes communication to only the neighboring nodes.
- Limitations of the medium: In a wireless network, is not possible to transmit and to listen at the same time. Message loss is more likely due to collisions and interference.
- Limited physical security: In MANETs, data packets travel across the air. Hence, it is relatively easy for an intruder to eavesdrop data packets by operating in promiscuous mode and by using a packet sniffer. Nodes may also be affected by intentional jamming or denial of service (DoS) attacks.
Gimer Cervera
Visit:
[1] D.-P. Agrawal and Q.-A. Zeng. Introduction to Wireless and Moile Systems. Thomson, 2ed edition, 2006.
[2] M. Barbeau and E. Kranakis. Principles of ad hoc networking. John Wiley and Sons, Ltd , ISBN: 9780470032909, 2007.
[3] D. Raffo. Security schemes for the OLSR protocol for ad hoc networks. PhD thesis, L’Université Paris 6 - Pierre et Marie Curie, INRIA Roquencourt, France, September 2005.
Excelent post gcervera! I never undestood the Characteristics of MANETs until now! crystal clear!
Congratulations @gcervera! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPGreat intro to the MANET. The day that we are able to have world wide high speed MANETS in combination with Block Chains and no further need for a centralized monetary system along with the ability to manufacture the required components locally, is the day that we become truly; Spaceship Earth!