INTRODUCTION
Robotic surgery also called computer-assisted surgery or robotically-assisted surgery are terminologies that define the technological development in medicine that uses robotic systems to assist surgical operations. This was invented to aggrandise the capacity of surgeons performing open surgery and to defeat the restriction of minimal-invasion (little incision) surgery. This is a new technology and one of the most discussed topics in surgery today. It is doubtless that they will become essential tools in the surgery armamentarium though still developing.
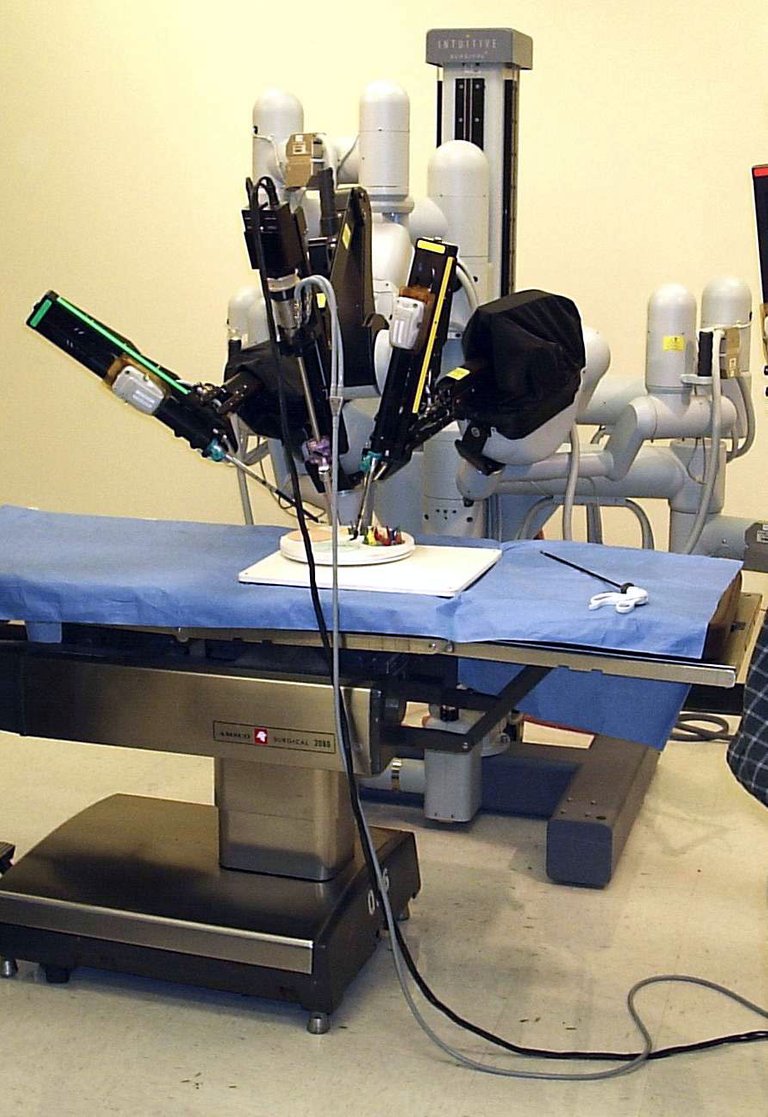
HISTORY OF ROBOTIC SYSTEMS
Successfully documented in 1985 was the first robotic surgical procedure using PUMA 560 robotic arm to place a needle for brain biopsy (an examination of tissue removed from a living body to discover the presence, cause, or extent of a disease), using CT guidance. Two years later, the PROBOT built at Imperial College, London was used to carry out a Prostatectomy (a surgical removal of prostate gland or all of the prostate) at Guy’s and St Thomas’ Hospital, London. Ever since then, several robotic surgery systems have been developed such as the ROBODOC from integrated surgical systems which was introduced in 1992 principally to mark out precise fittings in the femur for hip replacement. Now, the most used robotic system for surgical operation is the Da Vinci System which comprises of a high definition 3-dimensional system, a surgeon console and a patient-side which consist of four arms manipulated by the surgeon (one of which is used to operate the camera and the rest for instrument control).
HOW DOES ROBOTIC SURGERY WORK?
Robotic surgery involves a computer-aided surgical operation in which remote surgery is robotically controlled by a surgeon not close to the operation site. The robotic arms are controlled with the aid of a computer console by the surgeon while observing all the vital organs surrounding the operating tissues on a live big screen. With the help of a high resolution camera which is operated by the fourth robotic arm, the surgeon is able to capture the full area of operation. The remaining three arms are used to control the main operation from all angles.
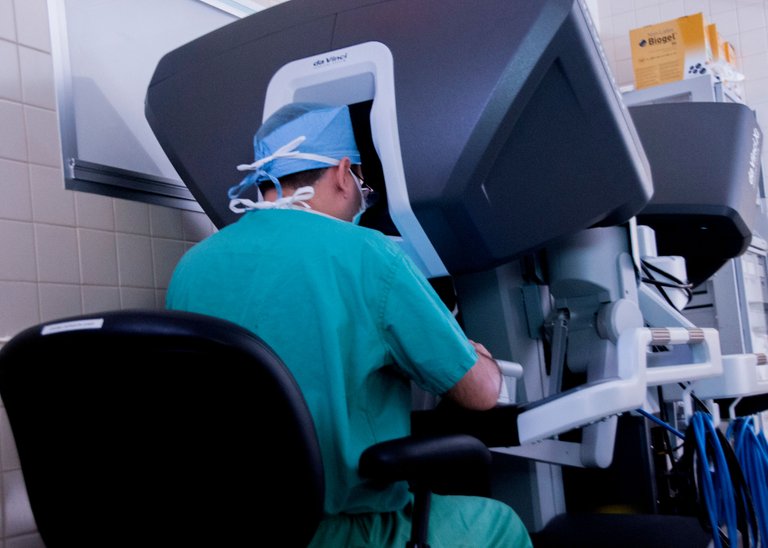
CONDITIONS THAT CAN BE HANDLED BY ROBOTIC SURGERY
Virtually every kinds of surgical operations traditionally done by surgeons can be done also with the computer-assisted surgery. This makes the work easier, less stressful and with more fun to the experienced surgeon (just like playing your video games, but with more carefulness as it involves life). Some of these conditions include:
• GENERAL: Pancreatic cancer, benign pancreatic lesions, liver tumors (benign and malignant), gallbladder cancer, severe gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD), obesity (gastric bypass, bariatric surgery, gastric banding)
• UROLOGICAL CONDITIONS: Bladder cancer, kidney disorders (kidney stones, kidney cysts, kidney blockage), kidney cancer, kidney removal, prostate cancer, incontinence, vaginal prolapse
• HEART: Mitral valve prolapse and repair, atrial septal defect, atrial fibrillation
• HEAD AND NECK: Head and neck cancer (oropharyngeal cancer), thyroid cancer
• GYNECOLOGIC: Endometriosis, gynecologic cancers (ovarian/cervical cancer), heavy uterine bleeding, uterine fibroids, uterine prolapse, ovarian cysts, benign cervical disorders
• LUNGS: Some lung tumors, esophageal cancer and diseases
John Hopkins Medicine
It is obvious that computer-assisted-surgery has all it takes to replace the traditional style of carrying out these operations coupled with the fact that they are not left to operate independent of human supervision, which directly implies that human intelligence of making moral judgement is involved.
BENEFITS OF EMPLOYING A ROBOTIC SURGERY
During the traditional surgical operation, the long incision method is often employed which leads to scaring, pains and longer recovery period for the patient. But in the robotic method, the minimal incision method is most appreciated and effective, causing less pain, shorter recovery time and less tendency of infection.
Also, the use of a powerful, high resolution camera enables the operation site to be well visualized. A zooming technology is also made available to enable a clearer vision of the point of operation enabling the robotic arms controlled by the surgeon (the arm totally mimics the hands and finger motion of the surgeon at equal range) to get the precise site of target. The major advantages of using the computer-assisted surgery include:
• GREATER VISUALISATION: The surgeon, while in operation, looks through the high resolution camera which simply gives a clearer picture and magnifies the site onto the live big screen.
• IMPROVED DEXTERITY: The surgeon’s hand, wrist and finger movements are transmitted through the computer console to the instruments connected to the robot’s arms. The mimicked movements have the same range of motion as the surgeon allowing maximum control and manipulation.
• ENHANCED PRECISION: Now the surgeon working from the control room is capable of making tiny and precise incisions on the patient with the help of the camera which actually amplifies the area of concentration and reduces every possible mistake of handling the wrong point as we may easily experience in the traditional method.
Other benefits include:
• Shorter hospitalization
• Reduced pain and discomfort
• Faster recovery time and return to normal activities
• Smaller incisions, resulting in reduced risk of infection
• Reduced blood loss and transfusions
• Minimal Scaring
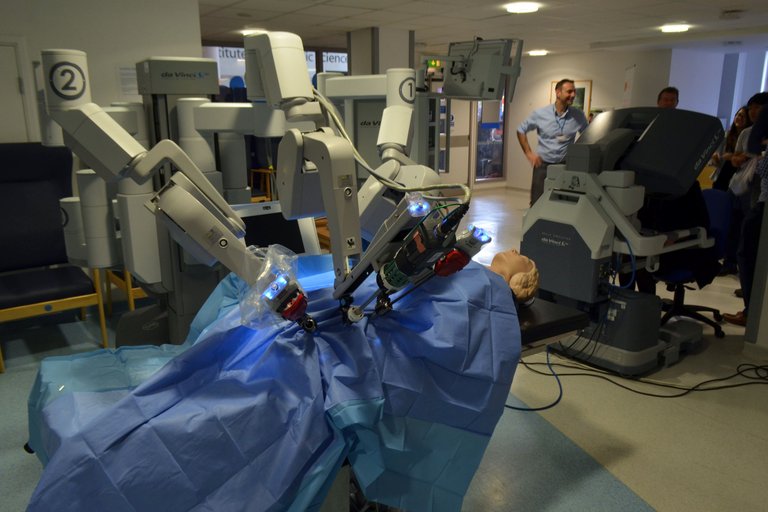
DISADVANTAGES OF ROBOTIC SURGERY
Someone may be desirous to ask “With all these benefits and potentialities affiliated to robotic surgery, do they still have disadvantages?”. Well, anything that has an advantage MUST also find itself a disadvantage. Some of these demerits are not directly associated with it, but arise as a result of it.
Basically, the most conspicuous drawbacks in robotic surgery include:
• It actually takes surgeons a longer period of time to master the functionalities of the robot and getting the necessary flexibility and manipulative capabilities to attend the zenith of a professional robotic surgeon. It takes hundreds of surgeries before the surgeon can boast of mastering the robots. So this extra training time can perhaps be better used to train a surgeon’s skill in manual operation. Surgeon might possibly not be able to make full use of the advantage of the robots if they have not mastered it yet.
• The cost of getting this advanced surgical operation done is very high. The first robotic surgery conducted was as high as $1 million although significantly, this figure has reduced. Compared to the traditional surgery, robotic surgery is far more expensive due to the cost of robots. Robots cost about $1.4 million with annual maintenance cost of about $120,000 makes it expensive to afford. There is also the additional cost of training a surgeon and the lost time that can be used to operate on patients.
• Robots are liable to malfunction just like all electronics and as the Murphy’s law goes (Murphy's law is a popular adage that states that "things will go wrong in any given situation, if you give them a chance," or more commonly, "whatever can go wrong, will go wrong.”). As a guide, the robotic assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RLRP) has a malfunction rate of around 2.6%. However, should a malfunction occur, a surgeon can readily take over from the robot to continue with the operation. A replacement robot can also be put in place to be ready for such mishap.
twcroboticsurgery
CONCLUSION
Robotic surgery is an advanced development in surgery that will have far-reaching implications. While improving precision and dexterity, this emerging technological development allows surgeons to carry out operations that were traditionally not amenable to minimal access techniques. Consequently, the benefits of minimal access surgery (an operation completed with one or more small incisions instead of a large incision) may be applicable to a wider range of procedures. Safety has been well deep-rooted, and many series of cases have recounted positive outcomes. However, randomized, controlled trials comparing robotic-assisted procedures with the open techniques are generally lacking. If cost and availability of this method of surgical operation is handled, then robotic surgery will be the choice of every patient (both the rich and the average). Finally, it is believed that the future holds greater potentials for surgery with robotic surgery.
photo credits to COMMONS: 1, 2, 3

This post has received a 0.16 % upvote from @drotto thanks to: @banjo.