Hi,
Structure of a conventional neural network
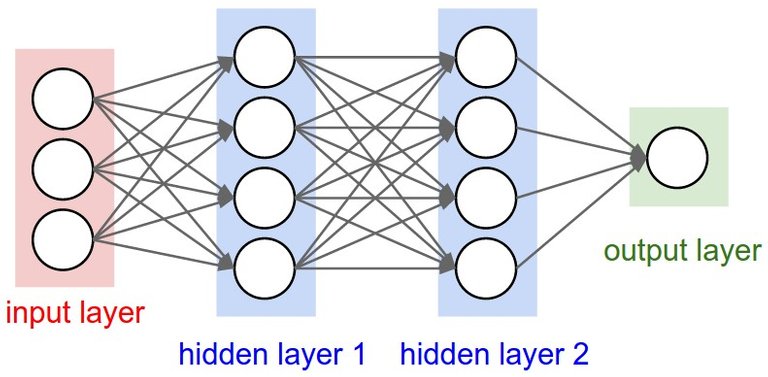
Please refer to the below image to get an idea about a conventional neural network. In a conventional neural network, we can see the input layer, output layer and some number of hidden layers. Each layer has several numbers of neurons. Each neuron is created from the values of the neurons of the previous layer, weight values, and bias value. Also, each layer consists of the activation function and the activation function decides the value which should be pass to the next layer. I will post another blog to explain the functionality of the activation function. If we increase the number of layers and the number of neurons in each layer, the conventional neural network transfers to a deep neural network(dnn). In my future blogs, I will discuss other types of neural networks such as dnn, rnn, etc
Forward propagation
We can calculate the values of each layer, by multiplying the weights and values of the previous layer and adding them together. Also, the bias should be added too.
scalar equation:
z1(i) = w1x1(i) + w2x2(i) + ... + wnxn(i) + b
vectorized equation:
Z = WX + B
In the next blog, I will present an example to get more intuition.
Cost function
After we calculate the output layer, we should get the cost. Here the cost means the difference between the calculated value(using forward propagation) and actual value. The cost function can vary from a neural network to a neural network.
Backward propagation

w = w - α∂J/∂w
b = b - α∂J/∂b
This is called the Gradient Descent. The gradient of the point A is a negative value and the weight should be increased to minimize the cost. Therefore the negative gradient should be subtracted from the weight(w = w - α∂J/∂w). Also, the gradient of the point B is a positive value and the weights should be decreased to minimize the cost. Therefore the positive gradient should be subtracted from the weight(w = w - α∂J/∂w). Here α denotes the learning rate. The learning rate decides the rate of reducing the cost. I will post a separate blog post to explain the effect of the learning rate.
Notations
| Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|
| [l] | l th layer |
| {m} | m th mini-batch |
| m | size of the dataset |
| n | number of neurons in one layer |
| simple letter | scalar |
| capital letter | vector |
| (i) | i th sample |
| x1(i) | first input value of the i th sample |
| w1[l] | first weight of the l th layer |
| g() | activation fucntion |
In the next blog, I will explain to you how to implement a neural network by using a real-world example. Please feel free to raise any concerns/suggestions on this blog post. Let's meet in the next post.
Congratulations @boostyslf! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!