Cancer is the second leading cause of death after cardiovascular diseases. Approximately 40% of men and women will be diagnosed with cancer at some point in their lifetimes. There are around 14 million new cases every year, out of which more than half die. These numbers are really huge. Despite being so prevalent in our society, most people lack the understanding of cancer.
In this article, we will discuss the notion of cancer, its types, causes and treatments. We will also talk about cancer in ancient times and some future possibilities of cancer treatments.
Even Egyptian Mummies And Dinosaurs Had Cancer Too!!!
Cancer is not a modern disease. It has been in the world for a long time. The word cancer comes from a Greek word "karkinos" which means crab and was first used by Hippocrates around 2500 years ago. But Hippocrates was not the first one to discover it, some of the oldest cases of cancer are found in Egyptian manuscripts dated around 4000 years ago. There was no treatment for it and they performed surgery to remove surface tumors.
Recently, in December 2017, a team of researchers from University of Granada (Figure 1A) has discovered the oldest case of breast cancer and multiple myeloma in Egyptian mummies dating back to around 4000 years.
| A | B |
|---|---|
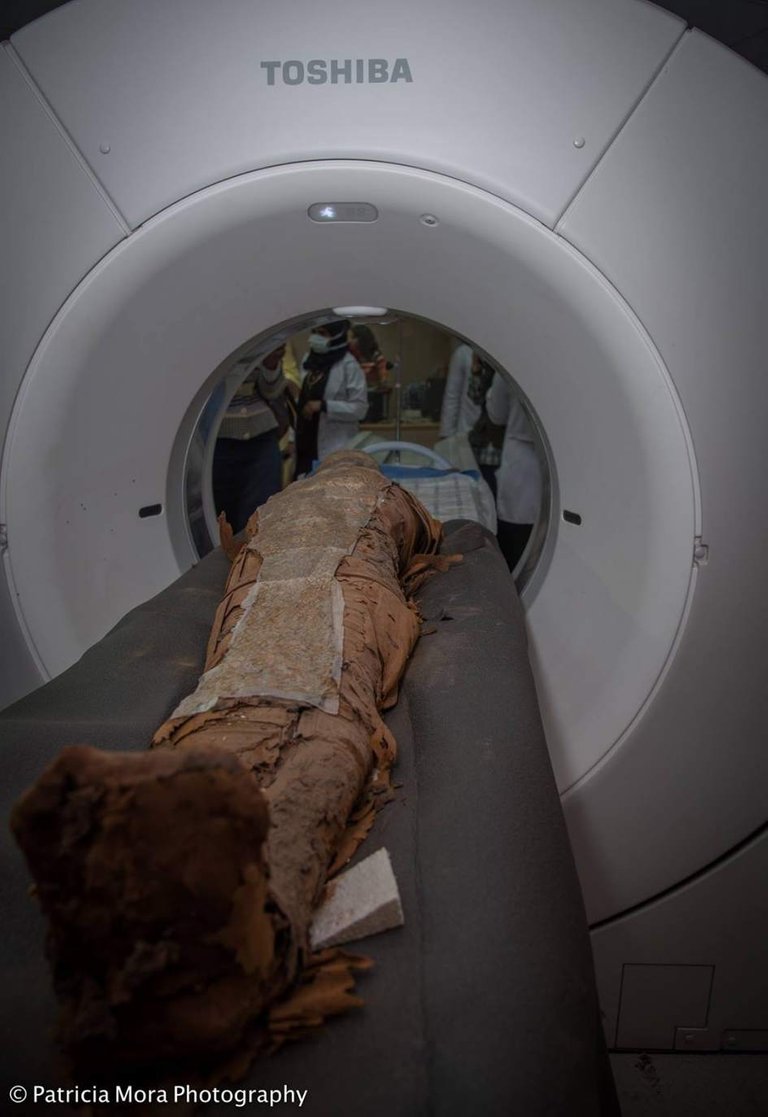 |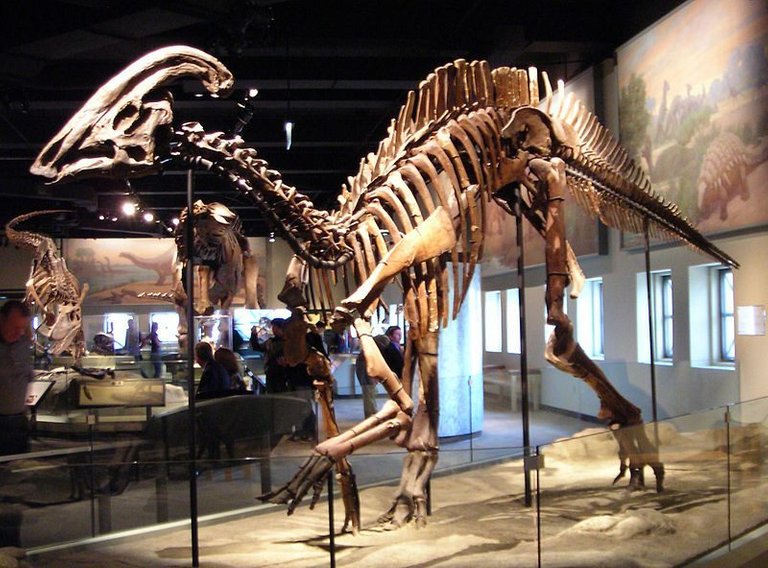  |
Figure 1: (A) UGR researchers conducting CT Scans on mummies (Image Credit: Patricia Mora). (B) Skeleton of Hadrosaur, Field Museum.
Many Dinosaurs had cancers, researchers have discovered. They scanned 10,000 dinosaur vertebrae from more than 700 museum specimens and found 29 tumors in bones of 70 million years old dinosaurs (Figure 1B). Their tumors are just like that of humans. This shows that cancer has been around for a long time without changing much.
So What Is Cancer?
Our body has more than 30 trillion cells. These cells divide and grow to replace old and damaged cells. This division happens at a controlled rate. A cancer cell is one which escapes from this control and divides uncontrollably. (Figure 2)
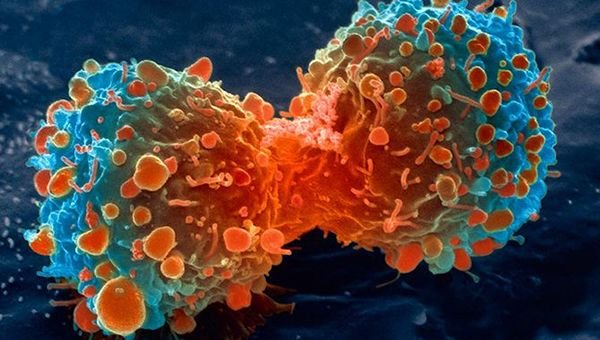
Figure 2: A dividing lung cancer cell. (Image Credit: National Institutes of Health)
These abnormal cells together are called a tumor. Tumors can be categorized into two categories,
1. Benign:
These tumors grow but do not spread to the other parts of the body.
2. Cancerous or Malignant:
These are the tumors which grow and can spread to many parts of the body.
Cancer can occur anywhere in the body because there are cells everywhere in the body (Figure 3). Depending on the position of cancer in the body, it can be categorized mainly into the following:
- Carcinoma:
This type of cancer starts on the skin or the tissues covering the internal organs as kidney etc. These are the most common cancers around the world. - Sarcoma:
This happens in the connective and supportive tissues such as bones and cartilage. - Leukaemia:
This cancer starts in bone marrow and causes blood cancer. - Lymphoma and Myeloma:
This is the cancer of immune system.
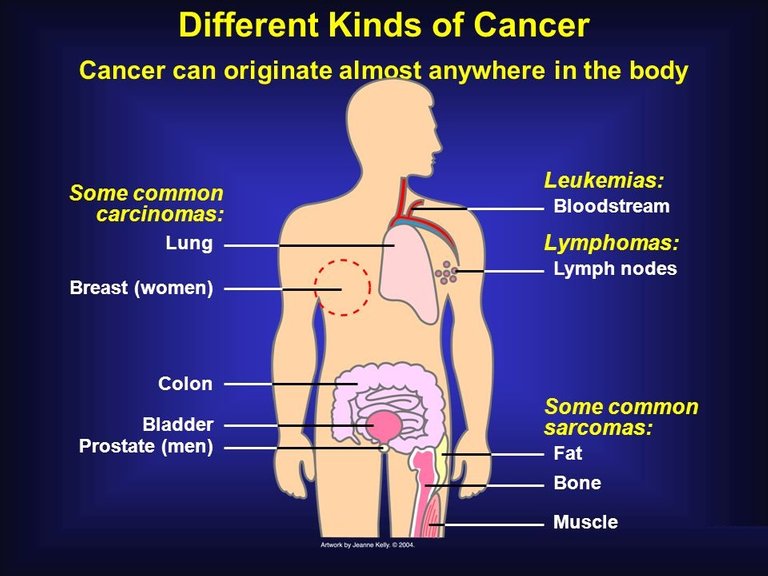
Figure 3: Types of cancers described above shown in the pictorial form. (Image Credit: National Cancer Institute)
Diagnosis Of Cancer:
There is not a single way to diagnose cancer. The most important methods are,
1. Imaging And Scans: This method involves X-Rays, Ultrasounds, MRI, CT-Scan etc. Doctors take images of the affected part and assess whether it is cancer or not.
2. Biopsy: In this method, a small piece of tissue is taken and tested for cancer.
3. Genome Sequencing: This is a new method in which the DNA of a cell is isolated and read to check if one has any mutation which may cause cancer.
What Causes Cancer?
Cancer is a genetic disease. The information that when to divide is encoded in DNA within the cell. When there are mutations (changes in DNA), this information may be destroyed and that is when a cell does not know when to stop dividing and growing. This unwanted growth of cells causes tumor that can be cancerous.
Once the tumor is formed, it needs nutrients and oxygen to survive, it induces blood capillaries that grow into a tumor and supply blood into the tumor. The formation of blood vessels in the tumor is called angiogenesis. Now through these blood vessels, cancer cells get the nutrients and travel across the body to spread to the other parts (Figure 4). In principle, if we cut the blood supply to the tumor, it will starve to death and would not spread.
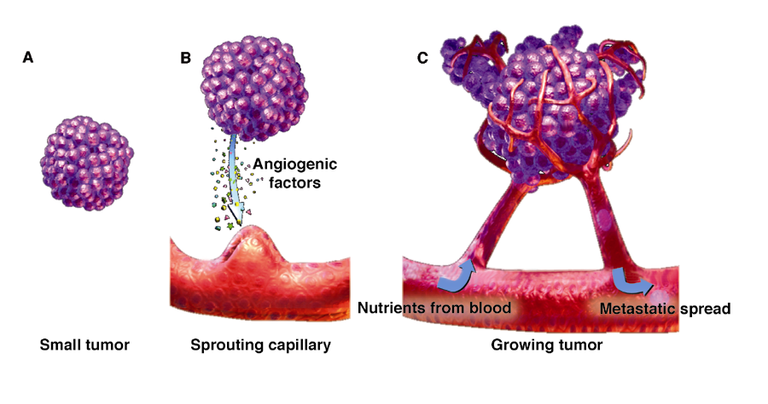
Figure 4: Tumor expansion induced by the sprouting of blood vessels. (Image Credit: http://www.townsendletter.com)
Present Methods To Treat Cancer:
Cancer has many kinds of treatments but the type of treatment depends on the stage of cancer. One might have to get a combination of treatments in order to defeat cancer. Surgery, Chemotherapy and Radiations are some types of treatments. When surgery is used, doctors remove the tumor, while in Chemotherapy, a combination of drugs is used to kill the cancer cells. Anti-angiogenics block nutrients and oxygen from a tumor so that it can starve. Radiation therapy targets the affected area with high doses of radiation that kills the cancer cells and shrinks tumors. But all these treatments can have severe side-effects. In order to minimize side-effects, targetted medicines are needed.
Future of Cancer Treatment:
Although a lot of advancement is made in the direction of cancer treatment, it is not always curable. Traditional therapies against cancer, chemo- and radiotherapy, have many limitations that lead to treatment failure and cancer can occur again. This happens due to cancer stem cells (CSCs), a type of stem cells that play important roles in tumor formation, metastasis (spreading to different parts of the body) and cancer relapse. Therefore in order to have a better treatment, we must develop something that hampers the regeneration of CSCs. Most of the treatments involve both traditional and targeted drugs that destroy the CSCs so that they cannot differentiate and grow again. Certain types of cancers e.g. blood cancer, myeloma and lymphoma can be treated with stem cell transplant.
Despite the past failures to treat cancer completely, we still have hopes left. There are various new ways coming into the light to cure cancer, few of which are mentioned below.
1. Precisional Medicine: We are very near the customized medicine era where treatment will be provided based on individual's genetics. Scientists are working in the field to even reverse the effect of cancer-causing gene mutation.
2. Immunotherapy: A healthy immune system fights off cancer daily. It kills cancerous and precancerous cells as they are formed. When the immune system becomes weak, it no longer can kill all the cancerous cells and thus cancer develops. By boosting body's immune response, we can cure cancer.
3. Cell-Based Therapy: T-cells are the cells which fight off the threats from outside of the body. T-cells of patients can be genetically engineered to attack cancer cells vigorously and put back into the bloodstream. This is one kind of immunotherapy.
4. Epigenetic Therapy: Mutations cause cancer. What if instead of destroying the cancer cells, we change them back to normal ones? There are a number of drugs developing which would change the genetics of the cell back to normal.
There is a lot more to say about cancer, but in this small article, I had to restrict myself. There are many misconceptions about it in public (probably some other time, we will talk about that). Despite being not so successful so far, we still have hopes that cancer will be cured completely someday.
I used the term stem cell many times in this article. If you do not know what stem cell is, please see my earlier post on stem cells: The Secret Of Stem Cell's Power.
Also, if you want to know how molecular dynamics can help in understanding cancer here is one interesting post by @dexterdev.
References:
1. http://www.nature.com/news/2003/031020/full/news031020-2.html
2. https://www.ugr.es/en/about/news/oldest-cases-breast-cancer-and-myeloma-revealed-scans-mummies
3. https://www.cancer.org
4. https://www.cancer.gov
5. https://www.mskcc.org
6. https://www.cancer.net
Hope you learned something new. If you liked it, keep yourself updated with my content by following me @treslotos.
My Earlier Posts:
Some of my earlier posts which might interest you,
I would like to see the reference.
One more interesting fun fact related to elephant and cancer can be seen here : https://www.nature.com/news/how-elephants-avoid-cancer-1.18534
Some how cancer in elephant is rare.
well, I have given the reference, but this is the exact link, you can follow,
https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/statistics
or if you want to do simple math, here are 2017 stats,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28055103
here is one just for UK,
http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/risk
And thanks for adding information. :)
40% is really high and it is scary. :(
I can't agree more.