Organic Chemistry:
Historical Background (old theory)
- “Organic” means concerning life
- Organic Compounds are made up of onlyplants and animals or Extracted from Plants and Animals
- Not synthesized in Laboratory.
- Obey “Vital Force” Theory.
(vital is latin word and Vital means Life)
Accidentally changed the concepts;
• Accidentally synthesized/prepared in the laboratory by the heating of inorganic compound “Ammonium Cyanate”
NH4Cl + 2KCNO ------> 2NH4CNO + KCl
Ammonium Chloride + Potassium Cyanate -----> Ammoniam cynate
O
NH4CNO ------> NH2----C-----NH2
Urea
Scientist Name: Friedrich Wohler in 1828
Modern definition of Organic chemistry;
• Study of chemistry of the Carbon Compounds.
• Organic Compounds are essentially formed covalent bonds.
Examples of organic compounds are food, clothes, petroleum, drugs, dyes, plastics, leather, perfumes, rubber, explosives, pesticides, polymers etc.
Natural resources of Organic compounds;
Important natural sources;
Plants: Starch, sugar, cellulose and drugs from plants and natural dyes
Animals: urea, proteins and fats
Coal: Aromatic compounds and fuels or gas
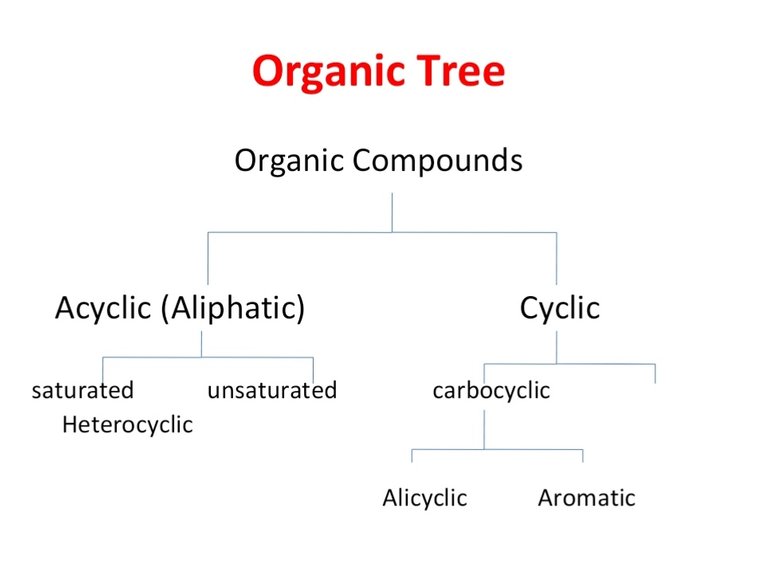
Types of Organic compounds;
The organic compounds are classified as
- Acyclic or Non-cyclic compounds
- Cyclic Compounds or Closed Chain
1. Acyclic or Non-cyclic compounds;
• Carbon atoms are attached in Straight Chain
• Long chain and a branched chain Compounds
• Also called Aliphatic Compounds
2. Cyclic or closed changed compounds;
Classified into two main types
Carbocyclic compounds
i. Alicyclic Compounds
ii. Aromatic Compounds.Heterocyclic Compounds.
1. Carbocyclic compounds;
• Those compounds which are made up of carbon atoms only in a ring.
i. Alicyclic Compounds (Non-benzenoid)
• Closed ring (Ring Structure)
• Only carbon atoms.
• Carbon atom joined by single bond
• Behave like aliphatic compounds
e.g. cyclobutane, cyclohexane, cyclopantane etc.
ii. Aromatic compounds (Benzenoid)
• Closed Chain Compounds
• Alternative single and double bond
• Resonance structure
• Aromatic compounds
e.g. Benzene, Phenol, Toluene, naphthalene etc.
2. Hetrocyclic compounds;
• Cyclic Compounds or Closed ring
• Contain one or two atoms other than carbon
e.g. O, N and S
Furan (Five membered),
Pyridine (Six membered)
Thiophene (Four membered)

Dear @shahidshah
Thank you for including the #steemstem tag in your post
Please be informed that there are certain guidelines for posts regarding STEM so I am inviting you to read this link for more information
In case of any questions, feel free to join us @steemstem on discord or to take a look at the FAQs
Greetings,
Katerina