The diamond sliver was discovered at South Africa's Cullinan diamond mine, that is best best-known for yielding 2 of the most important diamonds within the British Crown Jewels. the piece of CaSiO3 was visible to the oculus once the diamond was polished, however a world team of researchers collaborated on analyzing the valuable stone with X-ray and chemical analysis tests. They revealed the results of this analysis within the journal Nature.Scientists calculate that the mineral shaped a hundred and five miles below the Earth's surface.
A single grain of rock lodged in an exceedingly diamond contains a never-before-found mineral.
And that new substance may reveal uncommon chemical reactions flowering within the depths of the mantle, the layer of Earth that lies between the planet's crust and outer core.
Scientists unearthed the mineral from a volcanic website in African country called the Koffiefontein pipe. Shining diamonds speckle the dark, rock that lines the pipe, and therefore the diamonds themselves contain small bits of different minerals from many miles below Earth's surface. at intervals one amongst these sparkling stones, scientists found a dark inexperienced, opaque mineral that they calculable was solid regarding a hundred and five miles (170 kilometers) underground.
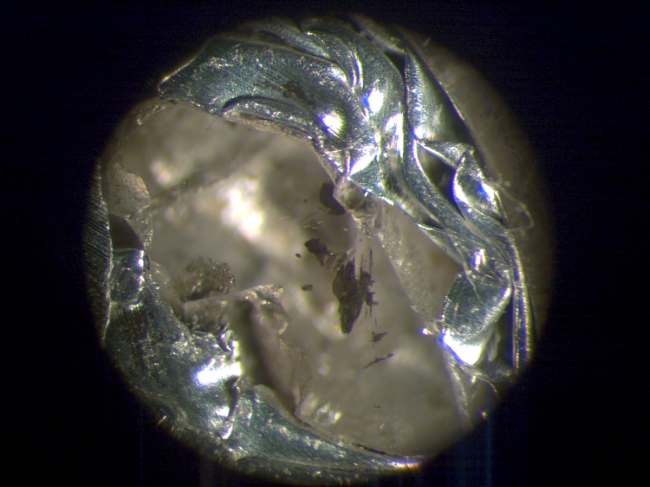
They named the new mineral "goldschmidtite" in honor of acclaimed geochemist Victor Moritz Goldschmidt, per the study, revealed Sept. one within the journal yank man of science.
The entire mantle is regarding one,802 miles (2,900 km) thick, per National Geographic, that makes the layer's nethermost regions troublesome for scientists to review. the extreme pressure and warmth within the layer rework humble carbon deposits into sparkling diamonds; the rocks entice different mantle minerals in their structures and may be pushed to the earth surface by underground volcanic eruptions. By analyzing mineral inclusions within the diamonds, scientists will take a peek at chemical processes that occur way below the crust.
The study authors noted that, for a mantle mineral, goldschmidtite features a peculiar chemical composition.
- "Goldschmidtite has high concentrations of atomic number 41, metallic element and therefore the rare-earth parts metal and metal, whereas the remainder of the mantle is dominated by different parts, like atomic number 12 and iron," study author Nicole Meyer, a scholarly person student at the University of Canadian province in Canada, same in an exceedingly statement. metallic element and atomic number 41 structure most of the mineral, that means the comparatively rare parts were brought along and focused to create the bizarre substance, despite different near parts being additional long, she said.
- "Goldschmidtite is extremely uncommon for associate degree inclusion captured by diamond and provides USA a snap of fluid processes that have an effect on the deep roots of continents throughout diamond formation," mantle geochemist Graham Pearson, Meyer's co-supervisor, same within the statement.
The odd mineral currently lies within the Royal Ontario repository in Toronto.