ABSTRACT
The aim of this study was to determine the antibiotic sensitivity pattern of Staphylococcus aureus collected from Seven Day Adventist Clinical Laboratory Hospital and transported to Oduduwa University Microbiology Laboratory in Ile-Ife, Osun State, Nigerian. S aureus isolated from patient samples were identified by standard methods. The antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed using the standard disc diffusion method recommended by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2008. On the samples collected different identification methods was performed and several biochemical test, the samples is tested against several drugs like Ciprofloxacin, Erythromycin, Vancomycin, Amoxicillin, Augmentin and Gentamycin, the test organism which is staphylococcus aureus was resistance to most of this organism, and susceptible to only few like Vancomycin and Ciprofloxacin which make the recommendation of the research based on the experiment performed in the laboratory that Ciprofloxacin and Vancomycin can be used in treatment of any infection caused by staphylococcus aureusbut this was not actually strong susceptibility so therefore resistant to this drugs might occur in future.
INTRODUCTION
Background of study
The genus ***Staphylococcus ***consists of spherical cells arranged primarily in irregular clusters and occasionally in short chains and pairs. Staphylococci have a typical Gram-positive cell wall structure. Like all medically important cocci, they are non-flagellated, non-motile and non-spore forming. Staphylococci grow best aerobically but are facultative anaerobic and are catalase positive. Staphylococci ferment glucose anaerobically and this is one distinguishing characteristic between this genus and micrococci. The genus Staphylococcus belongs to the family Micrococcaceae (Betty et al., 2007). Within this family Staphylococci are closely related in structure to another group of bacteria; Micrococci and the view was held that Micrococci could not be differentiated from Staphylococci (Shaw et al., 1951).
Aim of study
To test of antibiotics test of staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical isolates
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium found primarily on the skin and in the nose of humans. S. aureus belongs to the coccus family of bacteria. These bacteria have a spherical shape and appear as large round yellow clusters similar to grapes. S. aureus is an important human pathogen which causes a range of diseases ranging from minor issues such as minor skin infections to severe toxin mediated diseases (Online Textbook of Bacteriology, 2008).
METHODOLOGY
** MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT USED**
Glass petri dishes, Syringe, Nutrient agar, Peptone water, Ethanol, Non-absorbent cotton wool, Aluminum foil, Cover slips, Paper tape, Nose mask, Inoculating loop, Bunsen burner, Stirrer, Conical flask, Beaker, Distilled water, Measuring cylinder, Timer, Marker, Sterile glass slides, Ziploc bag, surgical blade, Refrigerator, Wash bottles, Spatula, Liquid soap, Detergent, Test tubes, Gloves, Disinfectant, Hot air oven, Autoclave, Incubators, Water bath, Wire loops, Weighing balance, Binocular microscope.
REAGENT AND CHEMICAL USED
Lugol’s iodine, Safranin, Distilled water, Citrate media, Crystal violet, Acetone, Methyl red indicator, Potassium hydroxide, Alpha-napthol.
**STERILIZATION OF MATERIALS **
All glassware were washed with detergent, rinsed with tap water and allowed to dry. The opening of the glassware were covered with foil, placed on a metal tray and kept in an oven at 160° C for 2 hours.
STERILIZATION OF MEDIA
All prepared media were boiled using water bath to dissolve well, followed by Sterilization of respective media using an autoclave at 121°C for 15 minutes, were allowed to cool up 45°C before pouring into the petri dish aseptically and allowed to gel.

plate 1 : An Autoclave
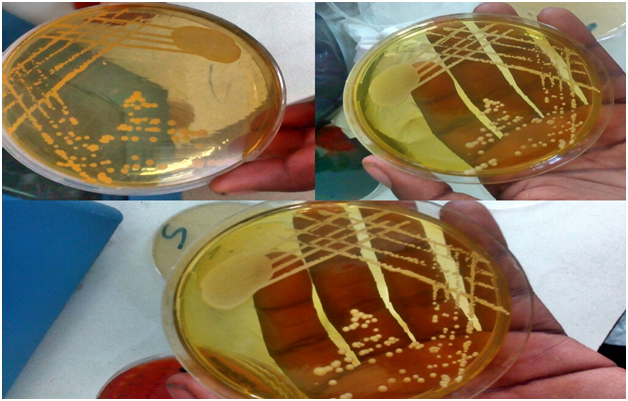
Plate 2: Appearance of Staphylococcus Aureus on Mannitol Salt Agar
IDENTIFICATION
Identification of the samples Staphylococcus aureus organism was done based on the culture characteristics ,Gram Staining and Series of Biochemical Test which include ,Catalase Test , Coagulase Test, Oxidase Test , Hemolysis and Gelatin.
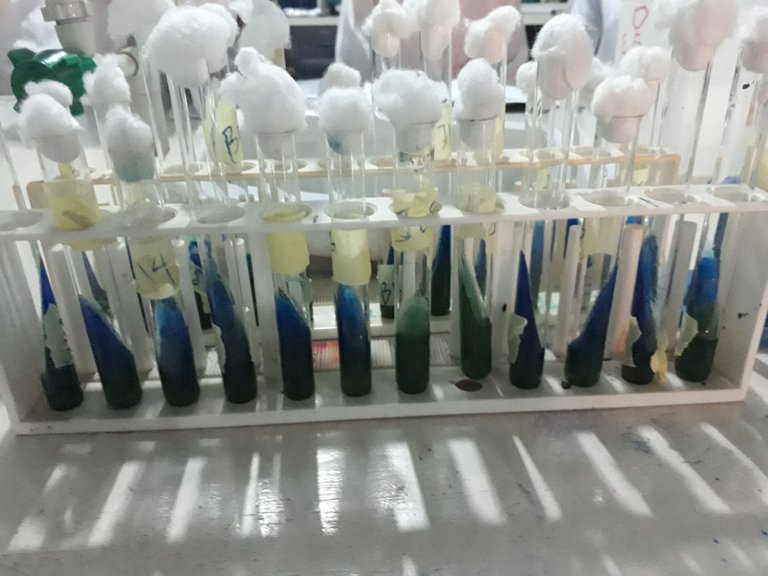

plate 3 : Appaerance of Simmon Citrate Agar after incubation ( citrate test).
 :
:
plate 4: A Microscope
Table 1: RESULTS OF GRAM STAINING AND BIOCHEMICAL TESTS
ISOLATE/GRAM STAINING/SHAPE/CATALASE TEST/OXIDASE TEST/COAGULASE TEST/UREASE TEST/HEMLYSIS TEST GELATIN TEST
S1 + COCCI + - + + BETA +
S2 + COCCI + - + + BETA +
S3 + COCCI + - + + BETA +
S4 + COCCI + - + + BETA +
S5 + COCCI + - + + BETA +
S6 + COCCI + - + + BETA +
S7 + COCCI + ¬- + + BETA +
S8 + COCCI + - + + BETA +
KEY:
+ = POSITIVE AND - = NEGATIVE.
Notes: S1 – S6 is used to indicate the test samples and this table shows that the organism is cocci shaped and test negative for oxidase test while positive for other tests.
Table 2: Results For Antibiotics Susceptibility Test( Clear zone of inhibition in mm)
S/N S.aureua isolates (Code) Vancomycin (V30 µg)
Oxzcillin
(OX 1µg)
Erytromycin
(E 15µg0
Ciprofloxacin
(CIP 5µG)
Amoxillin
(AMC 10µG)
1 S1 0 mm 0 mm 18 mm 19 mm 0 mm
2 S2 9 mm 0 mm 19 mm 17 mm 0 mm
3 S3 10 mm 0 mm 0 mm 24 mm 0 mm
4 S4 0 mm 0 mm 12 mm 15 mm 0 mm
5 S5 8 mm 0 mm 10 mm 23 mm 0 mm
6 S6 8 mm 0 mm 15 mm 16 mm 0 mm
7 S7 10 mm 0 mm 20 mm 18 mm 0 mm
8 S8 0 mm 0 mm 21 mm 19 mm 0 mm
Table 3: Interpretation Of The Result
S/N/S.aureua isolates (Code)/Vancomycin (V30 µg)/Oxazcillin
(OX 1µg)/
Erytromycin
(E 15µg)
Ciprofloxacin
(CIP 5µG)
Amoxillin
(AMC 10µG)
1 S1 R R I I R
2 S2 R R I I R
3 S3 R R S R R
4 S4 R R R R R
5 S5 R R S R R
6 S6 R R I I R
7 S7 R R I I R
8 S8 R R I I R
Key:
S = Susceptible,
R = Resistance,
I = Intermediate.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the results of this study showed the importance of regular surveillance of hospital associated infections including monitoring antibiotic sensitivity pattern and strict drug policy for antibiotics used within and outside the hospital environments. Moreover, in-vitro susceptibility testing of every isolate of Staphylococcus aureus in the clinical laboratories may be helpful for reducing the incidence of these infections. Ciprofloxacin is susceptible to S.aureus. This suggests that they are suitable for treatment of infections caused by this organism. The high rate of multi-drug resistances in this study reveals that the rate at which this organism has gained resistance cannot be overemphasized.
I need more update on how to arrange the result.Thanks
WELCOME TO STEEMITI appreciate if you follow me !!!
Your comments are always welcome,
I will try to answer as much as possible.
Good luck with your trip in this communitas,and upvote to your friends as much as possible, and the reverse.
Regards community steemit
Thank you
thanks for your comment
thank you all for voted me and looking for ur correction on this post.
Neatly done. We love tech. Keep steeming.