Hepatitis
Definition:
Hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver tissue or liver inflammation. Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful responses such as disease-causing organisms, damaged cells or irritant and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels and molecular mediators.
There are currently 11 viruses identified to cause hepatitis and these viruses are categorized in two groups;
- The Herpes virus and Epstein-Barr virus
- The Hepatotropic virus that are known to target liver hepatocytes.
These viruses cause the syndrome of fatigue, nausea and malaise. Hepatitis may be acute (temporary) or chronic (long term) depending on it’s duration which may be less than or more than six months. Acute hepatitis may sometimes resolve on it’s own, progress to Chronic hepatitis or rarely result in acute liver failure, overtime chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver, failure or cancer of the liver.
The major categories of hepatitis include; Hepatitis A which is also known as infectious hepatitis, Hepatitis B known as serum hepatitis, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D or delta agent and Hepatitis E.
Hepatitis A
Mode of transmission:
it is transmitted by fecal contamination of food/drink, shell fish that live in water contaminated with the virus.
Causative agent:
HA is caused by Hepatitis A virus of the genus Hepatovirus of the family Picornaviridae.
Characteristics:
It is a linear, icosahedral, non-enveloped, positive strand RNA virus, it multiplies within the intestinal epithelium immediately it enters the digestive system and actually causes mild intestinal symptoms. Sometimes viruses are found in the blood (viremia) and can spread to the liver, progress into the bile and released into the small intestine, and these explains why feces are so infectious.
Incubation period:
Incubation period of 4 weeks.
Symptoms:
Anorexia, general malaise, diarrhea, fever and chills. Most cases resolve in 4-6 weeks and give a strong immunity, although some patients recur showing symptoms for 6 months or more.
Prevention and control:
Simple hygienic measures, clean disposal of excreta and use of HAV vaccine.
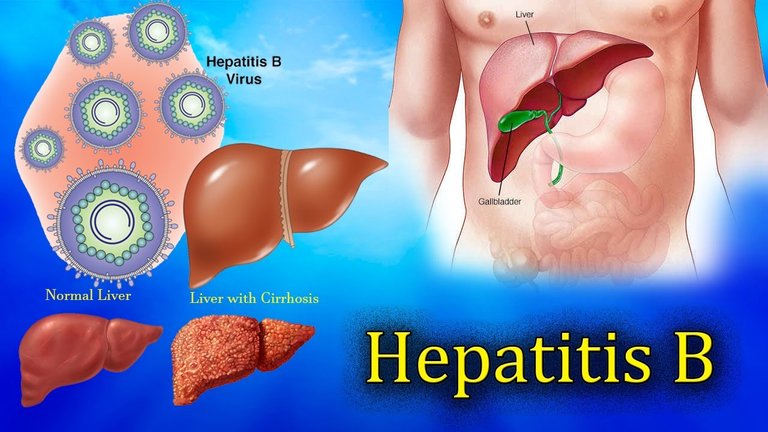
Hepatitis B
** Mode of transmission:**
Through body fluids or blood, contaminated body fluid equipment (intravenous needles), during pre-natal or natal period.
**Causative agent: **
Hepatitis B virus of the family Hepadnaviridae.
**Characteristics: **
Enveloped, partially double-stranded circular DNA genome of complex structure, they are reverse transcripting DNA viruses because they encode a reverse transcriptase enzyme that is used to generate their genomes.
Incubation period:
Incubation period of 1-3 months.
**Symptoms: **
Most cases are asymptomatic, HBV causes liver tissue degeneration, release of liver-associated enzymes into the blood stream, chronic hepatitis B infection also causes the development of primary liver cancer known as hepatocellular carcinoma.
**Prevention and control: **
Contact with infected HBV blood and secretions should be avoided, active prophylaxis with recombinant vaccines; Recombivax HB, Pediatrix and Twinrix. Treatment include Adenovir dipivoxil, alpha-interferon and Lamivudine.
Hepatitis C
**Mode of transmission: **
Contact with virus contaminated blood, fecal-oral route, mother-foetus and organ transplantation.
**Causative agent: **
Hepatitis C virus form the family Flaviviridae.
**Characteristics: **
Enveloped, single strand, linear RNA virus.
**Prevention and control: **
Hygienic measures, diagnosis by ELISA and treatment by Ribavirin and PEGylated recombinant interferon-alpha.
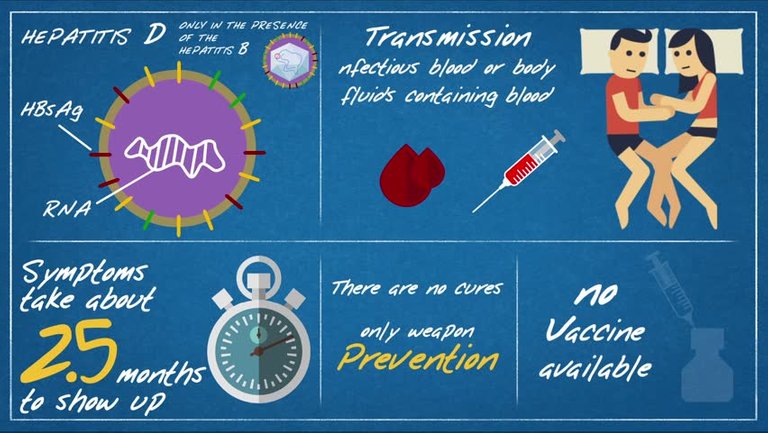
Hepatitis D
Delta agent, it is a unique agent, it is a satellite dependent on hepatitis B to provide the envelope protein for it’s RNA genome, it has similar characteristics to plant viroids and satellite. Satellite are sub viral infectious agent that may encode some proteins but require a helper virus for replication while viroids are infectious agents of plants that consist only of circular ssRNA molecules. Prevention is to improve sanitary conditions.
Hepatitis E
**Mode of transmission: **
Infection is associated with water contaminated with feces, HEV goes through the blood from the gastrointestinal tract, replicates in the liver and released in to the bile and is afterwards excreted in the feces.
**Characteristics: **
Spherical, non-enveloped, single, positive-strand RNA and the only member of Hepeviridae.
**Incubation period: **
Runs an incubation period from 15-60 days and on the average 40 days, often recorded in patients of 15-40 years of age.
**Symptoms: **
Asymptomatic patients are children with symptoms similar to those of other viral hepatitis including dark urine, fever, hepatomegaly, malaise, nausea and vomiting.
**Prevention and control: **
Diagnosis by Elisa, preventive measures include sanitation in affected areas and improving health level.
Read more:
https://www.healthline.com/health/hepatitis,
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatitis
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/145869.php
https://www.onhealth.com/content/1/hepatitis_causes_treatment
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hepatitis/
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs328/en/
https://www.medicinenet.com/viral_hepatitis/article.htm

.jfif)