
In this issue, we will continue to address botanical content related to the organographic, histological and pharmacological structures of the species Rhoeo discolor with synonymy Tradescantia spathacea, with the firm purpose of contributing to the dissemination of biological-technical and medicinal elements of this important plant resource.
Introduction
Rhoeo discolor, is considered in South American countries as a plant resource of wide ornamental value, this for the purple color that presents the foliar laminae in the back or abaxial face (inferior side of the leaves) in contrast to the green color that exhibits the beam or adaxial face (superior side of the leaves).
Besides the ornamental qualities that Rhoeo discolor shows, in Central American countries it is usually considered a powerful phytoanalgesic, equivalent to the effect to calm or eliminate pain, the extracts of this prodigious biological material also have antibiotic, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor activity.
Consequently, and in order to extend these topics, the manuscript will detail, in addition to their pharmacological properties, the organographic and histological characteristics and the ornamental use given to Rhoeo discolor seedlings.

Fig. 2 Growth of Rhoeo discolor seedlings in the UNESUR Botanical Garden. Author: @lupafilotaxia.
Biological classification
Kingdom: Plantae
Division: Magnoliophyta
Class: Liliopsida
Order: Commelinales
Family: Commelinaceae
Genus: Rhoeo
Species: discolor, sinonimia Tradescantia spathacea
Common names
In Venezuela it is domestically designated as Hoja de hígado, however in Guatemala, Mexico and Panama it is called Maguey morado, while in the Dominican Republic it is called Magueyito and in Cuba Cordobá.
Pharmacological properties
The high costs of drug production, coupled with the secondary reactions that produce synthetic compounds to human health, are circumstances that have guided the use of plant species to treat various diseases, it is universally known that plants have phytochemical elements of proven pharmacological effect, in this post we will limit ourselves to describe the medicinal properties that Rhoeo discolor;
A. Phytoanalgesic activity: Rhoeo discolor is characterized by the effect of its secondary metabolites in reducing headaches as well as muscular complications.
B. Antibiotic effect: It has been suggested that fresh leaf material from Rhoeo discolor contains ethanolic substances with antibiotic efficacy, mainly against skin diseases.
C. Anti-inflammatory property: The pigments that give Rhoeo discolor leaf tissue its purple color, including substances such as flavonoids, act positively on inflammatory processes.
D. Anti-tumor action: Although there are no reliable reports, it is estimated that the secondary metabolites of Rhoeo discolor are antitumoral in inhibiting the growth of cancer cells.
Ornamental Use
The bicolour (green and purple) of the leaves of Rhoeo discolor makes it a plant material of ornamental interest whose attractive colour is the purple of the leaf underside, a morphological attribute used for the beautification of urban gardens and squares.

Fig. 3 On the left adaxial face of Rhoeo discolor, on the right abaxial section (purple color). Author: @lupafilotaxia.
Origin and distribution
Rhoeo discolor, currently determined with synonymy Tradescantia spathacea, is native to the extensive geographical region of Central America, however, is usually attributed a specific origin relating to Mexico as the country of natural habitat, however, its distribution is wide in both tropical and subtropical countries.
Gender Tradescantia in Venezuela
In Venezuela the genus Tradescantia contains 04 (four) species among these Tradescantia pallida, Tradescantia pinetorum, Tradescantia spathacea and Tradescantia zebrine, it is also common to observe in Venezuelan ecosystems the Tradescantia spathacea var. vittata.
Botanical description
Way of life
Tradescantia spathacea, as it is taxonomically designated at present, is a herbaceous and perennial biotype plant.
Root
It has a fibrous, adventitious root with a thin morphology.

Fig. 4 Adventitious roots of Rhoeo discolor. Author: @lupafilotaxia.
Stem
It has a short stem, of considerable thickness and succulent biotype.
Sheets
It has leaf blades of filiform morphology and appreciably concave with grouping in rosettes and in alternate phyllotaxic disposition.

Fig. 5 Phyllotaxic arrangement of Rhoeo discolor. Author: @lupafilotaxia.
Inflorescence
It exhibits inflorescence made up of tiny flowers wrapped in violet bracts.
Flower
The flowers of Rhoeo discolor, have white petals.
Fruit
Rhoeo discolor,exhibits fruits arranged in capsules with ovoid morphology.
Seeds
It has seeds of a single cotyledon with abundant carbohydrates.
Reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Rhoeo discolor, has reproductive structures at the floral level that allow the germination of seeds.
Asexual reproduction
Vegetative or asexual reproduction in Rhoeo discolor, is generated by shoots or resprouts with lateral projection with emission of two leaves and main root in development.
Growth
The growth habit of Rhoeo discolor is accelerated, it is estimated that it can reach about 35 centimeters high and 50 centimeters wide (leaf canopy).
Ecology
The plant species Rhoeo discolor, thrives in natural ecosystems preferably tropical, usually in rainforest conditions with temperatures around 30°C and rainfall greater than 2,000 mm per year.
Histology and organography
Microscopic study
In order to extend the existing information, a histological study on the vegetative structures of Rhoeo discolor was developed, using the optical microscope for the morphological characterization at tissue level, which was carried out in the Botanical Laboratory of UNESUR.
Collection
The vegetative material of Rhoeo discolor, was collected from the Botanical Garden of UNESUR, located in the municipality of Colon in the state of Zulia - Venezuela.
Histological identification
The vegetative structures of Rhoeo discolor were placed in containers with water to ensure that the turgidity of the tissues was maintained. They were then transferred to the UNESUR Botany laboratory facilities.
Materials and reagents used
- Plants of Rhoeo discolor
- Carrier sheets and coverslips
- Botanical dissection team
- Petri dishes
- Optical microscope
- Distilled water
- Lugol
- Safranin
- Floroglucin
Tissue observation
The histological structures of Rhoeo discolor, were observed using microscopes OPTIKA brand, for the identification of epidermal tissue, parenchyma photosynthetic, cross sections, longitudinal and tangential to the leaves (both sides), first proceeded to focus 4x to locate tissue and then changed to 10x, for morphological characterization.
For the observation of xylem conduction and phloem tissues, cross sections were made to adventitious roots of Rhoeo discolor.
Histological results
Epidermal characterization
The adaxial and abaxial epidermis of Rhoeo discolor, have thin and smooth cuticle with cells of hexagonal morphology of green color in the superior face and purple color in the inferior one, with appreciable differences as far as the size, this could be determined when finding epidermal cells of the superior section more developed than those located in the back.
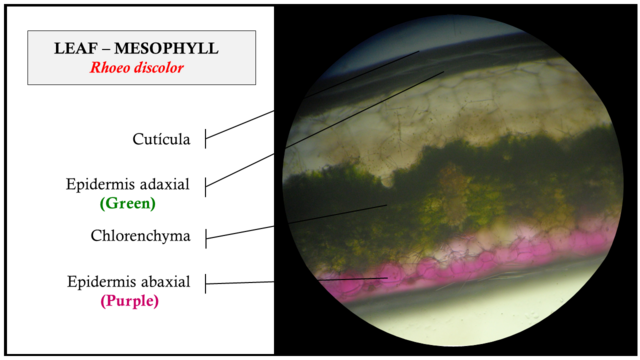
Fig. 6 On the right side, it is detailed cross section of Rhoeo discolor leaf, on the left side it is indicated, the location of the adaxial epidermis (green color), chlermenchyma and abaxial epidermis (purple color). Author: @lupafilotaxia.
Stomatic characterization
The stomas observed are of the hypostomatic type, which indicates that they are only located on the inferior or abaxial face (purple segment) of the leaves of Rhoeo discolor, as for the disposition of the annexed cells they are in Tetrachytic condition (four annexed cells per stomatic apparatus) .
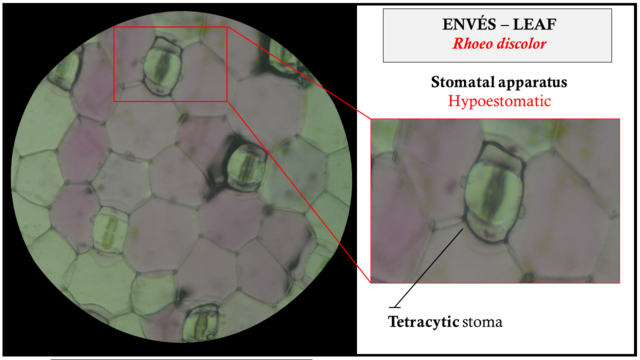
Fig. 7 On the right side, it is detailed the hypostomatic apparatus in tetrachytic disposition, on the left side it is shown tangential abaxial cut (purple color) of Rhoeo discolor leaf sheet. Author: @lupafilotaxia.
Parenchymal characterization
The mesophyll of the leaves of Rhoeo discolor is Dorsiventral type, which indicates that it has chlorenchymal cells in the beam and spongy cells on the underside, as for the morphology is irregular in the photosynthetic parenchyma, while the spongy tissue is well developed with the presence of crystals inside the cell.
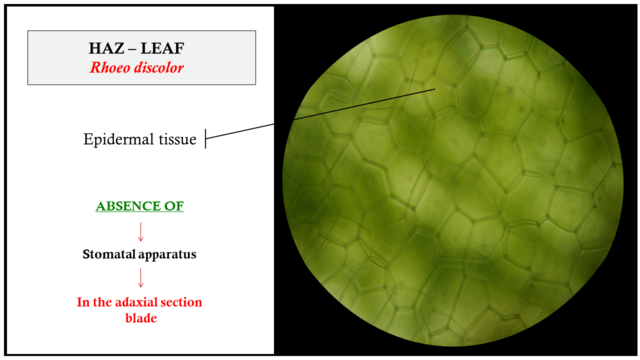
Fig. 8 On the right side, there is an adaxial tangential cut (green color) of the Rhoeo discolor leaf blade, indicating the absence of stomach apparatus in this section. Author: @lupafilotaxia.
Xylematic and phloematic characterization
Cross section of adventitious roots of Rhoeo discolor, showed concentric amphivasal vascular bundles (phloem cells surrounding xylem) in an ordered and circumferential arrangement around the medulla, with visibly developed rhizodermal tissue without intercellular spaces, followed by exodermal and endodermal cells.
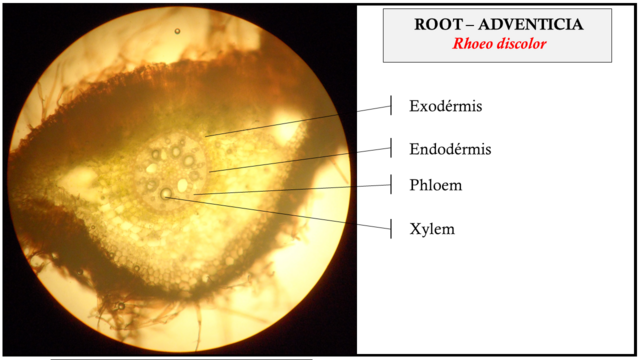
Fig. 9 On the right side, the location of exodermal, endodermal, phloem and xylem cells is detailed, on the left side, cross section of adventitious root of Rhoeo discolor. Author: @lupafilotaxia.
SCIENTIFIC CONTRIBUTIONS OF THIS PUBLICATION
- The manuscript describes unpublished contributions to the area of plant morphology, also highlights aspects of organography and pharmacological botany of Rhoeo discolor with synonymy Tradescantia spathacea, valid scientific basis for the recognition of the main biological attributes of this plant species, on the other hand, and like the previous posts the exhibition and audiovisual narration serves as an additional educational resource for the socialization of content in multimedia formats.
BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES CONSULTED AND CITED:
[1] APG II. The Angiosperm Phylogenetic Group. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG II. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society. 2003; 141:4: 399–436. Article: Online access
[2] Richard C., Sheila L., and Robert W. Plant Anatomy: A Concept-Based Approach to the Structure of Seed Plants. 2018. Book: Online access
[3] Domínguez O. Elucidación y Actividad Antimicrobiana de los Metabolitos Presentes en Maguey morado (Roheo discolor L. Hér Hance). niversidad de Colima. Tecomán Colima. 2003. Article: Online access
[4] Martínez C. Plantas utilizadas en medicina en el NO de Corrientes. Miscelánea Nº 69. Fundación Miguel Lillo. 1981; 1-135.
Article: Online access
[5] Zi Wan. Tradescantia spathacea. Linnaeus, Sp. Pl. 1: 288. 1753. Flora of China 24: 38. 2000. Article: Online access
ATTENTION / Readers and Followers
If you want to read more scientific articles of excellent academic quality, do not waste time, and visit the label #steemSTEM, is a large community that values and promotes scientific content, mainly in the areas of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics.

INVITATION
Dear reader, if you wish to obtain more information about it, join our server in Discord
OBSERVATIONS
✔ The POST ⌨ ✍ ✉ was uploaded using the official app of https://www.steemstem.io
OBSERVATIONS
✔ The POST ⌨ ✍ ✉ was uploaded using the official app of https://www.steemstem.io
You can visit the official app of our community
https://www.steemstem.io

Shame on you for voting Justin
Twitter publication link:
Hi, thanks for the post! I included a link to it in my daily Science and technology digest, and you'll get a 10% share of that post's rewards.
Greetings @aaaa.
Thank you for supporting and including the article in your report.
Shame on you for voting Justin
I didn't vote for Justin, I mistakenly completed 30 votes, I have my 22 votes for the community witnesses. I was informed and I withdrew the votes.
This post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team
and voting trail. It is elligible for support from @curie and @minnowbooster.
If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness @stem.witness. Additional witness support to the curie witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Thanks for having used the steemstem.io app and included @steemstem in the list of beneficiaries of this post. This granted you a stronger support from SteemSTEM.