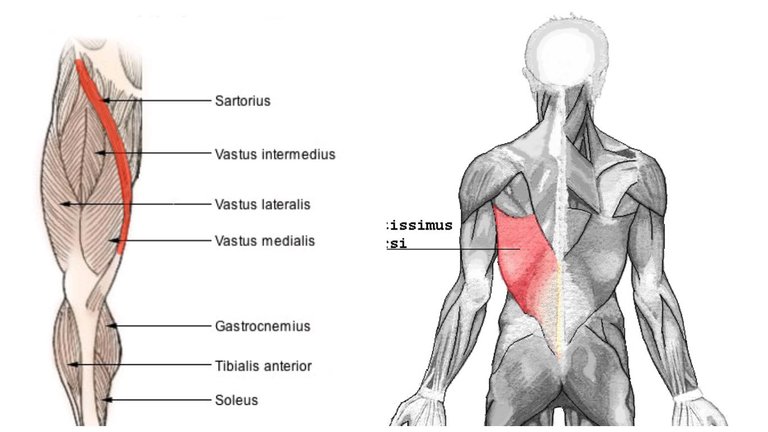
Spasticity refers to a condition that manifests with tense and rigid muscles with deep and exaggerated tendon reflexes, it may interfere with the activity of walking, movement or language.
Muscles should normally have enough tone to maintain posture and allow voluntary movement against the force of gravity, while giving flexibility and speed to movements.
The function of flexing, tensing or increasing the tone of the muscle comes from the spinal cord from the brain and through the nerves or sensory nerve fibers that each of them has, which must be perfectly coordinated so that the muscles work properly. soft and continuous, while maintaining strength.

When for various reasons and diseases, the area of the brain that controls the tone and movement of the muscle or the area of the spinal cord that controls the voluntary musculature, suffer some damage, the muscle becomes very tense or spurious. Detection can often be done during the first year of life, but it is usually detected later.
Spasticity is a symptom that reflects a disorder of the nervous system in some muscles are permanently contracted causing rigidity, shortening of muscles and interference in movements and functions.
It also causes deambulation, balance problems, manipulation of objects, speech and swallowing, among others.
Spasticity affects muscles and joints of the extremities causing abnormal movements, or inhibition of movement; It also inhibits the longitudinal growth of the muscle and the synthesis of the protein in the muscle cells, limits the stretching of the muscle and develops deformities also in the joints that can develop over time.
This problem is due to some trauma or associated to diseases such as multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, diplegia, quadriplegia or hemiplegia, hypoxia or cerebral stroke, adrenoleukodystrophy or phenoceturia among other conditions.
It manifests with:
- Increased muscle tone or hypertonia.
- Cramps in the form of rapid contractions without noticeable movement.
- Exaggerated reflexes or hyperreflexia of deep tendons.
- Muscle rigidity that can be mild or very severe and painful.
- Uncontrollable muscle spasms.
This disease can be treated but not definitively cured. Among the forms of treatment are: oral or injected muscle relaxants, use of botulinum toxin or Botox and even in some cases the use of orthoses, external devices that help control the affected part.
The use of Botox injected into the muscle has shown great effectiveness, since it weakens muscles for a long time, reducing spasticity in a limited group of muscles. In extreme cases, surgery can also be performed to release or lengthen the tendons or nerve channels.
Physical therapies such as massage, hydrotherapy, laser and others such as infusion of baqclofen using a pump implanted in the wall of the abdomen is very effective in reducing spasticity in spinal cord injuries but the side effects of each technique have to be assessed.
Muscular distension is part of the group of closed muscle injuries, which also include fibrillar rupture, fascicular tear and muscle tear. The severity of the muscle injury increases from the distention of the muscle to the tear. However, unlike all other muscular injuries of this group, in the case of muscle distension there is no damage or tear of the muscle fibers, fascicles of muscle fibers or the whole muscle.
Muscular tension altered
When a distension occurs, it means that there has been an alteration in the regulation of muscle tension (muscle tone) is altered. After a few moments, the muscle tenses massively, for example, due to a sudden effort. The consequence is that the muscle hardens while appearing pains that can intensify spasmodically. In the case of presenting a muscle strain, in general, those affected should immediately conclude the sporting activity. If they do not, there is a danger that the distension of the muscle will progress to a fibrillar rupture or a more serious injury.

CAUSES
The cause of muscle distension is the alteration of the regulation of muscle function and not the damage of individual muscle fibers, as occurs for example in the case of fibrillar rupture. The distension can cause it for example, a rapid change of the load, as it would be the case of a change at an excessively strong rhythm when running.
Added to this are concomitant factors that also increase the likelihood of distension. In addition to the muscles fatigued by excess exercise, among these factors is mainly a musculature with a poor blood supply due to a low ambient temperature and / or an insufficient heating program. A poor general condition (for example, due to illness such as a cold, inadequate footwear and certain orthopedic features (for example, a flat transverse foot) can also increase the risk of strains. liquid and / or electrolyte, as well as unbalanced feeding, also contribute to increasing the risk of a distension.
In addition, certain forbidden substances that serve to increase the musculature quickly (the so-called anabolic) favor the appearance of distensions. To date, sports doctors are still discussing whether the active substance creatine, which some athletes take to increase potency, increases the risk of strains.
SYMPTOM
A muscle strain is especially characterized by symptoms such as partially spasmodic pain in the affected muscle. In many cases, as a result of distension, the muscle only partially functions or does not work at all. As a symptom of distension, muscle cramps can also occur. The muscle hardens. Often a muscle strain can also develop slowly generating increasing discomfort. This distinguishes it from sports injuries such as fibrillar rupture, in which the pain appears suddenly and directly.
Muscle distension begins with symptoms such as an unpleasant sensation or tension in the affected muscle, for example, in the thigh. In the case of muscular distension, this sensation increases with time until you feel a pull in the muscle, which finally transforms into pains that can intensify spasmodically.
PREVENTIONS:
For the prevention of both cases, it is recommended: act correctly with respect to the main risk factors: among them, above all, a low ambient temperature. For this reason, when the weather is cool or cold, the muscles must be heated with special care in order to prevent distension effectively. The duration of the warm-up must be at least 15 minutes. However, the reverse conclusion is not that the risk of muscle distension is lower with hot weather. Although the higher ambient temperature reduces the risk of muscle distension due to cold, the body also loses (as a result of the higher ambient temperature) more fluid and electrolytes due to intense sweating. These losses also increase the risk of distension. Thus, liquid and electrolyte deficits must be balanced regularly and, above all, in time.
The importance of adequate sports equipment
The choice of suitable sports equipment also helps to prevent muscle strain. Appropriate clothing should be purchased for the type of sport and appropriate footwear. In case of orthopedic problems, such as flat feet, it may be convenient to use additional orthopedic insoles for athletic shoes.
Inconvenience of the stimulant ointments of the circulation The application of ointments, creams or stimulatory solutions of the circulation can not replace the specific heating program. Although they increase circulation, the depth of penetration is so low that irrigation is only greater in the superficial layers of the skin. The stimulating effect of the circulation leaves the deepest areas of the skin as intact as the musculature. Hence, this type of preparations is not appropriate to prevent muscle distension. The only thing they do is create a supposed sensation of good circulation and warm up of the treated muscles, when the only thing that is really heated is the skin.
SOURCE:
https://www.onmeda.es/enfermedades/desgarro_muscular-prevencion-15961-9.html
https://www.puntofape.com/espasticidad-o-rigidez-muscular-1336/