shock wave a basically waves travelling at greater mach number that is it travels faster than the speed of sound (supersonic/transonic level) , solid pressure wave in any flexible medium, for example, air, water, or a strong substance, delivered by supersonic air ship, blasts, lightning, or other marvels that make savage changes in weight. shock waves vary from sound waves in that the wave front, in which compression happens, is a district of sudden and fierce change in pressure, thickness, and temperature. Along these lines, shock waves engender in a way unique in relation to that of normal acoustic waves. Specifically, shock waves travel faster than sound, and their speed increments as the sufficiency is raised; however the power of a shock wave likewise diminishes quicker than does that of a sound wave, since a portion of the vitality of the shock wave is consumed to warm the medium in which it voyages. The plentifulness of a solid shock wave, as made in air by a blast, diminishes nearly as the converse square of the separation until the point that the wave has turned out to be weak to the point that it complies with the laws of acoustic waves. Shock waves modify the mechanical, electrical, and warm properties of solids and, along these lines, can be utilized to think about the condition of express (a connection between pressure, temperature, and volume) of any material.
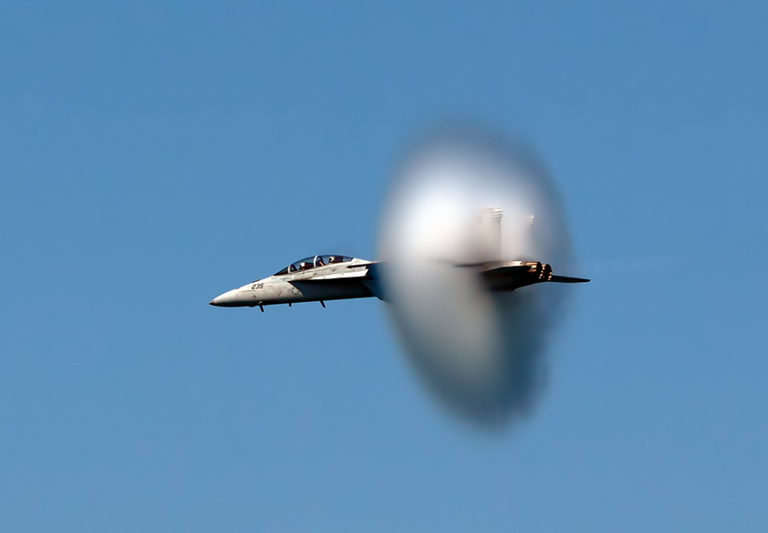

Shock wave in a jet travelling at a supersonic velocity
wikimedia creative commons CC BY-SA 3.0
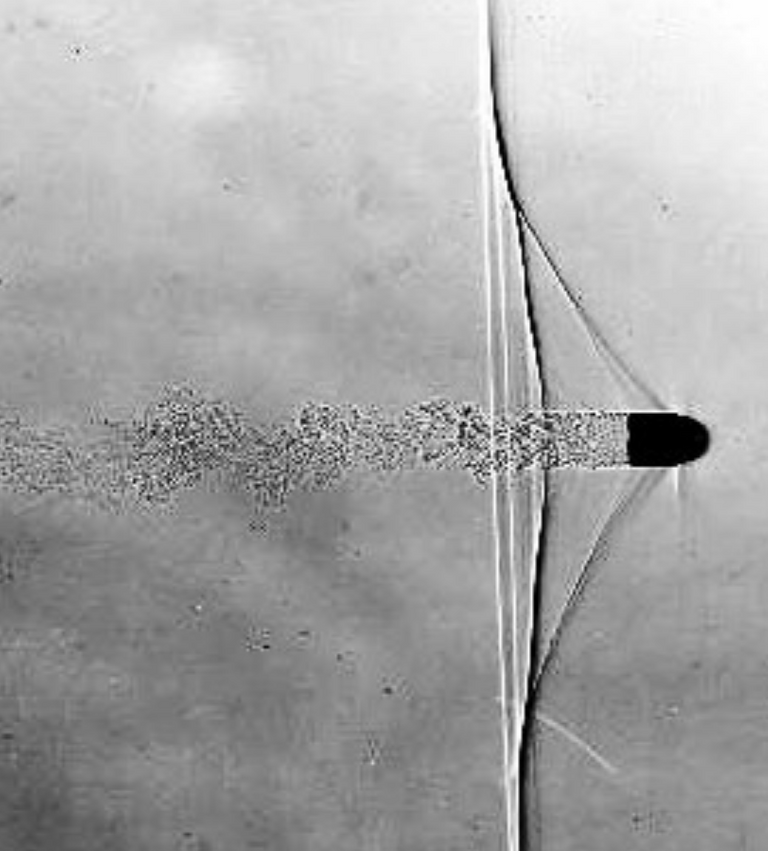
Shock wave in bullet flight
wikimedia creative commons CC BY-SA 3.0
BASIC CONCEPT
At the point when the speed of a source breaks even with the speed of sound (v = c) the wave fronts can't get away from the source. The subsequent heap of waves shapes an expansive adequacy "sound wall" that makes managed flight at this speed troublesome and dangerous.
The expression "sound wall" or "sonic hindrance" first came into utilization amid World War. Military pilots occupied with fast plunges saw a few anomalies as flying rates moved toward the speed of sound: streamlined drag expanded extraordinarily, considerably more than ordinarily connected with expanded speed, while lift and mobility diminished in a correspondingly irregular way. Pilots at the time erroneously believed that these impacts implied that supersonic flight was inconceivable; that some way or another planes could never travel faster than the speed of sound. They weren't right.
At the point when the speed of a source surpasses the speed of sound (v > c) the wave fronts fall behind the source in a cone-formed locale with the source at the vertex. The edge of the cone shapes a supersonic wave front with a surprisingly huge plentifulness called a "shock wave". At the point when a shock wave equals the speed of the spectator a sonic blast is heard.
Dissimilar to customary sound waves, the speed of a shock wave changes with its magnitude. The speed of a shock wave is constantly more note worthy than the speed of sound in the liquid and is reduced as the magnitufe of the wave diminishes. At the point when the shock wave speed breaks even(equal) with the typical speed, the shock wave dies off and is decreased to a customary sound wave.
The phenomenon of shock waves can best explain a wave effect called doppler effect.
DOPPLER EFFECT
The Doppler effect is a phenomenon used to explain the variation in sound waves with respect to the movement of the source producing the wave and the spectator. The Doppler effect can be portrayed as the impact created by a moving wellspring of waves in which there is an obvious upward move in recurrence for the spectator and the source are drawing closer and a clear descending movement in recurrence when the onlooker and the source is retreating. The Doppler effect can be seen to happen with a wide range of waves - most especially water waves, sound waves, and light waves.
The Doppler effect is observe because of the fact that the separation between the wellspring of sound and the eyewitness is evolving. On the off chance that the source and the spectator are drawing closer, at that point the separation is diminishing and if the source and the eyewitness are subsiding, at that point the separation is expanding. The wellspring of sound dependably discharges a similar recurrence. Along these lines, for a similar timeframe, a similar number of waves must fit between the source and the onlooker. on the off chance that the separation is huge, at that point the waves can be spread separated; yet in the event that the separation is little, the waves must be compacted into the littler separation. Consequently, if the source is moving towards the eyewitness, the spectator sees sound waves contacting him or her at a more incessant rate (high pitch). Also, if the source is moving far from the eyewitness, the spectator sees sound waves contacting him or her at a less continuous rate (low pitch). Note that the impact does not come about on account of a genuine change in the recurrence of the source. The source puts out a similar recurrence; the spectator just sees an alternate recurrence on account of the relative movement between them. Hence The Doppler effect is a shift in the apparent or observed frequency and not a shift in the actual frequency at which the source vibrates.
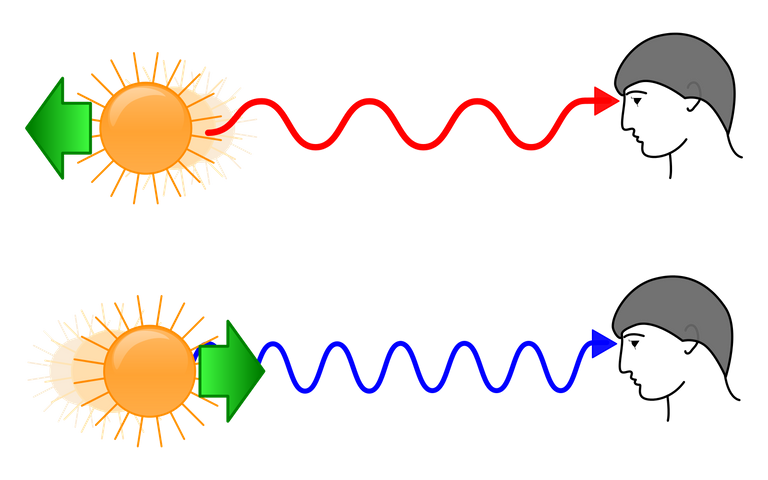
Principle of Doppler Effect
wikimedia creative commons CC BY-SA 3.0
The Doppler impact is watched at whatever point the speed of the source is moving slower than the speed of the waves. However, in the event that the source really moves at an indistinguishable speed from or faster than the wave itself can move, an alternate marvel is watched. In the event that a moving wellspring of sound moves at an indistinguishable speed from sound, at that point the source will dependably be at the main edge of the waves that it produces. The chart at the privilege portrays previews in time of an assortment of wavefronts delivered by a flying machine that is moving at an indistinguishable speed from sound. The circular lines represents the compressional wavefronts of the sound waves. Notice that these circles are grouped up at the front of the air ship. This wonder is known as a stun wave. shock waves are likewise created if the flying machine moves faster than the speed of sound. In the event that a moving wellspring of sound moves faster than sound, the source will dependably be in front of the waves that it produces.
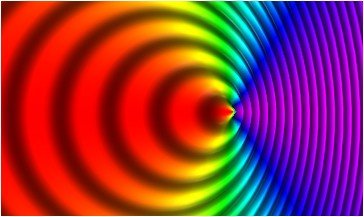
A source of light waves moving to the right, relative to observers, with velocity 0.7c. The frequency is higher for observers on the right, and lower for observers on the left.
wikimedia Creative CommonsAttribution-Share Alike 3.0
Shock waves in generally are now applied in creation of weapons like the supersonic bomb or sonic bomb.
REFERENCE
▪A Text Book of Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic Machines by Er. R.K. RAJPUT.
▪Textbook of Engineering Physics
ISBN 978-93-80408-44-6
Publisher: ACME LEARNING PRIVATE LIMITED,
▪DOPPLER EFFECT :
▪SHOCK WAVES:
Source
There is reasonable evidence that this article has been spun, rewritten, or reworded. Repeatedly posting such content is considered spam.
Spam is discouraged by the community, and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
More information and tips on sharing content.
If you believe this comment is in error, please contact us in #disputes on Discord
Hi @engr.martins. Some of the texts in this article were copied from an article that can be found here:
https://www.britannica.com/science/shock-wave
You have been changing words without changing the structure of the sentences. This is an act of plagiarism and let me remind you that plagiarism is a serious offence in the steemSTEM community.
sorry this was a mistake, my account was hack by a friend due to some misunderstanding, this action is a fiat accompli hence i accept any prosecution. thankx.