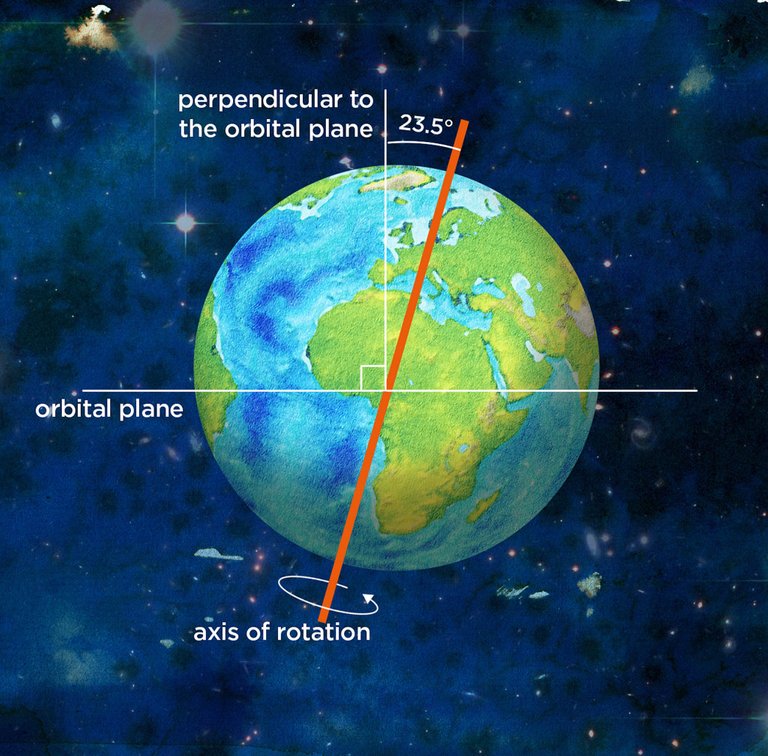
The earth spins about its axis which passes through its centre. This movement is called rotation. The ends of the axis are the north pole and south pole respectively. This axis is inclined 23.5 degrees away from the vertical, that is 66.5 degrees from the horizontal plane of its orbit.
The earth rotates from west to east , and once every 24 hours. As the circumference of the earth is 40084 kilometres round the equator, it means that its speed is 40084 kilometres in 24 hours, or 1670 kilometres an hour.
The following I am going to explain will help explain some certain phenomena on earth. These phenomena are the effects of rotation.
Determination of the north and south poles
The end points of the axis of rotation tell us where the north and south poles are respectively. These are important fixed reference points we use in telling directions on the earth.
Credit
Oblate spheroidal shape of the earth
Like every other rotating body, the earth generates a force called centrifugal force. This force tends to pull the body of the earth away from its axis of rotation. The result is that the earth bulges out at the equator and flattens at the poles . It is therefore the rotation which causes the oblate spheroidal shape of the earth.
Apparent daily movement of the sun
Everyday, we see the sun rise in the east, move across the sky and set in the west . The earth rotates from the west to east, that is why the earth appears to move from east to west across the sky. Notice what happens when you are traveling in a vehicle. All the trees and houses you pass by seem to be racing backwards, in the opposite direction.
Day and Night
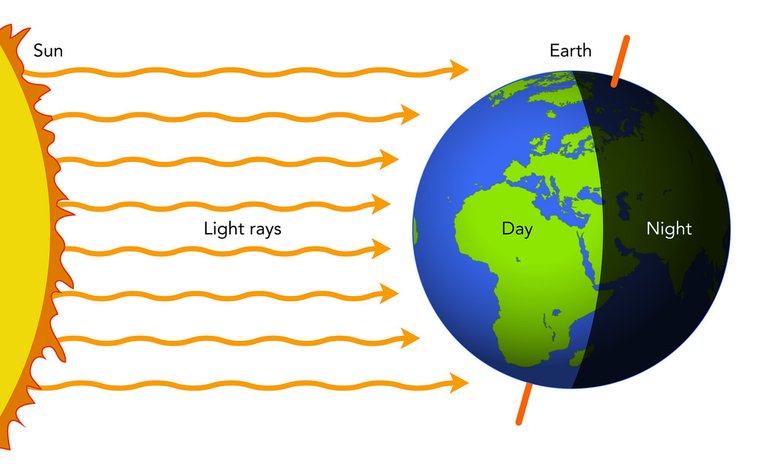
As the sun across the sky with rotation, at any particular time, the side of the earth facing the sun has daylight and the other side, darkness. The first side eventually turns away to have its night, while the side previously in darkness faces the sun to have its day.
Credit
Determination of one full day
Since one full rotation of the earth takes 24 hours, it's rotation helps us to determine one full day and to distinguish one day from the next. One full day is the time it takes the earth to rotate once, equal to one day and one night.
Difference in times
Since the earth rotates 360 degrees in 24 hours or through 15 degrees every 1 hour, and places in the east see the sun before places in the west, this rate helps us to measure differences in times. Thus, a place 15 degrees east of where you live sees the sun rise at 6a.m. 1 hour before you, and a place 15 degrees west of you sees it 1 hour after you. This means that places 15 degrees east of you are 1 hour in time ahead of you, and places 15 degrees west of you are 1 hour in time behind you.
Deflection of winds and currents
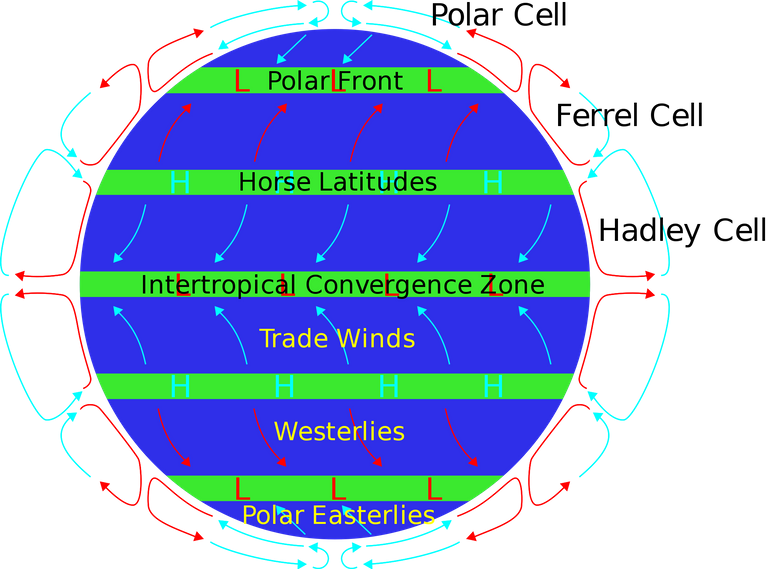
The rotating earth generates another force called Coriolis force. This force deflects all winds and currents blowing or flowing on the earth's surface to the right in the northern hemisphere, and to the left in the southern hemisphere. This is known as the Ferrel's law, because it was a man named Ferrel who first discovered and made it known to us.
Credit
The rhythm of tides
Tides are the rising and falling of the ocean waters as a result of the magnetic pull of the moon on the earth. There are two high tides and two low tide each day. This daily rhythm of the tides must therefore be connected with, and a direct result of, the earth's rotation.
Reference

Good old Earth rotation, we'd be....well dead without it.
Good explanation of the topic, it will be easy for other to follow.
Don't be shy to leave other comments, we'd love to hear some of your feedback :)
This subject is very interesting.
Why do you think the axis is inclined?
We tend to take night and day for granted and never realize that the slightest thing in space could change that. Interesting article.
It is important to note that the "centrifugal force" is just a bodies/objects inertia and is not an outward bound force.
Question! If "This axis is inclined 23.5 degrees away from the vertical" is this related to the magnetic poles?