Hello friends of steemit, days ago I spoke about communicable diseases. Today I continue with the same topic and this time I will talk about the most relevant viral diseases. In a next opportunity we will treat bacterial diseases.
If you want to see the first part, you can do it here: COMMUNICABLE DISEASES. FIRST PART
Among the viral diseases we have:
COMMON COLD:
The common cold or catarrh is an infectious disease caused by various viruses. It is not due to a single specific virus; At present, more than 80 different strains of respiratory viruses capable of reproducing them are known. The cold, the humidity and the abrupt changes of temperature are coadyuvantes factors. It is transmitted directly through coughing or sneezing and the incubation period is extremely short; maximum 24 hours.
Clinically, it presents with catarrhal inflammation of the upper respiratory tract: nose, pharynx, paranasal sinuses and middle ear; but sometimes it descends to the lower respiratory mucous membranes: larynx trachea and bronchi.
The symptoms are nasal obstruction, sneezing and abundant watery secretion, which later becomes mucous and mucopurulent.
It usually causes a slight fever and the treatment is purely hygienic and symptomatic. The administration of antibiotics is not justified.
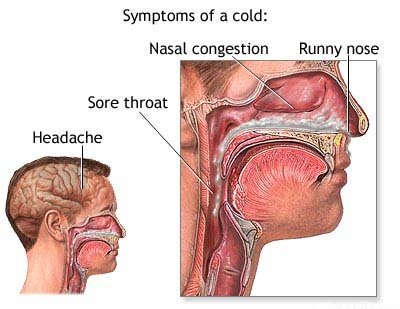
Source
FLU:
The flu is caused by a series of viruses. The incubation period ranges between 24 and 48 hours. It is mainly observed in cold seasons; the transmission route is similar to that of the common cold.
From the clinical point of view, it produces fever, headaches, muscular pains, decay and manifestations of upper respiratory tract similar to those seen in the common cold. In general, it is of acute and mild course but there are severe forms with pneumonia and bronchopneumonia, encephalitis, pleural effusions, among others.
The treatment is symptomatic since there are currently no useful antibiotics for the influenza virus. It is important to make an early diagnosis of complications.

Source
MEASLES:
It is an infection primarily of the child, which is transmitted directly by respiratory route. the incubation period is 10 days, with general manifestations of cough, fever and cold, the period of infection is from the time of incubation until the first three days of the eruptive period.
Measles is clinically manifested by a rash that begins behind the ears and spreads throughout the body, is a small and rough to touch rash.
Complications result in otitis, lagingitis, pneumonia, encephalitis. The treatment is symptomatic: antipyretic, adequate hydration and balanced diet.
The permanent protection is made through the measles vaccine that must be placed to every child that at twelve months of age has not had the disease.

Source
RUBELLA:
It is a benign eruptive disease that is transmitted by respiratory route, by direct contact with the patient or by indirect contact with newly contaminated items.
The incubation period is from 14 to 21 days, in children there is no symptom, but in the adult it can manifest high fever, general malaise and headache.
The period of infection is one week before and at least four days after the eruption appears. Clinically it is manifested by a diffuse pink and punctate eruption accompanied by cervical adenopathies (inflammation of the lymph nodes).
On the other hand, there is congenital rubella syndrome, which occurs in newborns of women who acquired the disease during the first trimester of pregnancy. This syndrome includes cataracts, cardiac malformations, deafness and microcephaly.
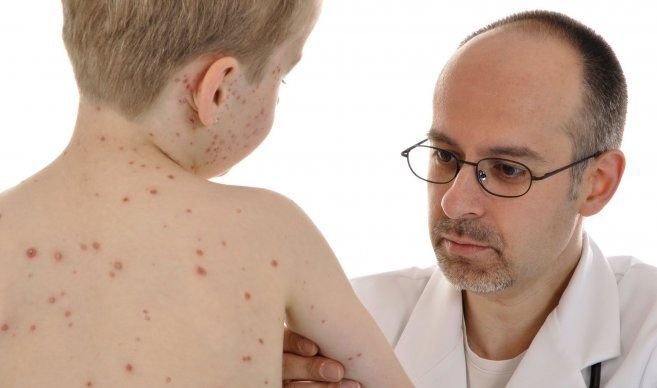
Source
HEPATITIS
Viral hepatitis is the generic term that includes both infectious hepatitis and hepatitis by homologous serum (human blood), since it is difficult clinically to make the differential diagnosis.
Infectious hepatitis occurs at any age. The reservoir is man. The incubation period is 10 to 30 days and the period of infection is during the second half of the incubation time. The mode of transmission is by contact, through the contamination of food and beverages by a virus carrier. Clinically, its onset is difficult to diagnose, with general symptoms such as anorexia, abdominal discomfort, nausea and high fever.
On the other hand, homologous serum hepatitis is clinically similar to infectious hepatitis, but the mode of transmission is by parenteral (intravenous, intramuscular or subcutaneous) inoculation of any blood derivative from an infected person. The incubation period is 50 to 180 days. Preventive measures basically include the disinfection of instruments contaminated with blood.
POLIOMYELITIS
Poliomyelitis is an acute disease whose severity varies from an asymptomatic infection to a paralytic form. The reservoir is man and especially children. It is transmitted by direct contact with the pharyngeal secretions of infected people. The virus can also be found in the stool.
The incubation period is from 3 to 21 days, and the contagious period is almost immediately after the introduction of the agent into the organism, persisting in the feces for six weeks. The most frequent symptoms that occur are fever, headache, intestinal disorders, discomfort and stiff neck and back.

Source
The most important preventive measure is vaccination, which provides a high level of immunity through an infection of the digestive system by attenuated poliomyelitic viruses.
References:
Curso de Orientación Familiar. Medicina y Salud. Ediciones Océano, S.A
If you want to know more about these diseases, you can visit the following pages:
http://nedo.gumed.edu.pl/wszpziu/skrypty/Atlas%20Dermatol/S_Derma/005S.pdf
http://cdigital.dgb.uanl.mx/la/1020082549/1020082549_027.pdf