
Source of image-1
Source of image-2
Contest Link: https://steemit.com/self-power/@upmewhale/upmewhale-writing-contest-restricted-and-unrestricted-internet-freedom-world

Introduction
In general, freedom of speech is very fundamental to the freedom of an individual and an individual must be able to express without having any fear. An individual can express orally, by writing or in any other mode such as internet, etc. The freedom to express and the freedom to use a medium are called freedom of expression. The freedom expression is a fundamental human right in almost all countries by laws and precisely it is an international law.
This article will focus on the medium of expression and the medium for today’s topic is internet. Further this article will also go into details about the state of freedom of Internet in my country which is India, the challenges to freedom of internet in India, possible solution, etc.The internet was introduced in India in the year 1995. Internet is facilitated to India through 9 undersea fibres and one overland internet connection at Agartala. India has a population of 1.3 billion as per the last census data and the internet penetration in India is 41%, i.e. 560 million internet users(2nd position in World). The e-commerce market is growing rapidly in India and the current state policy also supports digital India. When we say digital India, internet becomes a fundamental infrastructure.
Internet by default is decentralized and democratic. But when it enters a territory then it becomes a subject of supervision by the state authorities. It is true for almost all countries. The extent of supervision and censorship may vary from one region to the other. So India is also no different. The freedom of internet is challenged in India by so many vectors.
Another point to consider is that even though state bodies censor and supervise internet within the territory, they don’t have an outright control. Some of the connections to India are consortium owned and some are private. So the landing stations also play a role.
Until 2008, the internet censorship was not that extensive as compared to what it is now. India has been a victim of terrorism since 3 decades with 2008 Mumbai attack, 1990 ethnic cleansing of Kashmiri Pundit were the most brutal. So on many occasion freedom to internet and national security conflicts.
The IT Act, 2000 was not very comprehensive and that is why IT Act was amended in the year 2008(by introducing section 66A and 69) to address a wide array of internet related crimes & challenges which includes cybercrime, cheating, hacking, child porn, electronic commerce fraud, cyber terrorism, voyeurism, obscenity, misrepresentation, false information, etc. The section 66 & 66A were challenged in the supreme court of India. In the year 2015, the supreme court of India struck down 66 but upheld 66A which authorizes govt of blocking online contents.
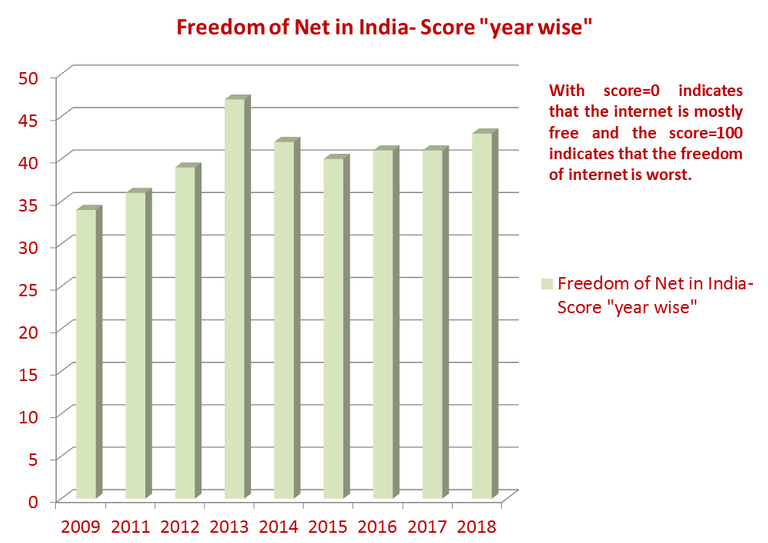
The point is that since 2008, the state of freedom of Internet in India has been facing many challenges and some of the challenges are really very complex to the extent that it becomes a conflict of interest with the democratic values. That is why the score of freedom of Net in India has been in the “partially free” range with average values around 40. But compared to other Asian peers it is better (For example China is highly restrictive with a score of 88).

Now coming to the various challenges India has been facing which is somehow forcing the state authorities to take preventive measures from time to time to preserve National security, communal harmony, and many other important national interest & objective.
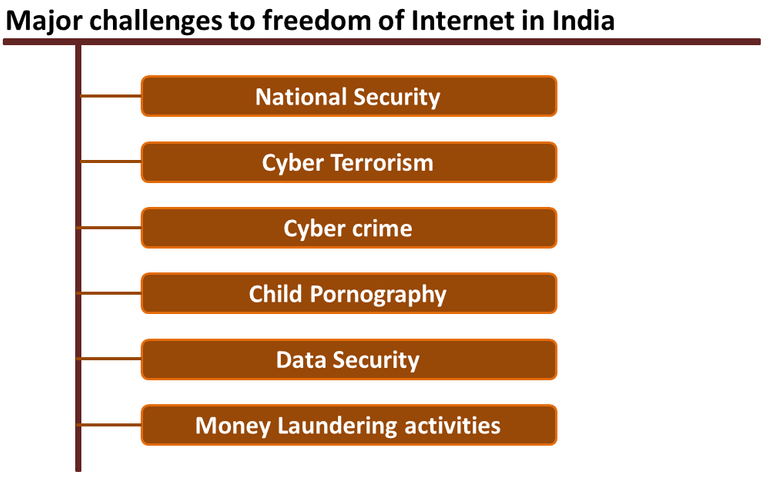
National Security
India has been a victim of terrorism since 1989 and till now more than 40000 people including civilian and army men have sacrificed their lives in their effort to fight against terrorism. It is apparent that the over ground workers of terrorist organizations use internet as a medium to propel their terror agenda. Most of the time they have been successful in doing so as well. So when it is about the national security and to safeguard the people of the state, it is necessary to take some preventive measures which necessitate censoring or banning internet services partly or fully and/or for a temporary period.
But I must also say that it is not a permanent and long term solution, the state authorities must also look for a robust solution and they should forge a suitable plan by working in collaboration with the domain expert so that both freedom of internet and national security can be brought to the same side. Banning a certain thing is a temporary solution only and this is not going to work in the fast moving technological evolution, where the tech-savvy people may always find the alternate route and/or they may join hands with foreign and malicious elements to fulfill their agenda.
Cyber Terrorism & Cybercrime
With the evolution of internet and its vast use in the public sphere, cyber terrorism and cybercrime cases are also on the rise. This is not just about India but to many countries, but as India is already facing terrorism, the cyber terrorism & cybercrimes are added burdens to India. The score of cyber terrorism and cybercrime is really high and many people interprete it in many ways. But by and large it is about the use of internet and internet related infrastructure by terror groups to push their terror objective, by criminals to cause harm to other and/or to loot people and for that using internet, etc. It can also be related to using internet for political, ideological, religious objective. India has been facing many instances of its official websites getting hacked in past and the cybercrime rate in India has also been on the rise. The official stat says that from 2011, the cybercrime rate has increased more than 300 percent.
Child Pornography
India already has an act called POCSO(Protection of children against sexual offenses). Despite this, the child pornography is on rise. Out of the total pornographic content, 35 percent are of child or teenager porn content. Child porn content consumers are also on the rise which is an alarming situation. So once again the freedom of Internet is clashing with the objective of preserving ethics and moral values in the society.
Data Security
Just like the freedom of expression is important so as the privacy. The Adhaar controversy in India has already been dragged to Supreme court. We have certain constitutional obligations, but how can we not take seriously to protect the privacy of the data. This is not just about Adhaar. Numerous telecom companies, private banks are selling the consumers data in the second channel and earning huge money. We don’t have a framework in place to catch hold of these people and punish these people. This pattern has been on rise in India. We should not forget that along with the evolution of Internet, the new kind of economy is also being evolved one of which is data trading. In line with that preserving data security is essential.
Money laundering Activities
There is an act called PMLA( Prevention of Money Laundering Activities) which was enacted in 2002. It has a guideline to combat terror financing and second channel economy which is very much prevalent in India. With digitalization and internet this kind of thing can be checked subject to the compliance with KYC(Know your customer). But the malicious elements always find some way or the other to route through the second channel economy. Probably that is why India is reluctant on legalizing cryptocurrency. India is a proponent of disruptive technology(Blockchain) but they are not in favor to legalize cryptocurrency. The number one reason is that India is putting all its effort and might to fight terrorism and it is a well known to everyone that how the terror financing happens.
But the point is that even before the invention of cryptocurrency the terror financing was there. So it is better to attach a legal framework for the use of cryptocurrency and it should be legalized. A complete ban is not a good step; nonetheless crypto-economy is also vital for the nation’s economy and it can potentially create numerous jobs.
The major challenges to freedom of internet in India as described above, at times forces the state authorities to put ban on the use of internet. But that can only yield short term solution. In the long run the state has to find an amicable solution so that the freedom of internet and the national interest may not collide as conflict of interest.

The dark side exercising executive power
The above are the real and genuine challenges India is facing. There is a dark side of exercising executive powers in India as well. There have many instances where the different service provides as well the state authorities exercised their power which suited their own objectives. India has an IT Act, based on the guidelines of that the state bodies issue directives to the ISPs. But the ISPs do not always follow that directive religiously. Rather they act and add something in addition to the directives to achieve and fulfill their business objectives. The state bodies also misuse their executive power to suit their own objective which is other than the national objective.
In the year 2011, many cartoonists were arrested just because they express and oppose the heavy scams and corruption by the then government. That was simply brutal killing of democracy.
The point is that if it is a genuine major challenge as explained above, even though people don’t feel comfortable, they will always stand by the government if it is an issue pertaining to the national interest. But if the internet policy is being exercised for catering the objective of the party(not the nation) and for corruption, scams, unethical & unconstitutional practice, then there will always be agitation. Such agitation may turn into a mass movement. That is what exactly happened in the year 2011 in Anna Hazare movement in India against corruption demanding Lokpal Bill.

Abuse of Internet Freedom by influential persons & politicians
Artificially portraying & boosting the popularity of politicians through the use of Internet must always be opposed. The fake information and the links must be dealt appropriately and the associated persons must be brought under the law. Any anti-national agenda with the use of internet and the probable violence must be checked.
Whatever is the case censorship must not come as a repression to the democratic voice of the people. Be it corruption, right to privacy or any other fundamental right which in no way conflicting with the national interest must be allowed to voice freely. Under such cases, the free flow information through the internet should happen.

Conclusion
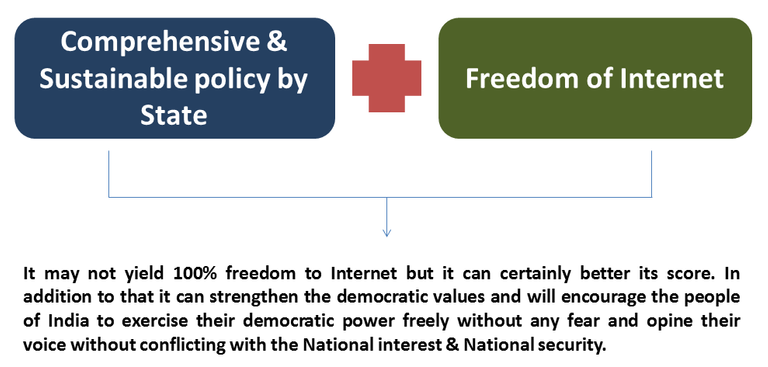
With the set of challenges that India is facing, India can still better its score from “partly free” if the policy will be robust and for that a comprehensive approach is needed which requires collaboration with the domain expert. The political parties may come and go and the power will switch from one party to the other, as the democratic system of India will exercise its voting power every 5 year. So the policy should be congruent to the national interest not any party’s interest. If a comprehensive framework in collaboration with the domain expert be made, then the internet policy in India will become sustainable and it can address various challenges effectively which can also balance both National Interest as well as freedom to Internet.
References
- Internet in India
- Freedom to Net in India & score
- IT Act in India
- Child Pornography law in India
- Anti money laundering law in India
Note- Where ever the image is derived from other websites, the source is indicated, rest are my original works.
This is my entry into the contest organized by @upmewhale

