TONSILS
¨The tonsils are lymph nodes in the back of the mouth and top of theoropharynx ¨ They normally help to filter out bacteria and other germs to prevent infection in the body.
¨Comoposed of lymphatic tissues and are situated on each side of the oropharynx.

source-http://r.search.yahoo.com
TONSILITIS-
¨Tonsillitis is inflammation (swelling) of the tonsils.
¨Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the glands of the throat
CAUSES- Tonsillitis can be caused by either viruses or bacteria. Whether viral or bacterial, tonsillitis is transmitted most commonly from one person to another by social contact such as droplets in the air from sneezing Most of the time, tonsillitis is caused by a viral infection.
significant causative agents:
beta-haemolytic streptococci (groups A, C and G)
adenoviruses
¡Epstein-Barr virus
¨other causative agents:
¡various bacteria and viruses which are rare and with little significance on treatment
¨Bacterial tonsillitis can be caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, the organism that causes strep throat.
¨If left untreated, strep throat may lead to a more serious condition called rheumatic fever, which can affect the heart several years later.
¨Symptoms of tonsillitis include:
¨Sore throat
¨Difficulty feeding (in babies)
¨Pain with swallowing
¨Fever
¨Headache
¨Abdominal pain
¨Nausea and vomiting
¨Cough
¨Hoarseness
¨Runny nose
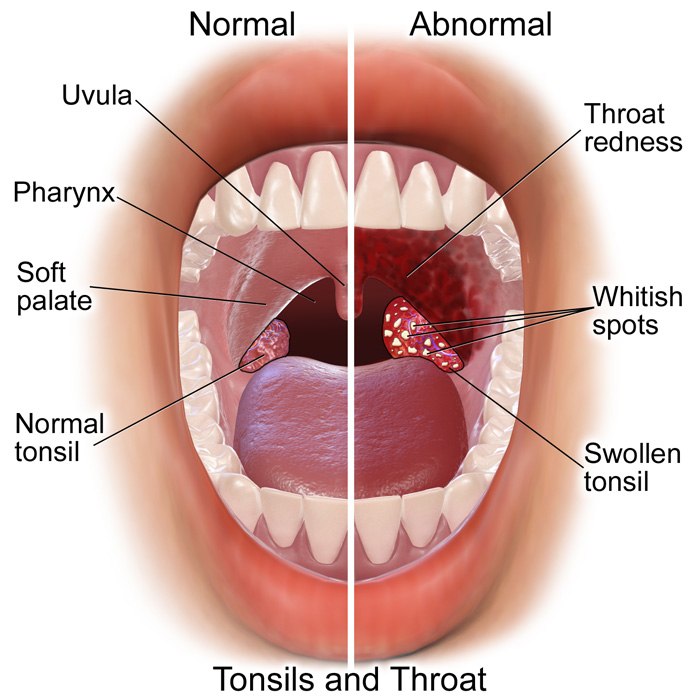
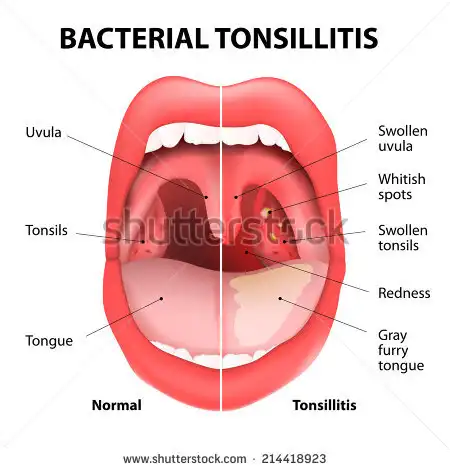
¨Redness of the tonsils and throat
¨Tenderness in the glands of the neck (swollen lymph glands)
¨White patches on the tonsils
¨Redness of the eyes
¨Rash
¨Ear pain (caused by nerves that go to the back of the throat also go to the ear)
TYPES OF TONSILITIS
ACUTE and CHRONIC
ACUTE-
Primarily, the tonsil consists of
a)surface epithelium which is continuos with the Oropharyngeal lining,
b) crypts which are the tube like invaginations from the surface epithelium and
c)The lymphoid tissue.
¨Acute infection of the tonsil may involve these components and are thus classified as:
Acute catarrhal or superficial tonsillitis 2) Acute follicular tonsillitis
Acute parenchymatous tonsillitis 4) Acute membranous tonsillitis
¨Chronic tonsillitis is of three types:
1.Chronic follicular tonsillitis
2.Chronic parenchymatous tonsillitis
3.Chronic fibroid tonsillitis
AETIOLOGY-
Complication of acute tonsillitis
Subclinical infections of tonsils without an acute attack
Mostly affects children and young adults, rarely occurs after 50 years
Chronic infection in sinuses or teeth may be a predisposing factor
DIAGNOSIS
¨The tonsils are usually red and may have white spots on them.
¨The lymph nodes in the jaw and neck may be swollen and tender to the touch.
¨A rapid strep test can be done in most doctor's offices. However, this test may be normal, and you can still have strep. Doctor may send the throat swab to a laboratory for a strep culture. Test results can take a few days.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
¨Tonsillitis caused by a virus will usually go away on its own.
¨ Treatment focuses on helping one feel better.
¨One may be able to ease throat pain if one gargles with salt water, drinks warm tea, takes over-the-counter pain medicine, and uses other home treatments.
¨ Aspirin is not given to anyone who is 20 or younger. It is linked to a serious disease called Reye syndrome.
¨If tonsillitis is caused by strep, treatment with antibiotics is needed.
¨First choice:
Penicillin V 1-1.5 mega units twice daily for 10 days (more relapses with shorter treatment period (A))
¨Second choice:
¡first generation cephalosporins (cefalexin 750 mg twice daily or cefadroxil 1g daily) or
¡procaine penicillin 1.2 – 1.5 mega units daily
for 10 days
¡macrolides – with caution (if local resistance patterns accept their use or they are indicated by sensitivity testing)
SURGICAL TREATMENT-
Tonsillectomy:
¨ when there are serious problems with the tonsils.
¨These include infections that happen again and again, or long-lasting infections that do not get better after treatment and get in the way of daily activities.
HOME TREATMENT-
¨The following tips may help your throat feel better:
¨Drink fluids, especially warm (not hot), bland fluids
¨Gargle with warm salt water
¨Suck on lozenges (containing benzocaine or similar ingredients) to reduce pain (these should not be used in young children because of the choking risk)
¨Take over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen to reduce pain and fever..
¨Some people who have repeated infections may need surgery to remove the tonsils
COMPLICATIONS-
¨Complications from strep throat may be severe. They can include:
¨Blocked airway from swollen tonsils
¨Dehydration from difficulty swallowing fluids
¨Peritonsillar abscess in other parts of the throat behind the tonsils
¨Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (kidney disease caused by strep)
¨Rheumatic fever and other heart problems
REFRENCE-
¨PL DHINGRA, Diseses of Ear, Nose and Throat, Fourth Edition,2009, Page no: 239-253
¨Smeltzer, Bare, Hinkle, Cheever, Brunners ans Suddharth’s Textbook"http://emedicalppt.blogspot.com/2011/05/tonsillitis">http://emedicalppt.blogspot.com/2011/05/tonsillitis http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002038/
¨http://www.emedicinehealth.com/tonsillitis-health UPVOTE RESTEEM FOLLOW