
In general light is known as the smallest quantity of energy that can be transported. A photon, whics is an elementary particle without a real size that can't be split, but created or destroyed. Light also has a wave particle duality being like a particle and a wave at the same time.
So when we usually trivially say: Turn on the light, we actually mean visible light which is a tiny part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is energy in form of electromagnetic radiation.
Image below is the presentation of the different visible wavelengths of the electro-magnetric spectrum. Frequency in hertz is the number of cycles of the repetitive waveform per second. Frequency has an inverse relationship to the concept of wavelength. The frequency f is equal to the speed v of the wave divided by the wavelength λ (lambda) of the wave: f = v / λ
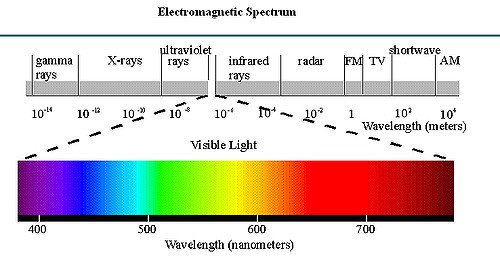
Electromagnetic radiation consist of an enormous range of wavelengths and frequencies. Gamma rays have the smallest wave lengths due the fact that they are the highest energy photons. Gamma radiation is extracted from radioactive elements, unseen parts of nuclear reactors, there is a lot of it in space. It penetrates quite well through hard matter. In excess, this radiation can cause radiation sickness or be lethal to tissues.
Visible light is in the middle of the spectrum in a range of about 400 nanometers to 700 nanometers. On the other end of the spectrum, radio waves can be up to 100 kilometers in diameter. But the biggest wave lengths we know exist can span from 10,000 kilometers to a 100000 kilometers.
Radio waves are "seen" by radio, television, radio telescopes. Microwavesare received by antennas of mobile phones, satellite, radar. Such waves are also produced in microwave ovens. Infrared is closely related to thermal radiation, because all heated bodies produce a lot of infrared light. Technical recording of such waves is possible by infrared cameras and infrared sensors. Ultraviolet tans, however, can cause skin cancer, disinfects killing bacteria, but before its excess it is worth protecting eyes and skin. X-rays is produced not only in X-ray tubes, because a lot of it for example is in space. X-rays used in excess on tissues cause various diseases, mainly cancer.
From the physics stand point, all these different waves are the same. They all have wave particle duality and travel with the speed of light which is 299 792 458 meters per second, but with different frequencies.
Light can be imagined as a piece of a constantly pulsating electromagnetic field. The patch rushes through empty space or through a transparent material center with great speed. The electromagnetic field consists of two simpler fields, closely coupled with each other. From the electric field and the magnetic field. The electric field dissipates free electric charges, or curves their path. In everyday life with a pure form of electric field, we meet when combing dry hair when the movement of the comb causes sparks. the magnetic field can only curl the load path, but it can also act as a force on the conductor with the current. This field is produced by conductors with current, moving charges as well as permanent magnets.
Visible light is the only set of electromagnetic radiation that propagates when in water. Then a phenomenon called the refraction of light appears, which I described in the earlier post.
The important issue is where light comes from. A vast range of electromagnetic waves are created when atoms or molecules drop from a higher state of energy to a lower one. They lose energy and emit it in a form of radiation. The visible light is created when an electron within an atom in an excited state drops to a lower energy state and loses this excess energy.
The moving charge of electron creates an oscillating magnetic field, which creates oscillating electric field perpendicular to it. The resulting beam moves around the cosmos also containing with it information about its place of create.
This simulation shows the approximate time needed for light to overcome the distance between Earth and the Moon.

References:
[1]http://home.agh.edu.pl/~zak/downloads/optyka-2012.pdf
[2]http://www.ifpan.edu.pl/~tomsow/popular/mlody_technik/mt0703.pdf
[2]https://rozumiem-fizyke.yum.pl/swiatlo-i-jego-wlasciwosci


Dołącz w końcu do Polaków, szybciej zarobisz niż po angielsku. Rób takie posty po polsku w tym tagu poniżej, a na pewno zarobią.
https://steemit.com/trending/pl-artykuly
Spróbuję :)
@simson1, I gave you a vote!
If you follow me, I will also follow you in return!
Enjoy some !popcorn courtesy of @nextgencrypto!