
- Geological compass
- Geological hammers
- topographic maps
Loupe - Field notes and rock description sheets
- Stationery
- HCl 0.1 N
- Rock comparator
- Ribbon or string
- Clip board
- Stone sample bag
- Camera
- Field Bag
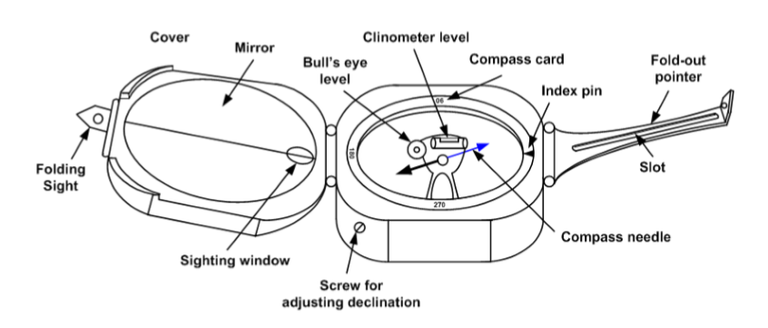
Based on the division of the degree circle, two kinds of geological compass are known:
Compass azimuth, this compass has two figures of the highest degree of circle that is 360 °. The 0 ° and 360 ° numbers coincide in the North compass.
Compass quadrant, this compass has a number of degree circles divided into 4 parts, while the highest number of 90 ° is located in East and West compass and 0 ° in North and South compass.
How to Use Compass Geology:
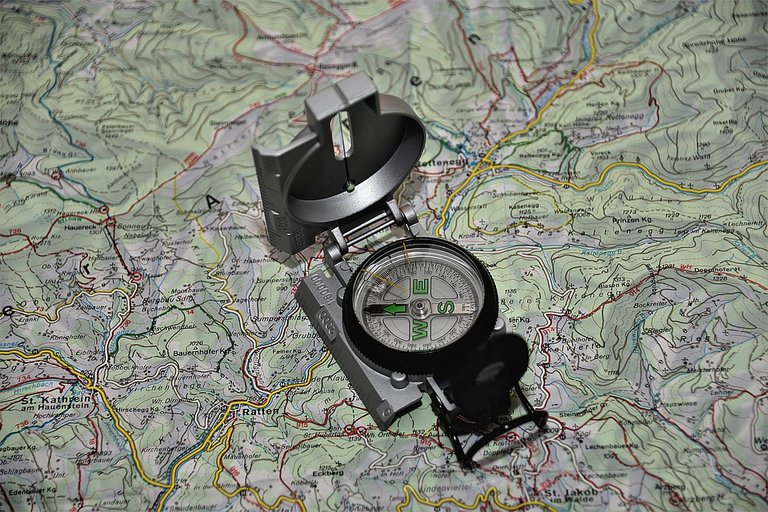

For measurement of direction components (azimuth, stance, line)
- Azimuth measurements (directions), can use two ways:
The compass is opened at an angle of ± 135 °, the hand of the pointer is erect, the compass is held at the waist. Goals are seen through the handheld handheld in the centerline of the mirror. After the bull's eye is in the middle, read the number of degrees dividing circle that coincides with the North compass needle, so that the price of the azimuth / forward direction is obtained.
The geological compass opens at an angle of ± 30 °, held near the eye, the target is seen through the peeping hole and the viewing window, and through the mirror is read the number of degrees circle that coincides with the north needle of the compass, the back azimuth price is obtained.
- The azimuth compass (E attached) is obtained = N 250 ° E
- The quadrant compass (E attached) is written = S 70 ° W
- The quadrant compass (W attached) is written = N 70 ° E
The compass is mounted on the back (the bottom of the mirror hinges) on the topmost plane, with the compass composition perpendicular to the jutsu.
For measurement of large angle components (dip, rake, slope)
The parts of the compass to watch out for are the clinometer, the degree of inclination, and the upright position of the compass.
- Dip / dip measurements (layer and caesarean field)
Compass attached to the layer of rocks / cauldrons, perpendicular stance, set the clinometer until the air bubbles are in the middle (clinometer regulator is on the back of the compass), then read the price of the degree of slope.
- Measurement of slope (slope slope)
The compass is opened at an angle of ± 45 °, held in an upright position close to the eye. The target of sight is a teammate or a peg that has the same height as the shooter / compass eye, the target is seen through the glass window. After the air bubbles are right in the center of the clinometer, read the price of the degree of inclination.
Measurement of location / positioning (plotting)
Location / positioning can be used with the following method:
- Resection is the way resection is used if we want to know the exact position on the map, that is by:
- Set the map correctly (North direction of map adjusted with north compass direction).
- Choose two well-known points, on the map or in the field, such as points A and B.
- Then shoot with the compass and note the angles that can be with the two marked points, for example: T.
- Determine the north direction of the map at the marked point, the way by making a straight line perpendicular to the sum of Y.
- Calculate and illustrate the angles obtained at points A and B, the angle calculation begins and the angle of the investigating compass to point A and B.
- From the angle obtained and illustrated, make a line extension to point A and B cut at one point.
- The intersection of the two lines is our position.
Example:
A = 297° (azimuth hill A against our position)
B = 75 ° (azimuth hill B against our position)
Determine our position:
back azimuth A' = 117° (297°-180°)
back azimuth B' = 255° (75°+180°)
- Intersection is a way to determine the location of a point (goal) in the field or on the map. Usefulness of this method is to know the position of someone or something on the map, such as knowing the exact plane that fell or the location of forest fires.
- Determine the two points in the field that are easy to recognize and recognize, either on the map or on the field and the distance between the two points to be determined.
- And the two points, determine the angle of the compass to the target to be known on the map (azimuth).
- Change the angle of the compass into a map angle.
- The line intersection is the location of a known target on the map.
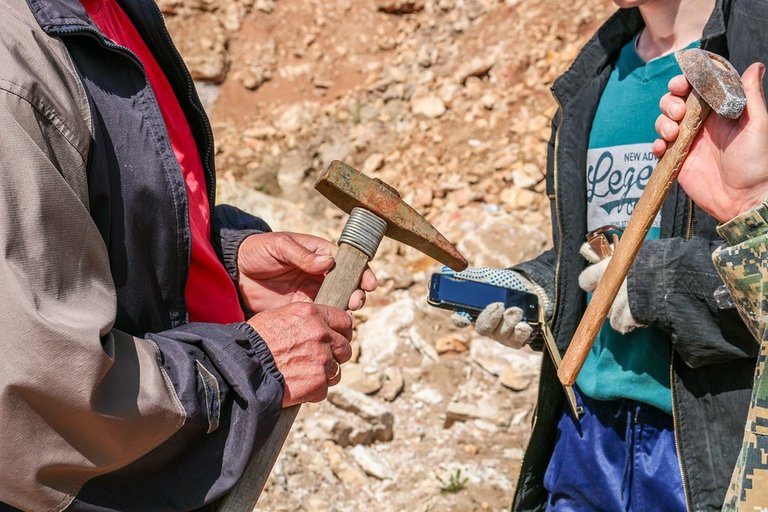

Geological hammers are useful for taking very hard rock samples. There are two common types of geological hammers:
- Pick point (common type of pointed hammer) commonly used for rock hard, such as igneous rocks.
- Chisel point (type of hammer-tipped like chisel) commonly used for rock-lined / sedimentary rocks.
1.HB or 2H pencil, used for recording and sketching, with the advantage of pencil drawing or writing not fade in contact with water, and easily removed.
- Colored pencils, used to clarify lithologic symbols in field notes and on maps.
- Eraser, to remove the pencil or colored pencil.
- Long and triangular ruler, used to help position placement on the map and to measure the distance on the map.
- Level bows, used to measure the direction (azimuth on the map, or to measure the size of the rake or pitch).
- Pencil or sharpener taper, to sharpened a blunt or broken pencil.
- Waterproof waterproof (water proof), used to write rock sample numbers and other information on rock sample bags.
(clip board), it is useful to cultivate data recording in the field or as a base of geological compass when measuring structural elements in uneven layers of rock.
Loupe/hand-lens, The commonly used lens is a lens that has 8%, 10%, 15%, and 20% enlargement. This magnifying lens is used to enlarge objects to be more easily observed and studied, such as granular minerals, fossils, etc.).
Rock comparators, commonly used comparators are igneous rock compactors and sedimentary rock comparators (Went-worth Scale). This comparator is useful for assisting in the description of rocks, by comparing examples of rocks and minerals recorded on the comparator.
solution HCl 0,1 N, Used to test carbonate content and rock samples observed (especially sedimentary rocks). How to test it is by dripping solution HCl 0,1 N directly to the rock sample. When bubbling / reacting, the rocks are carbonaceous (CaC03).
Ribbon or string, used to measure distances between observation locations. Commonly used in Measure Section (MS) Measurements Measurements, Types of commonly used measuring tapes are 30-100 inches long and short-sized (metered) measurements of 3-5 inches long.
Cameras, used for taking pictures from outcrops or other data, such as the morphology of economical mining materials, the location of observations, etc. The camera used should be practical and not difficult to use on difficult terrain.
used to carry geo-logic equipment and field equipment. It is best to distinguish between bags for equipment and maps with bags for supplies and rock samples. The size of the bag should be adjusted to the condition of the field Backpacks with the size of 40 liters are commonly used, because it is not too big and not too small.
Conclusion
Supporting literature / Reference
- Responsi, geology dasar, 2010, Departement pendidikan KM HMG “ARC-SINKLIN”
- Asikin, Sukendar. 1987. Buku Penuntun Geologi Lapangan. Geologi ITB. Tidak diterbitkan.
- Fry, N. 1985. The field description of metamorphic rocks. Geological Society of London Handbook Series, 110 pages : New York.
- Geni Dipatunggoro dan Febri Hirnawan. Diktat Mata Kuliah Metode Pemetaan Geologi. Jurusan Geologi, UNPAD, Bandung. Tidak diterbitkan.
- Handoyo, Agus Harsolumakso. 2001. Buku Pedoman Geologi Lapangan. Departemen Teknik Geologi, ITB, Bandung.
All about my article part1, part2, part3, part4,part5, part6, part7, part8, part9, part10, part11, part12, part13.part14.
by : @rabo
You received a 60.0% upvote since you are a member of geopolis and wrote in the category of "geology".
To read more about us and what we do, click here.
https://steemit.com/geopolis/@geopolis/geopolis-the-community-for-global-sciences-update-4
Mantap mamen @rabo
Thank-you @adilvakhri
Mantap that nyan... Terus berkarya om...
Siap MOD 😂
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by rabo from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.