Voltaic Cells
Hello all steemians and science lover. Now i want to share a new topic about Voltaic Cells that we know A voltaic cell is an electrochemical cell that uses a chemical reaction to produce electrical energy.
Galvani cells or also called voltaic cells are electrochemical cells that can cause electrical energy from a spontaneous redox reaction. spontaneous redox reactions that can lead to the occurrence of electrical energy is discovered by Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Guiseppe Volta.
The Volta cell is a series of cells that can generate electrical current. In the cell there is a change from the redox reaction to generate electric current.
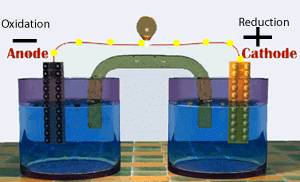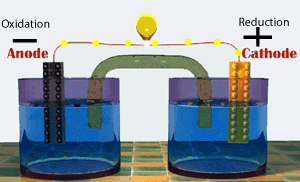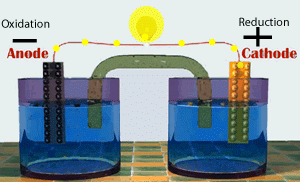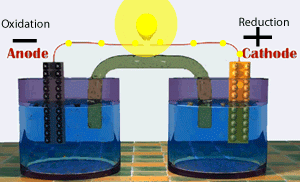
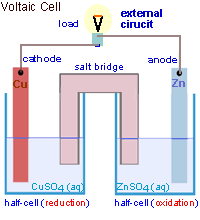
Voltaic cells consist of electrodes where the oxidation reaction is called anode (electrode negative), and the site of the reduction reaction is called the cathode (positive electrode).
Galvanic Cell Network
Galvanic cells consist of several parts, namely: 1. Voltmeter, to determine the magnitude of the cell potential. 2. Salt bridge, to keep the neutrality of the electrical charge in the solution. 3. Anode, negative electrode, the site of oxidation reaction. in the figure, acting as anode is a Zn / zinc electrode (zinc electrode). 4. Cathode, positive electrode, the site of the reduction reaction. in the figure, which acts as a cathode is a copper electrode (copper electrode).Process in Galvanic Cell
At the anode, the Zn metal releases the electron and becomes the soluble Zn2+.
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e –
At the cathode, Cu2+ ions capture electrons and settle into Cu metal.
Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
This can be known from the reduction of Zn metal mass after the rection, while the mass of Cu metal increases. The total reactions that occur in galvanic cells are:
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
Example of voltaic cell in daily life :
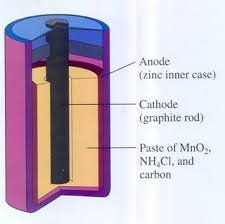
1. Leclanche cell
Known as battery it consists of a cathode derived from carbon (graphite) and zinc metal anode. The electrolyte used is a mixture of MnO2 paste, carbon powder and NH4Cl.Half Reactions:
At cathode: 2NH4+ + 2MnO2 + 2e- → 2MnO(OH) + 2NH3
At anode: Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
Cell reaction : 2MnO2 + 2H+ + Zn = Mn2O3 + H2O + Zn2
2. Lead Storage Cell
The battery cell is also referred to as a storage cell, as it can function electrically and at any time may be discharged. The anodenya is made of lead metal (Pb) and the cathode is made of lead metal coated PbO2Reaction usage :
Anode : Pb + SO4 2- → PbSO4 + 2e
Cathode : PbO2 + SO42-+ 4H++ 2e → PbSO4 + 2H2O
Cell Reaktion : Pb + 2SO4 2- + PbO2 + 4H+ → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
3. A Silver-oxide Battery
A Silver-oxide Battery uses silver oxide as the positive electrode (cathode), zinc as the negative electrode (anode) plus an alkaline electrolyte, usually sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH). The silver is reduced at the cathode from Ag(I) to Ag and the zinc is oxidized from Zn to Zn (II) [Read more](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silver-oxide_battery). This cell is widely used for alroji, calculator and electronic tool.Reaction :
Anode : Zn(s) + 2OH-(l) → Zn(OH)2(s) + 2e
Cathode : Ag2O(s) + H2O(l) + 2e → 2Ag(s) + 2OH-(aq)
Cell reaction : Zn(s) + Ag2O(s) + H2O(l) → Zn(OH)2(s) + 2Ag(s)
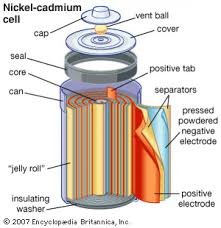
4. Nickel Cadmium Cell
Nickel Cadmium Cell is a rechargable dry cell. The anode is made of Cd and the cathode is Ni2O3. The resulting potential difference is 1.29 V. Other definition is The nickel–cadmium battery (NiCd battery or NiCad battery) is a type of rechargeable battery using nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes. Cell Reaction :NiO(OH).xH2O + Cd + 2H2O → 2Ni(OH)2.yH2O + Cd(OH)2
5. Fuel Cells
The fuel cell is a Galvani cell with its reactants (oxygen and hydrogen) being continuously flowed into a porous electrode. This cell consists of anode of nickel, cathode of nickel oxide and KOH electrolyte.
Reaction :
Anode : 2H2(g) + 4OH-(aq) → 4H2O(l) + 4e
Cathode : O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e → 4OH-(aq)
Cell reaction : 2H2(g) + O2 → 2H2O(l)
Conclusion
Thus, it can be concluded that Voltaic cells are divided into three parts, namely primary voltaic cells, secondary voltaic cells, and fuel cells. Examples of primary voltaic cells are Zinc-Carbon Dry Cells, Mercury Batteries, Silver Oxide Batteries, Lithium Batteries. Examples of secondary voltaic cells are Lead Batteries, Cadmium Nickel Batteries, Silver Zinc Cells, A Silver-oxide Battery, Fuel Cells.
Voltaic Cell is an electrochemical cell in which the chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Voltaic cells involve redox reactions and generate electric current. Volta cells are always formed from two electrodes with different Eo. The electrode with the more negative Eo undergoes oxidation and acts as anode (negative pole). While electrode with Eo more positive experience Reduction and acting as Cathode (positive pole). And the direction of electrons flow from Anode to Cathode. Salt bridges contain positive ions and negative ions that neutralize positive and negative charges in electrolyte solution.
Source :
How does an electrochemical cell work?


Source: https://esdikimia.wordpress.com/2011/09/28/sel-volta/
Not indicating that the content you copy/paste is not your original work could be seen as plagiarism.
Some tips to share content and add value:
Repeated plagiarized posts are considered spam. Spam is discouraged by the community, and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
Creative Commons: If you are posting content under a Creative Commons license, please attribute and link according to the specific license. If you are posting content under CC0 or Public Domain please consider noting that at the end of your post.
If you are actually the original author, please do reply to let us know!
Thank You!
This post recieved an upvote from minnowpond. If you would like to recieve upvotes from minnowpond on all your posts, simply FOLLOW @minnowpond