Good day Everyone, today is the 29th day of January 2018 and I wanna share some little things I learnt in class today. I'm a 300 level student of the department of Biochemistry in the University of Benin, so I'm gonna be sharing some Biochemistry related Topics from a particular course.
IMMUNITY
IMMUNITY is the ability of the body to protect itself against all types of foreign bodies such as bacteria, viruses and toxic substances which enter the body. Immunity is also called disease resistance and the lack of Immunity is known as susceptibility. Immunology is that branch of science that deals with resistance of the body to infection and how the resistance is produced (Immune Response). There are 3 lines of defence system put up by the body to fight infection.
The 1st line of defence (Physical and Chemical barriers) (Innate Immunity);
These include the physical part that are always ready to fight against infection like The Skin and the mucous membrane of the respiratory and digestive tract, The Hair, The Urine, Cilia, Defecating and Vomiting.
The 2nd line of defence (Non-specific Immunity) (Innate Immunity) ; These are the defence system that attacks nonspecific Invaders, that is, they don't target specific individuals, they attack in a generalized way,l. They counter attack by the production of neutrophils and macrophages (which are components of white blood cell) and they kill through phagocytosis.
The third line of defence (specific response) (Acquired Immunity);
They are Immune Response that works through the production of Lymphocytes which can target specific antigens for attack. The cells of the specific Immune system includeB and T cells and they serve different function in Immune Response.
That was where we stopped for today but I also got a little something to share that I learnt during my practical after the class.

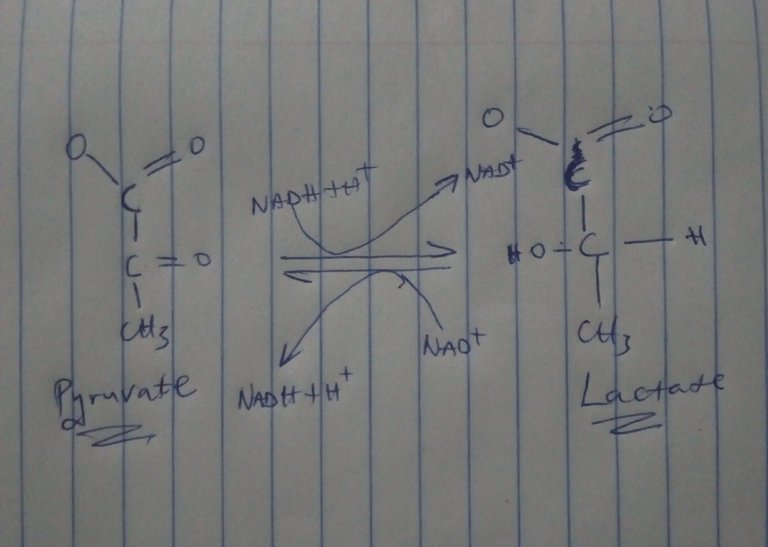
The practical was carried out on Lactate Dehydrogenase and co-enzyme function.
Formation of Lactate from Pyruvate
When there is insufficient oxygen in the muscle cells(anaerobic) for further oxidation of pyruvate and NADH produced during glycolysis, NAD+ is reproduced from NADH by reducing pyruvate to lactate. Pyruvate is then converted to lactate by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase.
A Co-enzyme
A co-enzyme is a biological substance that is Covalently bound to an enzyme in other for the enzyme to carry out it's biochemical function. Without the co-enzyme an enzyme cannot carry out it's activity. Example of a co-enzyme is NAD+.
A Co-factor
A Co-factor is a biological ion that is NOT Covalently bound to an enzyme but it's enhances the performance of the enzyme optimally. Without a Co-factor an enzyme can carry out it's biochemical function but at a slower rate.
And that's all for now!

.jpg)

Welldone.
Success in your studies!
Thank you sir!