Would not it be useful to get a material that can be made thin and resistant as silk threads with which spiders spin webs? Or create a plastic that, like naturally make living tissue is repaired only when sufirese a break?
These are two examples of how materials scientists look to nature for inspiration to improve the materials used industrial processes making them more useful, more effective, cheaper
Shrilk

The plastic of the future will be made from crustacean shells and insect silk. Of chitosan is extracted first and second fibroin.

It is hoped that it can replace plastics we use today in products such as garbage bags,packaging and diapers quickly degrade, plus medical supplies as suture or holder fortissue regeneration in wounds and injuries .
Vantablack

Carbon nanotubes are also the basis of this supermaterial, considered the darkest exists: the vantablack absorbs 99.96% of the light it receives.

This is because it is composed of a "forest" of vertical tubes. When light reaches it, instead of bouncing trapped, bouncing between the pipes until it eventually becomes heat.
Beyond curiosity, what's the use? For example, to prevent stray light reaching telescopes, improving performance of the cameras we use in space.
Aerogeles

Aerogel, which is not a single material, but a type of material, is also known as frozen smoke.

It is a colloidal substance (formed by two components, in this case microscopic solid particles dispersed in a gas). The result is a solid substance, often semi-transparent and ethereal appearance.

The less dense the world solid material is an airgel, weighing 0.0011 grams per cubic centimeter. In addition, aerogels are very good and extremely resistant thermal insulation: a few grams hold several kilos of weight.
Regenerating plastics

A mobile screen is fixed by itself when it is shattered after an unfortunate fall, the light of a car repair single small cracks, cracks that may suffer the fuselage of an aircraft are not a risk for flight are some of the applications seeking researchers working on creating plastics able to regenerate itself.

One of those teams is Spanish, Basque Cidetec company, which in 2013 introduced the first plastic regenerable world only at room temperature without any external agent or catalyst.
Nanocellulose

As a cellulose derivative, plant matter generated in large quantities, the nanocellulose has the advantage that is cheap and environmentally friendly.

It is transparent, lightweight, durable and good conductor of electricity. Why is investigated as applied to the manufacture of military armor, more resilient and efficient cars or medical equipment (to be also absorbent and pliable, can be manufactured with her gauze and bandages, as well as small implants) among others.

Aerographite

The aerographite airgel is an example of precisely the lightest in the world. It is also 5000 times less dense than water.

It consists of a network of carbon nanotubes can be compressed up to 95% and regains its original shape without damage.

It is stable, ductile and opaque, and conducts electricity. With these features, several industries are betting on it for their future: lighter lithium-ion battery, protective shields for satellites or waterproof fashion may be some applications in the future.
Graphene

A sheet of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal structure. Graphene seems a simple material, but getting it was so difficult that those who were able (thanks to a piece of tape), won a Nobel in physics for it.

Graphene is lightweight (0.77 kilograms per square meter), 200 times stronger than steel, flexible, elastic, transparent and a good conductor of temperature and electricity.

Therefore, it is expected to serve to build high-speed cables, batteries, flexible displays and sensors for cameras, and other electronic applications.
But it could also be used in water desalination processes, replacing the current membranes made by other graphene would be much more efficient.
Perovskita

Perovskite is technically not a new material as it has been known since 1839, but only now researchers are discovering their potential.

Applying to the manufacture of solar cells, you could get the same charge as silicon but still much cheaper to obtain and use.
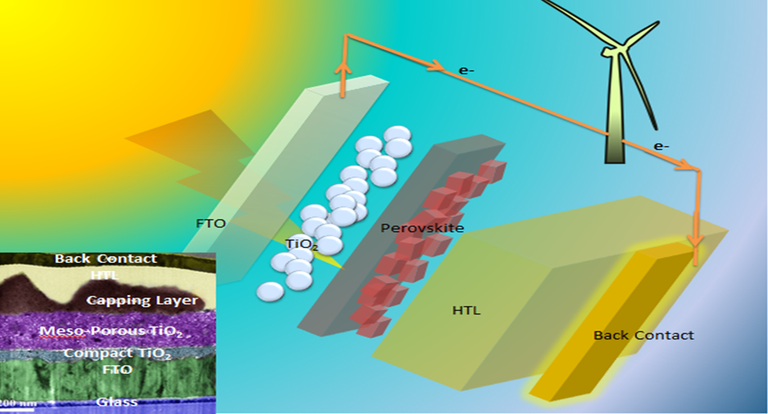
Moreover, being light and little thick, cells made from it could be semitransparent, so that could be placed in windows or roofs, braking sunlight and generate electricity at the same time.

Spiderweb

Spiderweb Scientists have tried for decades to reproduce on a large scale silk that spiders spin webs, without much success until recently.

They say that thanks to its natural characteristics, it would be ideal to make armor from military to medical equipment, such as wire sutures, artificial tendons, through high-performance sports clothing and the like.

A 'startup' Californian, Bolt Threads, announced this week that has managed to reproduce in the laboratory the substance that naturally generate spiders. Perhaps the future for this supermaterial come sooner than expected.
Estanene

Stanene properties, based on the tin material only been tested so far on a theoretical level, but are so promising that scientists work to bring them to trial field.

This is one of the topological insulators known, that conduct electricity only by its edges, not inside, and you would with a 100% efficiency at room temperature, so it would be perfect for use in circuits and replace silicon transistors with those made with computers today.

Nitinol

This is a shape memory alloy (AMF) made of titanium and nickel called nitinol. It has the ability to "remember" the shape it has taken.

It is estimated will be used for:
*Systems approach to repair bone fractures (Anson Medical, UK)
*Superelastic materials (medical instruments)
*Thermostats and control valves
*Unions in pipes submarines and underwater pipelines
*mechanical actuators
*Dentistry, Endodontics both instruments allow more control in curved root canals, orthodontics and arcs arcade *Regain form when heated in the oral cavity.
*Device to treat congenital heart disease
Great post! I love this technology. I saw some of that aerogel at the San Jose Science museum. Hard to believe it's a real thing!
I forget to mention also the hydrophobic spray, it is a very interesting technology
very interesting
Nice @djmedina
Shot you an Upvote :)
Nice post. Thx
Waiting till I walk into a vantablack spiderweb at night and look even crazier than I already do walking into a normal spiderweb, swatting at nothing.