best regards, this is my first post. making my first post feel confused what I will write for the first time. before I write first I see and read the posts of others. much I've seen, but having read the post about space makes me seem to have found something very interesting for myself. I imagine how mysterious nature there is like a dreamland. that's why I decided to start with an overwhelming spirit. I started with the writing of a thing that is almost impossible for man to do if we can start living in space on planets that we know very little about. sorry if my writing is very long :), and I hope you guys can give a lot of input to my writing. okay then, I will start it. thanks!
story
The moon has become our colony and the Earth-Moon flight runs several times a day, a space station becomes a transit point for moving planes, and in the near future, there are plans to send humans to Planet Jupiter. A journey that takes several years but is being implemented. Artificial gravity is created through wheels that rotate on its axis and most of the crew is put to sleep in a hibernation room. Only two crew who worked during the trip with assisted by super-sophisticated computers that monitor the state of the plane.

Colonization of Mars.credit image
At least that's what they imagined in 1968. The late director Stanley Kubrick and his colleague Arthur C. Clarke-a prominent science-fiction writer based in Sri Lanka-adapted Clarke's short story, The Sentinel, and gave birth to an influential film 2001: A Space Odyssey, which is not only very accurate in its description of space, but also describes the position of humans in space exploration. The beginnings of the third millennium, 2001, for them are the true space age when humans really realize their position in space: a baby in the womb that is ready to be born and explores the vast space world. So influential film until people wondered whether in the year 2001 is indeed technological progress is like that depicted film.
This optimistic view was not lost when Clarke wrote the Transit of Earth short story that took the year 1984. That year the Earth transit was seen from Planet Mars (seen from Mars, Earth could be seen moving across the Sun) and a stranded astronaut had time to enjoy the scenery is before exhaling his last breath because of running out of oxygen. Despite the tragic end, there was an explicit message that Clarke delivered here: In 1984, human exploration on Planet Mars was done.

earth is seen from the moon.credit image
exploration
Space exploration! In 1968, may Clarke with Kubrick, when giving birth 2001: A Space Odyssey, think optimistically because scientists and engineers contracted NASA has ten years of experimenting and sending humans into space despite being just Earth orbit. On Christmas Day of the year, 1968, Apollo 8 astronauts succeeded in becoming the first people to leave Earth's orbit and around the Moon. Eight months later, July 1969, for the first time a man set foot on the Moon. The mastery of space by humans seems to be one step away.
The dream of exploring space is as old as any other human dreams. Ever since the unlimited sky was the realm of gods and ordinary people who tried to explore it would surely die. Icarus challenged this belief, flew near the sky, and lost his life. The sky lost its awesomeness when Newton and Kepler uncovered the secrets of celestial movement and Somniuum, Kepler's work, tells of the Moon's exploration with the help of a spirited creature. Furthermore, science fiction literature on space exploration and other worlds color our lives. And now ... the dream is realized.

Then how? Humans have sent unmanned rides to all corners of the solar system. All planets in the solar system except Planet Pluto have been researched through landing missions, orbiting, or simply fly-by. Venus and Mars have been repeatedly explored by the unmanned Soviet Union and the United States. Mercury has been mapped via the Mariner 10 cross-mission in 1974 and the Messenger rides. Wahana Galileo has for years orbiting Jupiter before being "turned off" by NASA. And the Cassini-Huygens rides have reached Saturn's satellite, Titan, after a long journey of 7 years. The solar system seems too small for humans. Then how? Does man send unmanned rides to the nearest star? That's it. The unmanned Pioneer 10, Voyager 1 and 2, launched 60 years ago, are now on the border of our solar system on our way out of the solar system.
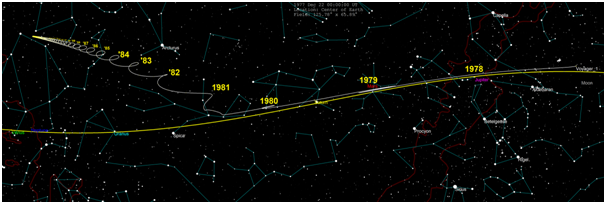
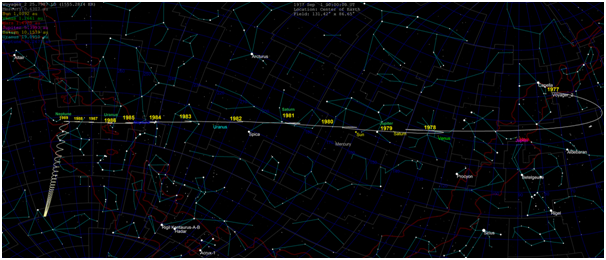
But behind all the achievements, humans were still sleeping deeply. The modern rocket pioneer, Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, said, "The earth is a cradle of thought but humans cannot stay in the cradle forever." Kubrick and Clarke's dreams are far from reality because to this day as far as humanity can go is 384,000 km, the distance from Earth to the Moon. Although the space shuttle into Earth orbit has become commonplace, the colonization of Planet Mars and manned flights to Jupiter is still far from reality.
The biggest problem that keeps people from exploring space is known since Jules Verne wrote From Earth to the Moon in 1865-astronauts spend most of their time in a state of no weight. Sometime before World War II, in 1939, when Arthur C. Clarke and some colleagues formed the British Interplanetary Society, they designed a cylindrical space station that rotated on its axis, so the centrifugal force generated gravity to the inhabitants which are inside the "floor" of the cylinder.

2001-A Space Odyssey Space Station.credit image
the price to pay
Stanley Kubrick pointed this out in 2001: A Space Odyssey. This design is made because no one knows how human reactions to the weightless state because it can not be generated for longer than a few seconds. The worst-case scenarios made were the uncontrollable heartbeat and rapid but terrifying death (it was these fears that made Soviet Union engineers in the Cold War period designing fully Earth-controlled rocket capsules, and which encouraged NASA engineers to send chimpanzees first into space). Now we know that the fear is excessive and the astronauts who are in the weightless state are all fine, although there are many long-term effects that we still do not fully understand.
In a state without weight, gravitational information disappears from the brain so that the "top" and "down" orientations disappear. The ear sends a confusing signal to the brain and the eye undergoes an illusion, for some, it can be cloying. Body fluids flow into the chest and head. Cuff neck expands, face flushed. The heart enlarges slightly and so does the other organs. The brain feels too much body fluid that the body throws away: Calcium, electrolytes, and blood plasma. Red blood cell production is reduced so astronauts suffer from anemia. With the loss of body fluids, the feet were smaller. During his time as Director of the Research Institute of Russian Biomedical Problems from 1968 to 1988, Oleg Gazenko saw cosmonauts returning from long flights down from capsules in a dull, pale, unbearable state and had to be guided. "We are creatures of the Earth. This change is the price to pay for a ticket to outer space, "he said. Not only weight loss, but also muscle mass and bone density will decrease due to work in a state of weight becomes very small. Osteoporosis threatens because bone loses its density by 1 to 2 percent in a month, comparable to the rate of loss of a post-menopausal woman within a year. Therefore before we send humans into space for long periods of time, these physiological issues must be answered first. With the existing rocket technology, the journey to Mars takes approximately 260 days. The total duration of the space journey is 522 days plus the time to stay on Mars for 455 days to wait for the best time.
The second problem is radiation. Outside Earth's atmosphere roam the high-energy particles thrown by the Sun through the Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) mechanism and cosmic ray radiation from the Milky Way or the rest of the supernovae. Exposure to radiation on astronauts on the way to Mars will be much greater than that of astronauts in Earth orbit or on the Moon's surface. Heavy ions carried by cosmic ray radiation can bombard body cells, break down the structure of DNA and cause cancer.
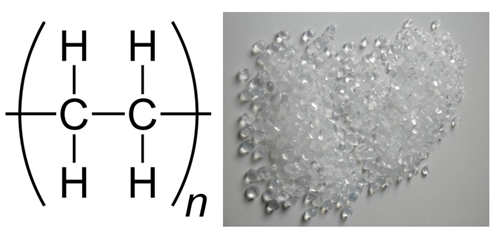
Various investigations have been undertaken to deal with these physiological and radiation problems. The regular exercise proved able to overcome some physiological problems. Cosmonaut Yuri Romanenko-who regularly exercises using treadmills at Mir Station-after completing a 329-day mission directly handstand with one hand in front of reporters. Polyethylene-like materials have been shown to absorb the radiation caused by cosmic rays. Polyethylene has long been used in nuclear submarines to protect sailors in it from radiation from nuclear reactors.
hope still exists
Then why should all these barriers-both natural and technological-are confront to bring people into space? In addition to exploration for science, space is the solution to settlement problems. With a very rapid population growth of almost 2 percent every year (this means the Earth's population doubled every 40 years), then within a few hundred years, Earth will run out of the shelter. Engineers start thinking about the concept of a space settlement before we move to colonize the Moon or Mars. The concept of a space settlement that orbits the Earth at a certain speed in order to produce the same centrifugal force as the magnitude of the gravitational force on the surface of the Earth is probably the most sensible design to be realized in the next several hundred years.

The construction of the Moon colony may be the next step, especially if the Moon has a promising economic prospect. Former US president George W. Bush has announced plans to build a colony on the Moon as a springboard for landings on Mars (although some science circles in the United States himself suspect the plan is merely boasting that Bush himself has not shown any interest great for science), and the far side of the Moon (a side never is seen from Earth) is itself a strategic land for the development of a radio astronomy observatory because it is free from radio signal interference from Earth's electronics equipment.
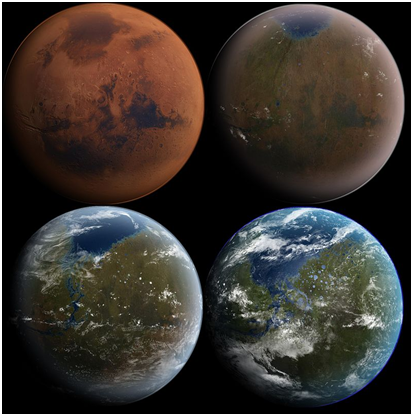

Mars has always been the object of colonization, not only through the science fiction novels about life on Mars that have sprung up since the time of Queen Victoria in the 19th century, but also a promising target since we know the composition of Mars atmosphere that is almost similar to our atmosphere with the content carbon dioxide and less oxygen. The dream to build permanent settlements on the Moon or Mars is still running. Gravity in both places is only one-sixth the gravitational force of Earth, so the objects weigh only one-sixth of the weight on Earth and the energy we need to work only one-sixth of the energy on Earth. But the children born to both worlds will face the problem of having to visit their ancestral planet Earth because of gravity being six times the gravitational force of their birth planet so the work becomes six times heavier (Akira Toriyama's Dragon Ball comic fan might be recalled the gravity engine that could alter the force of gravity so one could use it for weight training in greater gravity). In the next few centuries, our species may be gravitationally separated into some tribes that adapt to zero gravity (space), fractional gravity (Moon or Mars), and gravity one (Earth).
So far only Planet Earth is known as the most friendly place for human life. At some point in this third millennium we may face a dilemma: should we leave our neighboring planets unchanged, or do we modify them to be inhabited without the use of protective clothing? Terraforming technology, the technology to change the face of a planet, has been extensively researched and possibly realized on several planets in our solar system. Algae or other pioneering plants that can live without oxygen and other extreme conditions can be sent to Planet Mars and convert the existing carbon dioxide into oxygen with the help of sunlight, and in orbit, Venus can be built up to reduce sunlight. Certainly, ethical issues will arise in this policy and protests will emerge from primarily from environmental groups that will pinpoint the mistakes we have made on our own planet.
In this third millennium, we will begin the true space age. As the late Carl Sagan in Cosmos says, we are on the ocean shore of the cosmos and across the ocean of the cosmos awaiting another island we are ready to explore. The waves on the beach invite us to wander farther, but are we ready to wade through the oceans? Outside our solar system unfolds other stars forming galaxies, each with its own uniqueness and some with our solar system like our sun. It is not impossible that one of these planets also has a human-like life. Whatever we will experience and find in space later, it will shape the future of humanity. A new human adventure will begin. Thank you for your time!
references and related reading :
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_habitat
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colonization_of_Mars
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colonization_of_the_Moon
http://spacecolonization.wikia.com/wiki/Colonization_of_the_Moon
https://futurism.com/discovery-hope-colonization-moon/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Sentinel_(short_story)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2001:A_Space_Odyssey(film)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transit_of_Earth_from_Mars
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Apollo_missions
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apollo_program
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_missions_to_Mars
https://www.space.com/13558-historic-mars-missions.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somnium_(novel)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_exploration
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/From_the_Earth_to_the_Moon
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/British_Interplanetary_Society
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coronal_mass_ejection
https://www.swpc.noaa.gov/phenomena/coronal-mass-ejections
https://www.space.com/25786-how-to-become-an-astronaut.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Terraforming
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polyethylene
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosmic_ray
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Konstantin_Tsiolkovsky
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pioneer_10
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravitation_of_the_Moon
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravity_of_Mars
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosmos_(Carl_Sagan_book)
Hi, I found some acronyms/abbreviations in this post. This is how they expand: