I love web scraping, especially in the beginning of learning how to code. It is fairly easy, you can learn a lot about how to handle data and you get immediate results!
But I see a lot of tutorials which get overly complicated and focuses mainly on a framework called Beautiful Soup. It is a fantastic and mighty framework but most of the time - and especially for a beginner - it is completely over the top. Let's be honest, we don't want to index a complete website, most of the times we just want to download images or ask for a few values.
This can be done a lot of easier with one magic word, Regular Expressions.
Okay, okay, I hear you "whaaat? Regular expressions and easy? WTF?"
Yeah, you are not wrong, RegEx aren't that easy. Personally I found it much easier to learn RegEx than an arbitrary framework which has only one use case.
What are regular expressions?
The concept of regular expressions occurred in the 1950s. In theoretical computer science it is a sequence of characters that define a search pattern. (Wikipedia)
So, what does a regular expression looks like?
Imagine we have a string:
Hi, I'm KurzGedanke and www.kurzgedanke.de is my website.
Now we want to get the website with the specific domain. We can assume that every input looks like www.websiteName.tdl.
One solution to match this with regular expressions might be looking like this:
www\.(.*)\.([a-zA-Z]*)\s
wwwas you might suspect, this matches exactlywww\.matches the.after thewww. Because the dot has a function in RegEx we need to escape it with the\.(.*)the.matches any single characters. Is it theaor a tab, it will match it. Besides of newlines. With the asterisc we match zero or more characters of the expression before it. In this case zero or more of any single character. The parentheses()puts the match in a group which can be accessed easily.\.this dot matches the dot before the top level domain.([a-zA-Z]*)here we have the top level domain, which is put in a group again with the().[]are used to match a single character. In this case a character between the lowerato the lowerzor the capitalAto the capitalZ. To get more than a single character the*is used.[^This is funny and a classic mistake. I didn’t thought it through completely. A URL can of course contain a dash-and I missed it.^^]\smatches white space. In this case it is used to end the regular expression.
To be honest, I think there are smarter ways to do this, but I find this way easy to see what’s going on and not to get overwhelmed by a 50 character long RegEx string.
To learn regular expressions I used an interactive tutorial like this: regexone.com. This is not the only one out there and you can look if you find one that suites you.
Another great tip are sites like regex101.com. You can paste text in it and write directly your regex while you can see in realtime which parts are matched.. I use it everytime when I write some regex.
Lets write some python
We can use this knowledge to scrap websites. And... to be honest... I will rely on a module called Requests: HTTP for Humas. But this module is so easy to handle and pythonic - sometimes I have the feeling it is more pythonic than python itself.
Our goal is to scrap my website and get every article title of my landing page, as well as the link to it.
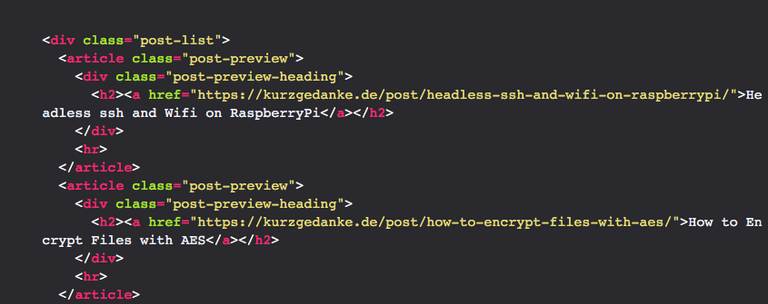
A simplified version of the HTML looks like this:
<div class="post-list">
<article class="post-preview">
<div class="post-preview-heading">
<h2><a href="https://kurzgedanke.de/post/headless-ssh-and-wifi-on-raspberrypi/">Headless ssh and Wifi on RaspberryPi</a></h2>
</div>
<hr>
</article>
<article class="post-preview">
<div class="post-preview-heading">
<h2><a href="https://kurzgedanke.de/post/how-to-encrypt-files-with-aes/">How to Encrypt Files with AES</a></h2>
</div>
<hr>
</article>
<article class="post-preview">
<div class="post-preview-heading">
<h2><a href="https://kurzgedanke.de/post/problems-with-flask-and-pycharm/">Problems with Flask and PyCharm</a></h2>
</div>
<hr>
</article>
<article class="post-preview">
<div class="post-preview-heading">
<h2><a href="https://kurzgedanke.de/post/decentraland-hot-to-mine-on-a-mac/">Decentraland | How to Mine on a Mac</a></h2>
</div>
<hr>
</article>
<article class="post-preview">
<div class="post-preview-heading">
<h2><a href="https://kurzgedanke.de/post/welcome/">Welcome</a></h2>
</div>
<hr>
</article>
</div>
So, what are we looking for in this HTML? Let's see, we want the titles and the url of all posts. We have a few articles with the class post-preview. And down below we have a h2 heading inside a div called post-preview-heading. The h2 contains a a href which assembles a link. Might be good to go! Every h2 has the same structure and, we are lucky, this is the only h2 with this structure on this whole side. So we can assume, like above, that every input looks exactly like this:
<h2><a href="linkToPostTitle">postTitle</a></h2>
On other websites the h2 or the a href would have a dedicated class or id like
<h2 class="post-preview-title-header"></h2>
this is even better because we would have a persistent pattern which could be used to match against.
Now let us write our RegEx to search for.
<h2><a href=\"https:\/\/kurzgedanke\.de\/post\/
This simply represents the <h2><a href="https://kurzgedanke.de/post/ string. Again the backslashes as well as the double quotes have to be escaped.
Note: You can leave the escaping of the double quotes out when you use single quotes in your python code. But escaped double quotes are always the safe option.
Now the rest:
<h2><a href="https:\/\/kurzgedanke\.de\/post\/(.*)\/">(.*)<\/a><\/h2>
(.*)selects everything after thepost/till the/">and puts it in a group.(.*)matches the post title
<\/a><\/h2>closes of the</a>tag and the</h2>tag.
Now that we've written the regular expression let's take a look at the python code.
import re
import requests
r = requests.get('https://kurzgedanke.de/')
regex = r'<h2><a href="https:\/\/kurzgedanke\.de\/post\/(.*)\/">(.*)<\/a><\/h2>'
titleURL = re.findall(regex, r.text)
for urlAndTitle in titleURL:
print(f'Title:\t {urlAndTitle[1]}')
print(f'URL:\t https://kurzgedanke.de/post/{urlAndTitle[0]}/')
print('-------------------------------')
import reimports the regular expression module from the standard libraryimport requestsimport the requests module from Kenneth Reitz.r = requests.get('https://kurzgedanke.de/')makes an HTTP request to kurzgedanke.de and safes the data in a requests object.regex = r'...'declares a variable with the regular expression as a value.r'...'tells python that this string is a regular expression.titleURL = re.findall(regex, r.text)we use the regex module to find all matches with the use of our regex variables andr.textwhich contains the html of our http request. After everything is found it will be a list with all matches assigned totitleURL.for urlAndTitle in titleURL:we can easily iterate over the list and access the different matches with an array notation because we grouped them up in our regular expression with the().
When you run the script it should look like this:
Title: Headless ssh and Wifi on RaspberryPi
URL: https://kurzgedanke.de/post/headless-ssh-and-wifi-on-raspberrypi/
-------------------------------
Title: How to Encrypt Files with AES
URL: https://kurzgedanke.de/post/how-to-encrypt-files-with-aes/
-------------------------------
Title: Problems with Flask and PyCharm
URL: https://kurzgedanke.de/post/problems-with-flask-and-pycharm/
-------------------------------
Title: Decentraland | How to Mine on a Mac
URL: https://kurzgedanke.de/post/decentraland-hot-to-mine-on-a-mac/
-------------------------------
Title: Welcome
URL: https://kurzgedanke.de/post/welcome/
-------------------------------
I hope you found this little write up useful and learned a bit.
If you have any question or remarks, please leave a comment, contact me on twitter or write a mail.
You can read this post as well on kurzgedanke.de.