
Previously On
DAY 1 | DAY 2 |
|---|---|
Contents
- Setting Up Connection To Algorand testnet
- Data Types
- Comments In Python
- Constructors
Requirement
- Window 10 or higher, 64bit.
- At least 4 GB RAM
- Python 3.0 +
- Code editor (VSC)
Although, it may change in future, currently, there are three ways to connect to Algorand chain as specified in the documentation.
Now, open your terminal (in the search box, type CMD and enter). Type and enter the following in the terminal.
pip3 install py-algorand-sdk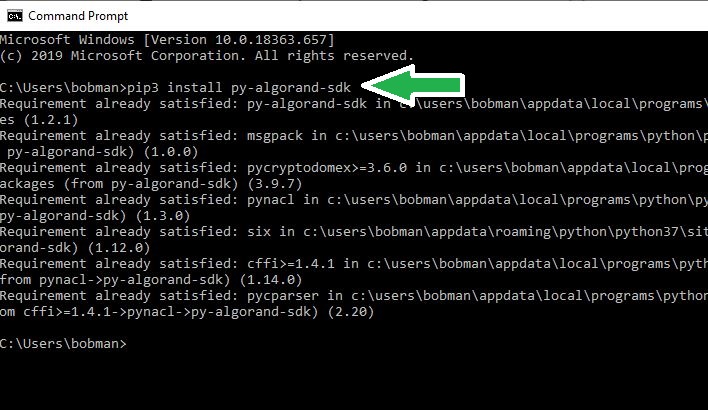
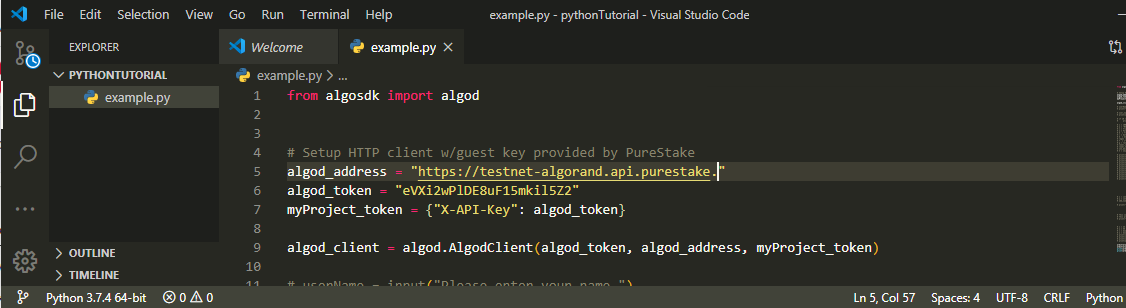
from algosdk import algodalgosdkis the package containing tool we need to set up a connection. There you will findalgodmodule containing theAlgodClientclass. Inside this class are few other functions: mostly, an hierarchical structure of object oriented programming. It requires 3 parameters to perform its function thus:create a variable
algod_addressto hold the purestake API.Another variable
algod_tokento hold the token (i.e a unique key given you on Purestake.com)The third parameter is variable
myProject_tokenwhich is a dictionary data type mapping our token to keyword"X-API-KEY"to our secret token. The Algorand Virtual machine requires it in this very format.Now, we can use the class
AlgorandClientto establish the connection. To access a class and its functions, we will create an instance of the class claiming that we are the child hencealgod_clientand passed in the three variables we have created as parameters.
Understanding Data Types In Python
Variables are used to hold data in storage and it can hold different types of data. Below are inbuilt data types in Python.
str | msg = "Welcome" | |
|---|---|---|
int, float, complex | int --> dozen = 12, float --> one_decimal = 12.1, complex --> y = 12j | |
list, tuple, range | list --> vowel = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'], tuple --> vowel = ('a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'), range --> x = range(10) | |
| x = {"name" : "James", "age" : 30} | ||
| y = True | ||
| set --> veges = {"cucumber", "pumpkin", "garden egg"}, frozen set --> x = frozenset({"apple", "banana", "cherry"}) | ||
| bytes --> a = b"My name", bytearray --> y = bytearray(8), memoryview --> memoryview(bytes(6)) |
Note: Python treats data without quotes as number. So, to save and get values as text, you must use " " (double quote) or ' ' (single quotes).
double quotes and can use as many single quotes within the text. See example below.
Comments In Python
# in VSCode. Python uses it to denote a comment and it ignores whenever it comes across it. As a good developer, you should develop the habit of leaving short and precise comments in your code. The importance is to enable other programmers who will read your code in the future to understand your code and what you are trying to achieve.
How To Know The Type Of Data You Input Into Your Program?
x = 100
y = "What did you notice?"
z = True
a = False
b = x = frozenset({"apple", "banana", "cherry"})
c = bytearray(8)
d = memoryview(bytes(6))
veges = {"cucumber", "pumpkin", "garden egg"}
f = {"name" : "James", "age" : 30}
g = range(10)
vowel_list = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u']
vowel_tup = ('a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u')
one_decimal = 12.1
h = 12j
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
print(type(a))
print(type(b))
print(type(c))
print(type(veges))
print(type(f))
print(type(g))
print(type(vowel_list))
print(type(vowel_tup))
print(type(one_decimal))
print(type(h))
Copy the codes above and paste in your code editor, you get the result in the image.
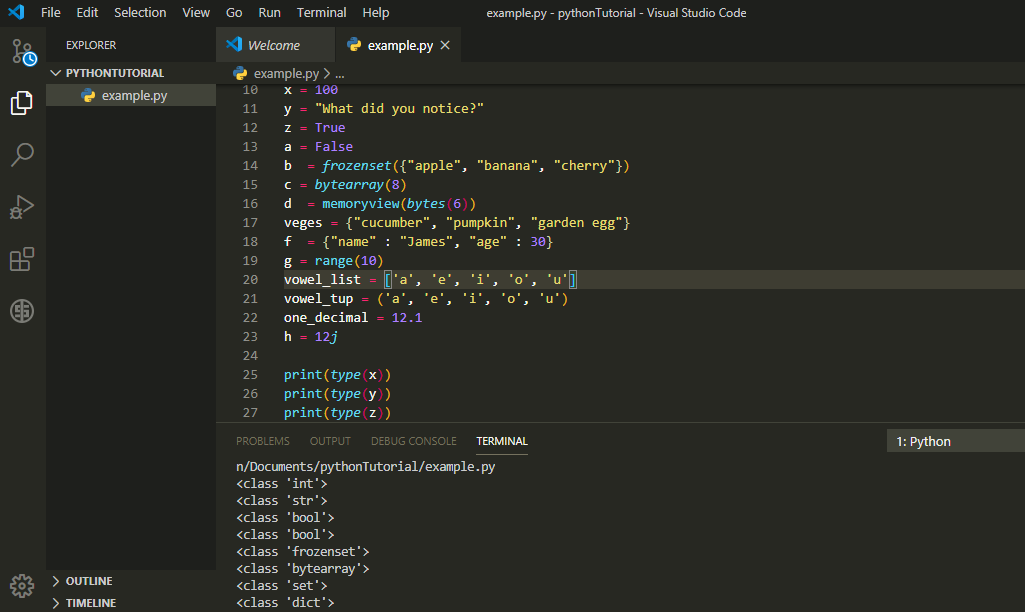
Int is short for integer, It is a whole number and can either be a positive integer or negative. Usually, int object does not contain decimals and are of unlimited length.
score_number = 20short_number = 133333long_number = 15392099222126744To convert a float type of number or integer literal or from a string literal to a whole number, you will have to do what is called casting.
- Casting is a process of converting one data type to another type. This is done using a constructor function i.e enclosing the data or variable holding the data in a parentheses preceded by the keyword to which type you want to convert. Example
int( ),str( ),float( )etc.
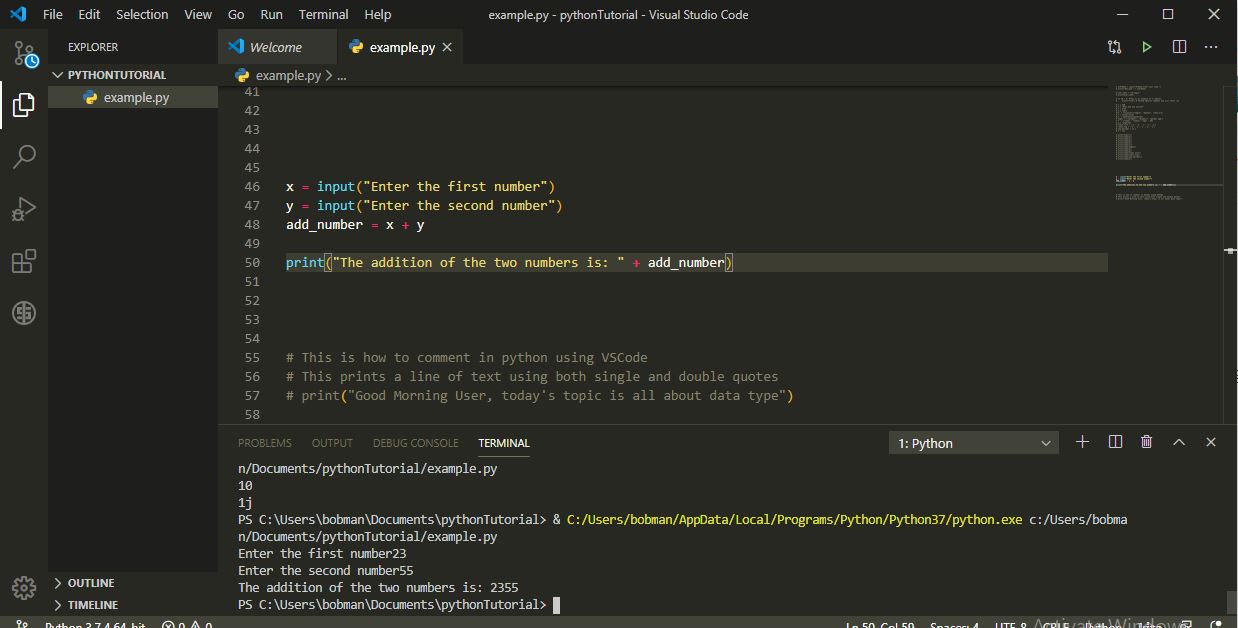
46 and 47, add the numbers together (line 48) and print the result to user on line 50. Oops! we get an undesired result of 2355 in the terminal after user entered 23 and 55 as separate numbers. That's not what we want right? In programming, you as the developer should already know the result a line of code will give and not a kind of guess game except where you expressly want Python to select random numbers on your behalf.23 and 55 together. But we will have to tell python what exactly we want. That is why you're the smart guy not python. It does exactly what you ask it to do.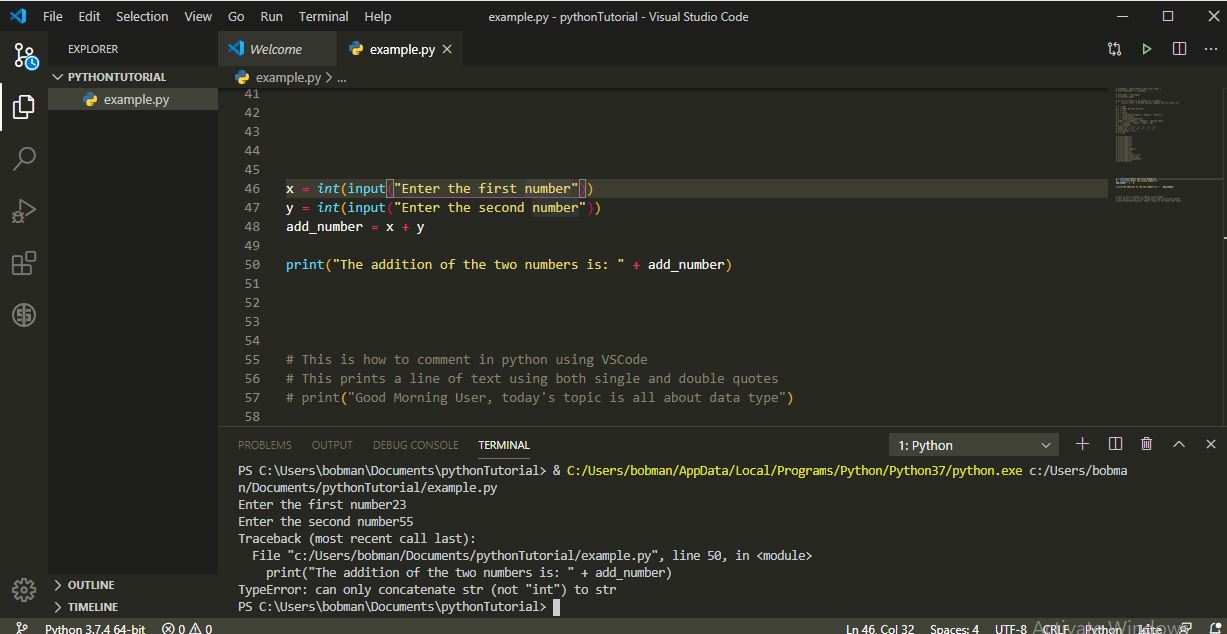
Can only concatenate str (not 'int') to str. Print() function can only concatenate(a way of joining data together) data of same type. So let us cast the result back to string.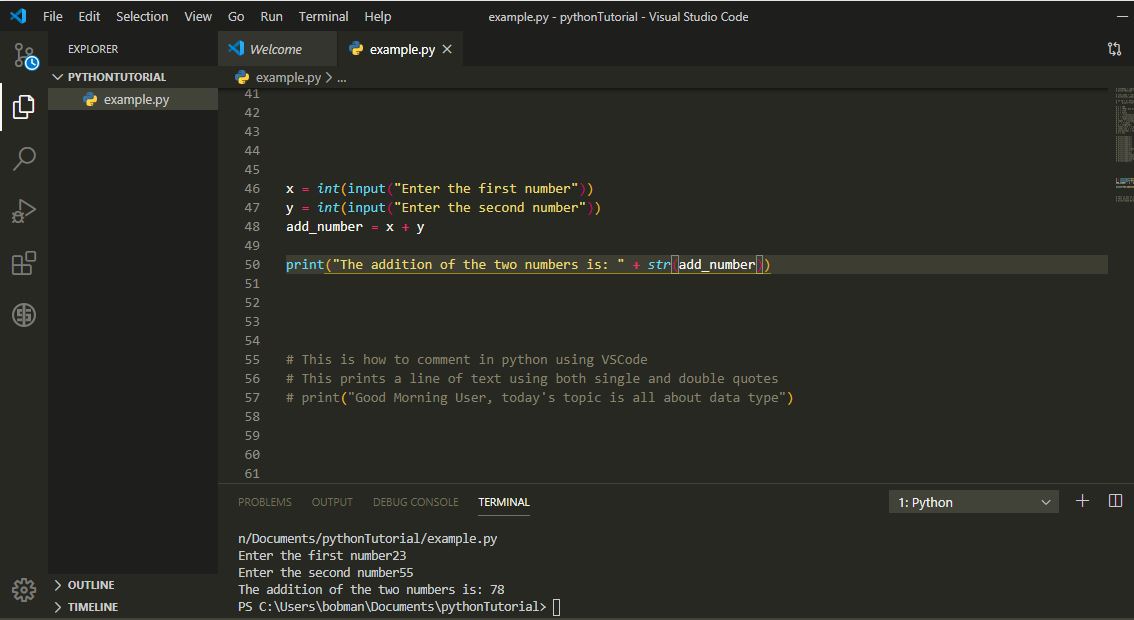
Note: The same method of casting applies to other data types.
- Constructor is a special kind of method(method is same as a function usually enclosed in parentheses preceded by a function name) that Python calls when it instantiates an object using the definitions found in your class. Python relies on the constructor to perform tasks such as initializing (assigning values to) any instance variables that the object will need when it starts.
In any programming language, parentheses ( ) is very important and powerful. It is used as access control and restriction to sensitive objects. So don't be surprised that blockchain codes are a function of parentheses. I will expatiate more on it shortly.
A constructor is incomplete without parentheses which is used to create an instance of a Classobject. More on 'class' later.
String (str)
score_number = "twenty"short_number = str(133333)Boolean (bool)
True or False. Comparing two situations, states, variables, expressions etc, evaluates to either of the boolean values. To compare two objects, the following operations are used: comparison sign
==-->a == b--> Doesaequal tob?
"greater than" sign>-->a> b--> Isaequal great thanb?
"less than" sign<-->a < b--> Isaless thanb?
Other operator in Python
Arithmetical Operators
+Addition-Subtraction*Multiplication/Division//Floor Division%Modulus (Returns the remainder by dividing the left operand by the right operand)**Exponential
Assignment Operators
=-->a=6(sets the value of a to 6)+=-->a += 6ora = a + 6(The value of a equals the value of adding 6 to its existing value.-=-->a -= 6ora = a - 6(The value of a equals the value of subtracting 6 from its existing value.*=-->a *= 6ora = a * 6(The value of a equals the value of multiplying 6 by its existing value.**=-->a **= 6ora = a ** 6(The value of a equals the value of its existing value to the power of 6.%=-->a %= 6ora = a % 6(The value of a equals the remainder of its existing value after divided by 6.
[] square brackets.menu = ["sausage", "fish pie", "meat pie"]arbitrary_list = ["sausage", 10, "fish pie", True, "meat pie", {"name": 'James', "age": 49,}]`
menu and assigned a list containing 3 items to it.Here, Python sees "menu" as one object which contains 3 food items - a way of grouping series on objects that are of same or different types together. You would notice arbitrary_list contains four different data types - string, integer, boolean and dictionary.Tuple
A tuple is denoted with parentheses
(). It is a collection of ordered items that cannot be changed. It can take arbitrary number of data types.
arbitrary_list = (["sausage", 10, "fish pie", True, "meat pie", {"name": 'James', "age": 49,}], 10, {"email": "bob@gmail.com"}, ["country", "town"])
this is really helpful. wished i could code. well written
Yes you can if you indeed want to actualize your wish. If you follow these tutorials closely, you will start to code in no time. Thank you @barineka
are serious, but i dont know the basics of coding
Here are the basics I started on my blog. This is just the third series. You only nerd to take your time and read through it. You will understand better.
thanks for the tutorial