"without better environmental stewardship, development will be undermined; and without accelerated development in (developing) countries, environmental policies will fail" (Serageldin, 1994).
A variety of physical, economic, and social forces that are affected by many different actors, from individuals to governments
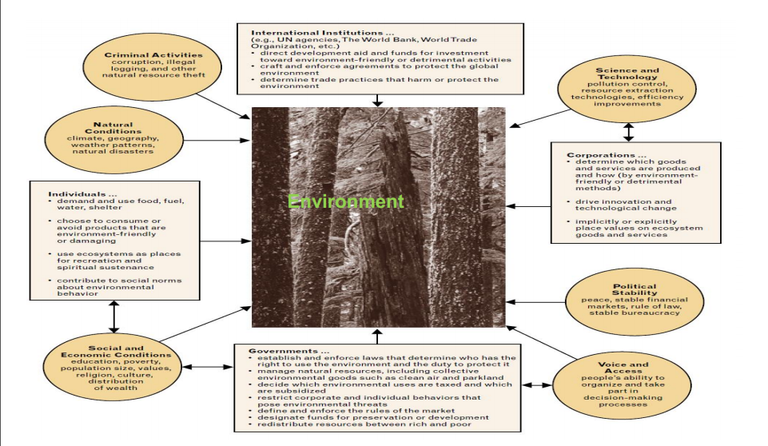
Key Environmental Challenges
Human interaction with the environment for socioeconomic growth and survival has resulted in some
challenges:
• loss of biodiversity and long-term damage to ecosystems.
• pollution of the atmosphere and the consequences of climate
change.
• damage to aquatic ecosystems.
• land degradation.
• the impacts of chemicals use and disposal.
• waste production.
Sustainable Development – Concept and Practice
• Rapid economic growth in the last two decades has lifted many out of poverty, but has been accompanied by depletion of natural resources and deterioration in environmental quality.
• Serious call to make environmental conservation and development compatible since 1970s
• In 1984, the UN General Assembly appointed the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED) to propose long-term strategies for achieving sustainable development by the year 2000 and beyond.
• The work of WCED culminated in the Brundtland Commission's report, Our common Future in 1987 (WCED, 1987). Which defined sustainable development as "development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs" (WCED, 1987:8)
• The report has stimulated renewed discussion of development with emphasis on sustainability leading to the first Rio Earth Conference of 1992., and also a lot of debate on the concept and its practice.
• Presently there are about three broad approaches to sustainability: economic, biophysical and socio-cultural
Dimensions of Sustainable Development
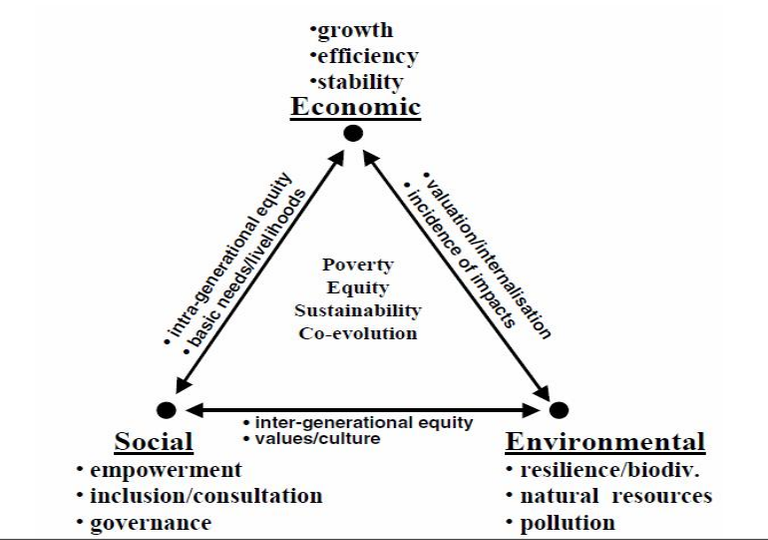
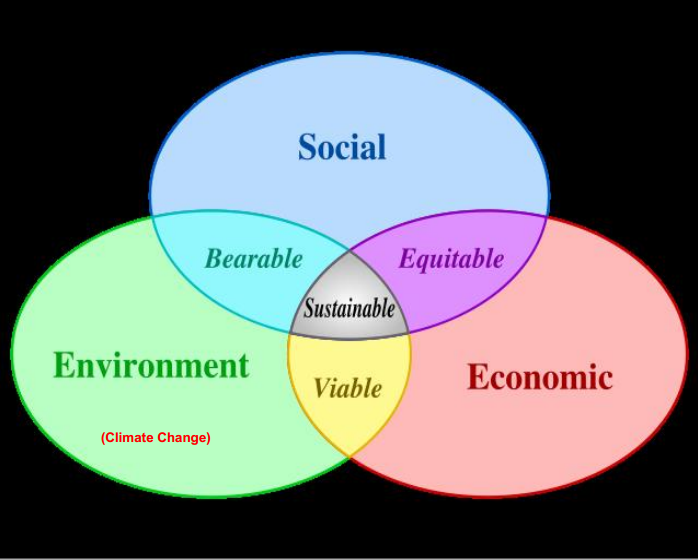
Sustainable development paradigm rests on the
followings planks:
- development must not damage or destroy the basic life support systems (air, water and soil, biological systems, etc)
- development must be economically and socially sustainable to provide a continuous flow of goods and services derived from water and associated land resources
- It requires sustainable social systems at international,national, local and family levels to ensure equitable distribution of the benefit of the goods and services produced and to sustain our life support systems (i.e air, water, soil, and land (fauna, flora)
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- Drexhage, J. and Murphy, D., 2010: Sustainable Development: From Brundtland to Rio 2012
- Dixon, J. A. and Fallon, L. A., 1989: The Concept of Sustainability: Origins, Extensions and
Usefulness for Policy. The World Bank Environment Department Division Working Paper No. 1989-1. - Munasinghe, M, 1993: Environmental Economics and Sustainable Development. The World Bank. Washington, D.C
- Serageldin, I and Steer, A. (ed.) 1994: Making Development Sustainable: From Concepts to Action. The World Bank.
- Singh, N. and Titi, V. 1995. Empowerment for sustainable development: An overview. in Titi, V. and Singh, N. (ed.) Empowerment for Sustainable Development: Towards Operational Strategies. Zed Books, London. 6 - 28.
very interesting