These technologies are: 1) private key cryptography, 2) a distributed network with a shared ledger and 3) an incentive to service the network's transactions, record-keeping and security.
1 Cryptographic keys
Two People wish to transact over the internet 
Each of them holds a private key and a public key.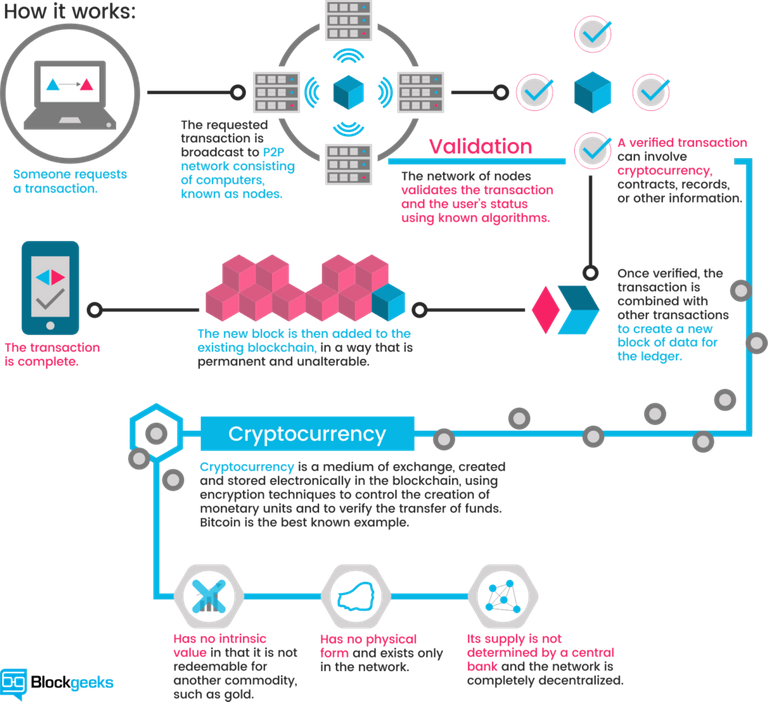
The main purpose of this component of blockchain technology is to create a secure digital identity reference. Identity is based on possession of a combination of private and public cryptographic keys.
The combination of these keys can be seen as a dexterous form of consent, creating an extremely useful digital signature.
In turn, this digital signature provides strong control of ownership.
Network servicing protocol
A realist might challenge the tree falling in the forest thought experiment with the following question: Why would there be a million computers with cameras waiting to record whether a tree fell? In other words, how do you attract computing power to service the network to make it secure?
For open, public blockchains, this involves mining. Mining is built off a unique approach to an ancient question of economics — the tragedy of the commons.
With blockchains, by offering your computer processing power to service the network, there is a reward available for one of the computers. A person's self-interest is being used to help service the public need.
With bitcoin, the goal of the protocol is to eliminate the possibility that the same bitcoin is used in separate transactions at the same time, in such a way that this would be difficult to detect.
This is how bitcoin seeks to act as gold, as property. Bitcoins and their base units (satoshis) must be unique to be owned and have value. To achieve this, the nodes serving the network create and maintain a history of transactions for each bitcoin by working to solve proof-of-work mathematical problems.
They basically vote with their CPU power, expressing their agreement about new blocks or rejecting invalid blocks. When a majority of the miners arrive at the same solution, they add a new block to the chain. This block is timestamped, and can also contain data or messages.
A Distributed Network
The benefit and need for a distributed network can be understood by the 'if a tree falls in the forest' thought experiment.
If a tree falls in a forest, with cameras to record its fall, we can be pretty certain that the tree fell. We have visual evidence, even if the particulars (why or how) may be unclear.
Much of the value of the bitcoin blockchain is that it is a large network where validators, like the cameras in the analogy, reach a consensus that they witnessed the same thing at the same time. Instead of cameras, they use mathematical verification.
In short, the size of the network is important to secure the network.
That is one of the bitcoin blockchain's most attractive qualities — it is so large and has amassed so much computing power. At time of writing, bitcoin is secured by 3,500,000 TH/s, more than the 10,000 largest banks in the world combined. Ethereum, which is still more immature, is secured by about 12.5 TH/s, more than Google and it is only two years old and still basically in test mode.
Thanks for reading my articeabout what is blockchain technology and how it works
leave your comments and upvote the post if you have any question ask me i will answer for sure
Thank you
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://www.coindesk.com/information/how-does-blockchain-technology-work/