Diabetes is an epidemic disease that affects more and more people nowadays. No need to panic when diagnosed with diabetes. It's bad news. It could be devastating at first. Fortunately, diabetes is a manageable condition. By following some simple steps you can keep your diabetes under control and still live a healthy life you deserve. Here are some tips on how to manage your diabetes successfully:
Learning more about your diabetes - Knowledge about this disease will help you do what's good and avoid what's bad for this disorder. Planning a healthy diet - A healthy and balanced meal plan plays an important role in controlling your diabetes. It makes you feel better and help to reduce the chances of developing serious complications. A balanced healthy diet including a variety of foods from each group of grain products, vegetables and fruit, milk products and meat and alternatives will keep your blood glucose at the normal level. Choose low fat foods and foods with a lower glycemic index. Avoid high fat foods and foods with a high glycemic index. Keeping your weight in a healthy range, shed off extra pounds if you're overweight, especially if you have type 2 diabetes - Keeping normal and healthy weight will help your body's ability use its insulin properly and maintain your blood glucose at normal level. Try to keep your Body Mass Index (BMI) at 18.5 - 24.9 You can calculate your BMI using the following formula:
English Formula
BMI= weight in pounds/ (height in inches x height in inches) x 703
Metric Formula
BMI= weight in kilograms/ (height in meters x height in meters)
Trying to be physically active - 20-30 minutes of exercise on a daily basis will be very helpful. Exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, lower the risk of heart disease, and lose some extra pounds to keep you weight at a normal level. However, some diabetic complications will probably make some types of exercise program not suitable for you. Activities like weightlifting, jogging, or high-impact aerobics may be a little risky for people with diabetic neuropathy due to the risk for further blood vessel damage and possible retinal detachment. Consult your doctor before you get started. Make an action plan. Start slow and gentle. Gradually work your way up. Taking medications and/or insulin (in applicable) as prescribed by your doctor - Depending on types of diabetes you may need medications and/or insulin to assist the body in making or using insulin more effectively. Monitoring how your diet and/or treatment (if applicable) affect your blood glucose levels - Using a glucose meter to monitor your blood levels to see if they are affected by your meal plan and/or treatment . Keeping diary of your blood glucose readings and reviewing them to see if there are any noticeable patterns
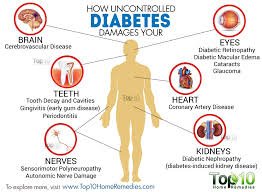
Type 2 diabetes occurs when cells become resistant to the signal from insulin to receive and use glucose as fuel. Oxygen is used to break down glucose and fats, but in the case of glucose, 28% more oxygen is needed to create an equal amount of energy. Using oxygen requires anti oxidants to clean up afterwards. Anti oxidants such as glutathione are present within the cell, (within the mitochondria where metabolism occurrs) so this is not a problem. When glutathione is inadequate to clean up left over oxygen particles, healthy tissue gets damaged. This damage is what causes the cells to ignore the insulin signal and become “insulin resistant”. We are able to tolerate carbohydtrates to the degree that we can clean up the “after-burn”. Diabetes is caused by anti oxidant depletion, making carbohydrates a sub optimal fuel source. It looks like Polyunsaturated fats are the root cause the oxidatative stress that is robbing all our glutathione from where it was needed. If this sounds interesting, I write about this and other biological mechanisms on my page. Thank you for your article, upvoted!