About medicine?

Medicine has two basic meanings, it refers to 1. The Science of Healing; the practice of the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease, and the promotion of health. ... Medications, drugs, substances used to treat and cure diseases, and to promote health.
About medicine plant??
.jpeg)

.jpeg)

Medicinal plants, also called medicinal herbs, have been discovered and used in traditional medicine practices since prehistoric times. Plants synthesise hundreds of chemical compounds for functions including defence against insects, fungi, diseases, and herbivorous mammals. Numerous phytochemicals with potential or established biological activity have been identified. However, since a single plant contains widely diverse phytochemicals, the effects of using a whole plant as medicine are uncertain. Further, the phytochemical content and pharmacological actions, if any, of many plants having medicinal potential remain unassessed by rigorous scientific research to define efficacy and safety. In the United States over the period 1999 to 2012, despite several hundred applications for new drug status, only two botanical drug candidates had sufficient evidence of medicinal value to be approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The earliest historical records of herbs are found from the Sumerian civilisation, where hundreds of medicinal plants including opium are listed on clay tablets. The Ebers Papyrus from ancient Egypt describes over 850 plant medicines, while Dioscorides documented over 1000 recipes for medicines using over 600 medicinal plants in De materia medica, forming the basis of pharmacopoeias for some 1500 years. Drug research makes use of ethnobotany to search for pharmacologically active substances in nature, and has in this way discovered hundreds of useful compounds. These include the common drugs aspirin, digoxin, quinine, and opium. The compounds found in plants are of many kinds, but most are in four major biochemical classes: alkaloids, glycosides, polyphenols, and terpenes.
Medicinal plants are widely used in non-industrialized societies, mainly because they are readily available and cheaper than modern medicines. The annual global export value of 50,000 to 70,000 plants with suspected medicinal properties was estimated to be US$2.2 billion in 2012, and in 2017, the potential global market for botanical extracts and medicines was estimated at several hundred billion dollars.In many countries, there is little regulation of traditional medicine, but the World Health Organization coordinates a network to encourage safe and rational usage. Medicinal plants face both general threats, such as climate change and habitat destruction, and the specific threat of over-collection to meet market demand.
you can find out here also.
it just about only the way to use plants and how can we make medicine from it.plants are very useful for us like many ways its give us oxygen shelter, food,medicine,wood,cloths etc if we use them in stragised way .
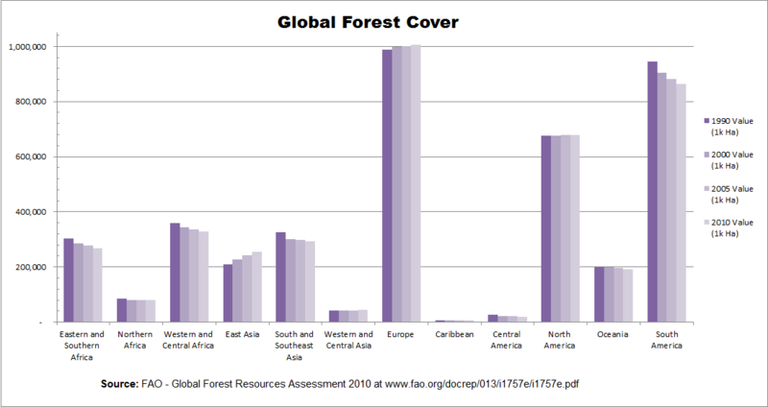
we all know that Rates and causes of deforestation vary from region to region around the world. In 2009, 2/3 of the world forests were in 10 top countries: 1) Russia, 2) Brazil, 3) Canada, 4) United States, 5) China, 6) Australia, 7) Congo, 8) Indonesia, 9) Peru and 10) India.
World annual deforestation is estimated as 13.7 million hectares a year, equal to the area of Greece. Only half of this area is compensated by new forests or forest growth. In addition to directly human-induced deforestation, the growing forests have also been affected by climate change, increasing risks of storms, and diseases. i can show you here
if i talk about only india In just 30 years, India has lost large forests to 23,716 industrial projects.the 14,000 sq km of forests cleared over the past three decades in India, the largest area was given to mining (4,947 sq km), followed by defence projects (1,549 sq km) and hydroelectric projects (1,351 sq km).

so it is big question why the great lost of forest??
why a such need we have ???
let have some look on income.
Forests represent the second largest source of income
for small-scale farmers and their families. This includes a
‘hidden harvest’ (non-cash), comprising commodities such as food,
energy and building materials, that makes up 50 % of forest-
based income.
Deforestation can cause climte change ,soil erosion,thunder etc it can also pollute our environment and destroy the "ecosystem".
so conservation of forest and plants is become nessasry for us because
Forests cover 31 percent of the world's land surface, just over 4 billion hectares. (One hectare = 2.47 acres.) This is down from the pre-industrial area of 5.9 billion hectares.
Here i am giving you the way how to conserve forest and plants.
.jpeg)
Some of the steps we can take to conserve our forest resources are as follows:
.Regulated and Planned Cutting of Trees: ...
.Control over Forest Fire: ...
.Reforestation and Afforestation: ...
.Check over Forest Clearance for Agricultural and Habitation Purposes: ...
.Protection of Forests: ...
.Proper Utilisation of Forest and Forests Products: