Hello to all space enthusiasts! Today we will consider a little about the Internet from SpaceX and Co.
At first, I will tell you what is planned in coming years: launching a large number (up to 12,000) of small spacecraft (weighing up to 400 kg) to low orbits (up to 1200 km). These devices will operate on the principle of mesh-network. **A mesh network is when satellites are combined into cells in which each device can redirect data to other satellites. **Due to this, fault tolerance and dynamic routing between nodes are achieved. Laser communication at a frequency of 10 THz is going to be organized between the satellites.
This is not a new principle, it has long been known to the military, such networks were deployed on the battlefield. Also mesh-network you can find in Moscow network "c2_free" - Wi-Fi mesh-network, which gives access to the Internet.
Satellites look a little cooler than just Wi-Fi, although the principle will be the same, however, you can not catch the Internet directly from the satellite using a smartphone. We will have to buy a subscriber's equipment - a phased array antenna (FAR) the size of a pizza box for 100-300 dollars. At least that's how Musk described it. And only then to distribute from this device Wi-Fi.
Why FAR? It's simple - directional antennas are usually directed at geostationary satellites, these satellites are constantly hanging at one point in the sky, once pointed the antenna and forgot. Immediately this does not happen, every time you have to catch a satellite (ie, it's not geostationary satellites, they will move quickly enough across the sky). FAR solves this problem. Moving the beam (electronic scanning) or changing the antenna pattern of the antenna array is solved programmatically, without a mechanical rotation. You put it on the roof or on the ground and you have the Internet.
The download speed (and the speed of sending) promises to be very good (even compared to terrestrial providers), about 500 Mbit / s, in the future up to 2.5 Gbit / s. The existing satellite Internet can ideally give up to 100 Mb / s for a lot of money. And, as I understand it, this is exactly the speed of work for one user terminal.

Photo - An example of a receiving-transmitting subscriber device from OneWeb, SpaceX will have something similar. Distributes 3G, LTE, Wi-Fi.
High speed will be achieved due to the cellular structure of the constellation of satellites. Satellites can regroup traffic in such a way that in the busiest area more satellites serve customers, simply redirecting the rays there (most likely, it will be so). By the way, the high-speed Internet will be mostly answered by low-orbital 7500 devices operating in the V-band (at frequencies of 40-75 GHz) located at altitudes of about 320 km. And those satellites, whose orbit is higher (by ~ 1100 km) - for the accessibility of the Internet on a larger territory. (see the picture below)
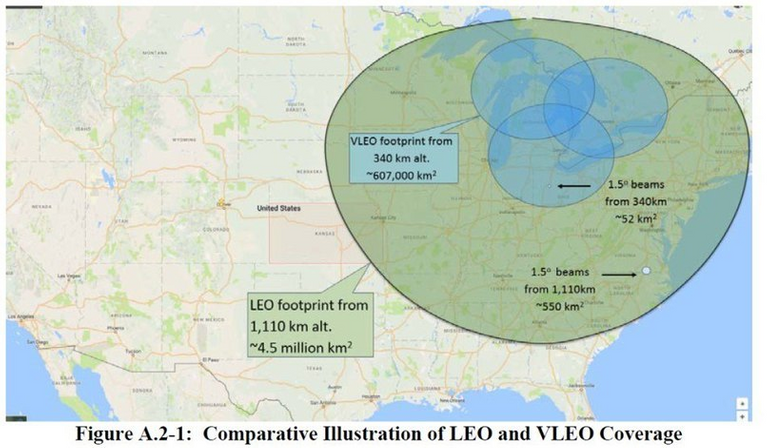
Photo - The green oval is the coverage area of one satellite from an altitude of 1100 km (responsible for the availability of the Internet over a large area), blue - the coverage areas of satellites in low orbits (340 km) - are responsible for high speed. Will work together (see the picture below).
Satellites at both altitudes will be able to interact in a way to provide the most flexible capacity of the communication channel in the terrain. For example, two satellites in different orbits will be able to divide the surface portions among themselves in order to increase the throughput. (see the pictures below).
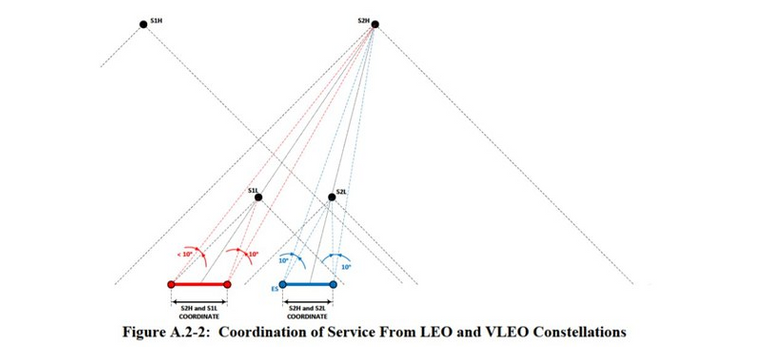
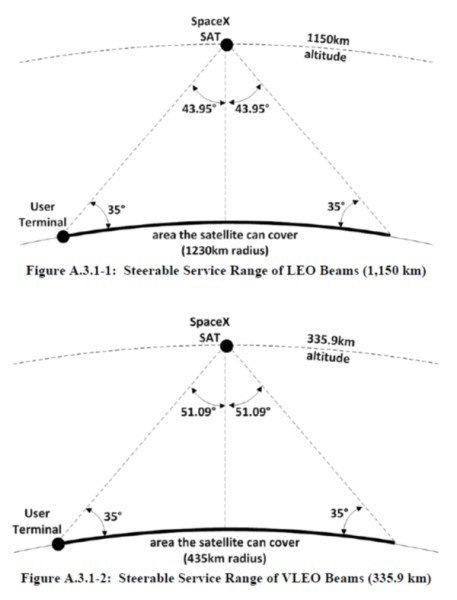
Ping (signal delay, ping) is an important characteristic for fans of playing shooters, as is assured in SpaceX, it will not be more than 25 ms. If you have a cable Internet, then ping your major Internet services is in the region of 5-10 ms. Wi-Fi increases ping, so gamers choose a cable. Accordingly, 25 ms is a theoretical ping to the equipment, but to your device, on Wi-Fi, there will be all 50 ... Naturally, everything depends on where the data centers and ground stations for receiving and transmitting information will be located on satellites. After all, somehow "the Internet on the satellite should appear" :) It will come from ground stations.If 25 ms ping in the US is still achievable, since the servers will be located in the same place, then in Russia, if the base stations in Europe or in Asia it will not be - naturally, no, because the signal going even through the laser link through low-Earth orbiting satellites will have to travel several thousand kilometers in both directions, and it is unlikely that it will be possible to achieve less than 100 ms from the US.
Another important detail is regional restrictions on content. Often you can see an inscription on Youtube that this video is blocked for display in your country ... Added to this is censorship on the Web. How they will solve these problems is not yet very clear. Most likely, each country will supply its base stations and act as a real provider, and SpaceX is only an intermediary (but does SpaceX need this?). In this there is no particular problem, each provider will be able to host a ground station for receiving and transmitting information and quietly serve subscribers in their country, there will also be SORM. Either something specifically will change in the world, in digital rights and finally, the Internet will become free of censorship :), but I think the first option.
Completely ban or suppress, of course, no one will, yet we are not barbarians and accept technology. It's not that through the enemy Internet will be "available truth", but that terrestrial providers will lose money when subscribers move to the heavenly Internet. This is, in my opinion, the reason and is the main one in trying to combat the Internet from SpaceX or OneWeb. Russia will have to create either joint ventures, or install base stations in the territory of the Russian Federation and produce equipment.
It's not entirely clear how the server will be organized and connected to the Internet from SpaceX, so every owner of the terminal from SpaceX could open the site and make it accessible in the mesh network, bypassing the usual Internet, practically p2p. If this is possible, then the censorship will not be able to do anything, the information will be available to people directly. Here, most likely, will introduce some restrictions. For example, it will not be possible to access directly to the subscriber terminal, but only through SpaceX. Or the variant with regional base stations will work.
And by the way, why not take this server into space? Indeed, this idea is also being implemented. For example, companies Kepler Communications plans to bring to the space of a mini-server with a large disk space for storing data received by remote sensing, etc. and the transfer of these data to Earth, bypassing the intermediaries on earth. If such a system is connected to SpaceX, we will simply transfer the entire Internet to space, there will be data centers, services and a global independent of the terrestrial Internet! Just imagine!

Photo - The problem of space pollution worries many, but SpaceX and other companies will solve this problem. Low-orbit satellites will be reduced from orbit and burn in the atmosphere until failure, at the end of their service life. The device will unfold, turn on the ion engine and slow as much as possible.
If Mask or someone else does a ping at least 60 ms anywhere in the world - then this will be just a fairytale!
Thank you for your attention and have a nice day!
Best regards, @ostapko
Thank you for collaborating with me to promote this post as explained at https://steemit.com/steemit/@jerrybanfield/10-ways-to-fund-a-steem-growth-project.