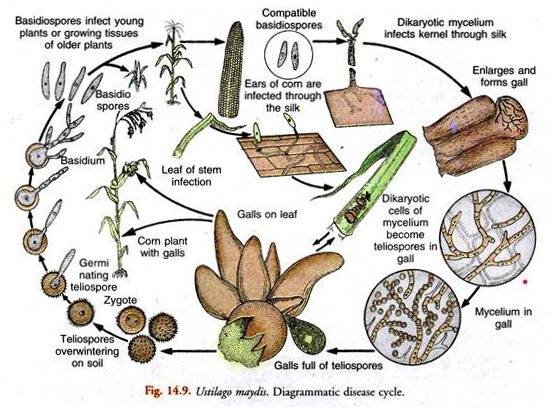
Life cycle of Ustilago
Ustilago is a genus of smut fungi.Smuts are called so due to their black spores that resemble soot or smut.Spores masses replace the grain such as wheat.It is a facultative parasite.There are 400 species of this genus.Its various species infect the ovaries of grasses some time destroying the whole ears and producing a black powdery mass of spores.All species of the ustilago complete their life cycle on the host and therefore known as autoecious parasite.Ustilagois very common in our country and its different species infect the wheat, maiz, corn, aot and barly.
Taxanomic Position
Kingdom: Fungi
Division: Amastigomycoyins
Sub-Division: Basidiomycotina
Class: Basidiomycetes
Order: Ustilaginales
Family: Ustilaginaceae
Genus: Ustilago
Species: U-tritici
Ustilago species attack on the wheat corn maiz and some other cereal plants.The disease makes its appearance when the flowering portion of the plant produced.The ears in the diseases plants emerges earlier than the healthy plants.In this disease the all flowers are replaced by black powdery mass of spores.These spores are known as teleuto or chlamydospore.In the young spikelets the spores are covered by slivery membranes which burst before emergence of ears.These spores are blown away by wind.It is seed born disease.The dikaryotic hyphae of the fungus are present in the seed.When these seeds are sown then the embryo starts germination the dormant myclium also become active and keep on growing in the apical meristem without causing harm to the plant.The mass of hyphae has short cells which are binucleated.The wall of each cell gelatinized and its protoplast form a thick wall around itself and transformed into spores.The thick wall of spores has two layers exine the outer layer while the intine is inner layer which is nutritive in nature.
Dispersal of spores
The spores are dry and dispersed by wind, insects or by water.They are logged on the ears of healthy plants.
Germination of spores
The spores fall on the stigma of flower and germinate to infect the new plants.The optimum temperature required for germination is 20-30*c.The two nuclei fuses to produced a diploid zygotic nucleus.Then the zygotic nucleus undwergo reduction division.A germ tube is produced.The four haploid nuclei formed as a result of meiosis.In Ustilago tritici the promycelium germinate to produce hyphae.
Infection
The diplophasic mycelium infects the ovaries, which grow intercellularly and attack the embryo.The infected seeds are as healthy as the uninfected one.
smut and the second is covered smut.
Control of disease
Different methods are used for control of disease as following.
Rogueing:- the infected plants must be uprooted and burnt taking outside the fields.It helps in cotroling the spread of disease.
Seed selection:- seed selection is another way to control the disease.
Hot water treatment:- In this method the seeds are soaked in water of temperature of 26-30 for 4-5 hours in order to activate the dormant mycelium.Then these seeds are transferred to hot water to kill the mycelium.The grains then dried and sown.
Soler treatment:- This method is also used for controling the disease.The seeds are soaked in water from 8a.m to 12a.m noon at normal temperature in the monthsof may and june. It activate the dormant mycelium which are then killed by open sunlight.
Resistant varieties:- Disease resistant varietiesmust be sown for the control of disease.
Sort: Trending