
- Why we Die ?
Answer:
When Common parts of the body > like heart or lungs or brain > wear out and stop working, the person will die. When this happens, we say this person died of "old age." Sometimes younger people die. ... This may be the hardest kind of death for families and friends to deal with because it happens so fast.
When there's fluid in the lungs, it can cause a sound known as the death rattle. ... Clinical death occurs when the person's heartbeat, breathing and circulation stop. Four to six minutes later, biological death occurs. That's when brain cells begin to die from lack of oxygen, and resuscitation is impossible.
According to Biology :
Death is the cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include biological aging (senescence), predation, malnutrition, disease, suicide, homicide, starvation, dehydration, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury.
Symbol of Death :
Death is the cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include biological aging (senescence), predation, malnutrition, disease, suicide, homicide, starvation, dehydration, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury.
World Birth and Death Rates
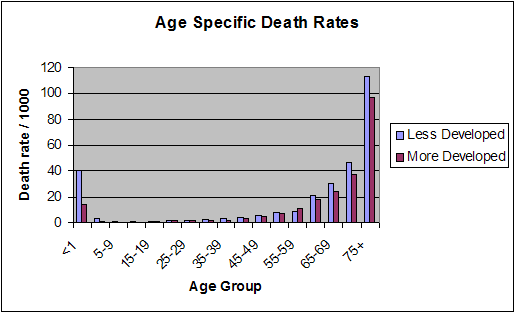
Birth Rate Death Rate
• 19 births/1,000 population • 8 deaths/1,000 population
• 131.4 million births per year • 55.3 million people die each year
• 360,000 births per day • 151,600 people die each day
• 15,000 births each hour • 6,316 people die each hourWhat happens to our bodies after we die?

Since the dawn of humanity,
an estimated 100.8 billion people have lived and died,
a number that increases by about .8% of the world's population each year. What happens to all of those people's bodies after they die and will the planet eventually run out of burial space? When a person's heart stops beating, the body passes through several stages before it begins decomposing.
Within minutes after death,
the blood begins settling in the lower-most parts of the body. Usually eight to twelve hours later, the skin in those areas is discolored by livor mortis, or post-mortem stain. And while at the moment of death the body's muscles relax completely in a condition called primary flaccidity,
they stiffen about two to six hours later in what's known as rigor mortis.
This stiffening spreads through the muscles, and its speed can be affected by age, gender, and the surrounding environment. The body also changes temperature, usually cooling off to match its environment. Next comes decomposition,
the process by which bacteria and insects break apart the body.
Many factors affect the rate of decomposition. There is, however, a basic guide of the effect of the environment on decompositon called Casper's Law. It says that if all other factors are equal, a body exposed to air decomposes twice as fast as one immersed in water
and eight times as fast as one buried in earth.
Soil acidity also greatly affects bone preservation. High-acidity soils with a pH of less than 5.3 will rapidly decompose bone, whereas in a neutral or basic soil with a pH of 7 or more, a skeleton can remain in relatively good condition for centuries.
Different cultures throughout history have developed unique approaches to burials.
As far back as the first Neanderthal burials, death was accompanied by rituals, like the positioning, coloring, or decorating of corpses. Traditional Christian burials decorate the body in dress, while in traditional Islam,
a body is wrapped in a piece of ritual fabric
with the face oriented toward Mecca. Traditional Hindus ceremonially burn the body, and Zoroastrians, followers of one of the oldest monotheistic religions, traditionally place bodies atop a tower to expose them to the Sun and scavenging birds.`
Before the Industrial Revolution, burials were simple and accessible.
These days, with suitable burial land running out in high-population areas, purchasing private gravesites can be costly, and many people can't afford simple burials. Even cremation, the second most common burial practice in the world, comes with a high cost.
As for the question of running out of space,
the issue isn't so much about total land in the world as it is that large populations cluster together within cities. Most of the big cities in the world may run out of suitable burial grounds within a century. For London, it's even sooner.
That may happen by 2035.
So are there alternatives to traditional burials that might help with the space issue? In some countries, skyscraper cemeteries enable vertical burials. Some options focus on the body's relationship with the environment. Promession, for example, freeze-dries and pulverizes the body,
creating a powder that can turn into compost
when mixed with oxygen and water. There are also green burials that use special materials, such as biodegradable caskets, urns that sprout trees, and burial suits that grow mushrooms.
Eternal reefs take that concept to the depths of the ocean
using a mixture of ashes and cement to create marine habitats for sea life. Death is an inevitable part of the human condition, but how we treat bodies and burials continues to evolve. We may each have different spiritual, religious,
or practical approaches to dying,
but the ever-increasing demand for burial space might give us a push to be creative about where our bodies go after the final stages of life.
*How to alive people after death ?

According to a scientist > we can regain life after death to restart the flow of blood in our body through every part especially Heart > He perform experiment to various peoples by lying them down on a see-saw like table and start vibrating them very rapidly to regain the flow but failed > Then he like to try on fresh died people but society restrict him to do so but he don't lose hope > He tried this experiment on Dogs - Proudfully he alive them again
Then he start collecting more education to do this experiment on Humans and Loss for years and never found again ...
Conclusion :

Yes we can regain life again But this is hidden trust by most companies like Google , NASA and more like them
Because i Believe that NASA should know about it
And Google once lunched a Company that reborn the dead peoples and that will hidden truth for us ....
Google stopped it by some restrictions ....Stay Happy > Share this Post as much as Possible
Follow me for getting my Creative Feeds
Upvote that post <3
Congratulations @alphaking-ak! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honnor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPBy upvoting this notification, you can help all Steemit users. Learn how here!