
Ciao amici,
oggi lasciamo da parte il mondo dell’architettura per un nuovo episodio de Anniversari Storici. Ricordate la rubrica che ho lanciato qualche articolo fa? Ecco, oggi compie ben 102 anni (quanto mi rode non aver scritto questo articolo due anni fa che erano 100 tondi tondi!) la famosissima Teoria della Relatività del celebre Albert Einstein!
Questa è, come dire, la seconda edizione di questa mia rubrica… e ancora una volta, dopo aver ricordato la scoperta del DNA, ho scelto di celebrare la scienza, sarà anche deformazione professionale ma non potevo non ricordare un così importante anniversario. Era, infatti, il 20 Marzo del 1916, quando il celebre studioso tedesco pubblicò la sua Teoria della Relatività.
Ma per farci un’idea chiara di cosa stiamo parlando ho deciso di organizzare il presente articolo per punti, cercando di rispondere in maniera sintetica e semplice alle 3 ovvie domande che immagino si porrebbe una persona che disconosce completamente l’argomento in questione:
1. Chi è Albert Einstein?
2. Quali sono le origini della Teoria della Relatività?
3. Cosa dice la Teoria della Reletività?
Volete conoscere le risposte, beh, non vi resta che proseguire… buona lettura!
- Chi è Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14/03/1879 – 18/04/1955) è stato un grande scienziato vissuto a cavallo tra il XIX e il XX secolo. Tedesco di nascita, è stato successivamente naturalizzato statunitense. Il suo genio spaziò in diversi ambiti, infatti, oltre ad essere uno dei più celebri fisici della storia della scienza, fu mosso da altre passioni come la musica, la filosofia e la politica. Per queste ragioni si ritiene, senza dubbio, che sia stato uno dei più importanti studiosi e pensatori del XX secolo.
Nel corso della sua vita Einstein si trasferì in diverse città del mondo. Il 1905 segnò una svolta decisiva nella sua vita e nel mondo della Fisica in generale, infatti. In quell’anno, che passò alla storia come annus mirabilis, nel giro di sette mesi pubblicò sei lavori su importanti argomenti dal contenuto fortemente innovativo come l’effetto fotoelettrico, la nuova determinazione delle dimensioni molecolari, il moto browniano, la relatività ristretta e così via. Fu proprio il lavoro fatto sull’effetto fotoelettrico che, nel 1921, gli permise di vincere il Premio Nobel per la Fisica.
La sua fama crebbe enormemente e in modo sempre crescente dopo l'assegnazione del Nobel ma soprattutto per merito della grande originalità della sua Teoria della relatività, che lasciò un segno nell'immaginario collettivo, che ne rimase profondamente affascinato e stupito.
In merito al difficile contesto storico che segnò la vita dello scienziato e non solo, ovvero il Primo Conflitto Mondiale, Einstein fu uno tra i pochi accademici tedeschi a criticare pubblicamente il coinvolgimento della Germania nella guerra. Egli, naturalmente, disprezza profondamente la violenza e, una volta conclusi questi terribili anni, si impegna attivamente nella difesa del suo pensiero pacifista e antirazzista.
Questa presa di posizione comporta, però, profonde ripercussioni sulla sua persona: diviene vittima di gravi attacchi da parte di gruppi di destra e si cerca di mettere in ridicolo le sue importanti teorie scientifiche, e in particolare la Teoria della Relatività.
Albert Einstein si spegne all'età di 76 anni negli Stati Uniti, a Princeton, il 18 aprile 1955, a causa di una improvvisa emorragia causata dalla rottura di un aneurisma dell'aorta addominale. Richiese espressamente che il proprio corpo fosse messo a disposizione della scienza. Il suo cervello fu l’unica cosa che venne conservata e studiata solo molti anni dopo, il resto del corpo fu cremato.
- Le origini della Teoria della Relatività
Le origini di questo principio si rifanno alle origini stesse della scienza moderna, infatti, in fisica, quando si parla di teoria della relatività ci si riferisce alla tematica delle trasformazioni matematiche che devono essere applicate alle descrizioni dei fenomeni fisici nel passaggio tra due sistemi di riferimento in moto relativo tra loro, secondo il principio, appunto, di relatività.
Il cosiddetto principio di relatività galileiano, sostiene che le leggi della meccanica abbiano la stessa forma matematica rispetto a qualunque sistema di riferimento nel quale valga il principio di inerzia. Questo principio, che lo si deve, appunto, a Galileo Galilei, risale al 1609 ed è tuttora valido.
Questo tipo di studi venne ripreso e rielaborato da molti scienziati nel corso della storia ma è con l’arrivo di Albert Einstein che la teoria della relatività ebbe un importante ed ulteriore sviluppo, tanto che oggi si tende ad associare al suo nome la suddetta teoria.
- Cosa dice la Teoria della Relatività
Questa teoria è, in realtà, il frutto di due distinti modelli matematici formulati da Albert Einstein, ovvero: la relatività ristretta o speciale e la relatività generale. La prima, nata da un articolo scritto nel 1905, in accordo con il principio di relatività galileiano, che include importanti principi tra cui la composizione delle velocità, le equazioni delle onde elettromagnetiche, nelle quali la velocità della luce è espressa come costante, ovvero indipendente dal sistema di riferimento. Sempre nell’ambito della relatività ristretta, Einstein enuncia la storica formula E=mc2, che spiega come l’energia cinetica (E) sia proporzionale alla massa (m) e alla velocità della luce (c).
La relatività generale, in buona sostanza, afferma che la velocità dell’osservatore influenza la percezione del prima e del dopo, e dunque lo scorrere del tempo non è universale. Pubblicata nel 1916, e si basa sull'assunto, noto come principio di equivalenza, secondo cui un'accelerazione è indistinguibile localmente dagli effetti di un campo gravitazionale, e dunque la massa inerziale risulta pari alla massa gravitazionale. Va detto che, pur dimostrandosi nel tempo estremamente accurata, la relatività generale si è sviluppata indipendentemente dalla meccanica quantistica con la quale, a tutt’oggi, non risulta riconciliata. D'altro canto, è pur vero che la fisica quantistica, seppur possa includere gli assunti della relatività ristretta, non tiene conto, invece, degli aspetti della relatività generale.
Questa teoria non è esente i limiti, questi infatti sono dovuti essenzialmente al trattamento delle singolarità e degli stati della materia in cui le interazioni gravitazionali e quantistiche arrivano ad avere lo stesso ordine di grandezza. Tra le evoluzioni di questa teoria, le più note e investigate sono la teoria delle stringhe e la gravitazione quantistica a loop.
Il tempo non è affatto ciò che sembra. Non scorre in una sola direzione, e il futuro esiste contemporaneamente al passato. Albert Einstein
Cari amici mi sono dilungato davvero tanto, lo riconosco, perciò mi congedo immediatamente col mio solito ma sentito grazie e con il buon auspicio che abbiate gradito quanto letto. Vi abbraccio tutti!
L'Ego dice: "Quando ogni cosa andrà a posto troverò la pace".
Lo Spirito dice: "Trova la pace e ogni cosa andrà a posto".

Hello friends,
today we leave aside the world of architecture for a new episode of Historical Anniversaries. Remember the rubric that I have launched some articles ago? Well, today he is 102 years old (how much I am bothered not having written this article two years ago which were 100 round rounds!) the very famous Theory of Relativity by the famous Albert Einstein!
This is, how to say, the second edition of my rubric... and once again, after recalling the discovery of DNA, I chose to celebrate science, it will also be professional deformation but I could not forget a so important anniversary. It was, in fact, March 20, 1916, when the famous German scholar published his Theory of Relativity.
But to get a clear idea of what we are talking about, I decided to organize this article by points, trying to answer in a simple and concise way the three obvious questions that I imagine would be a person who completely disregards the topic in question:
1. Who is Albert Einstein?
2. What are the origins of the Theory of Relativity?
3. What does the Theory of Relativity say?
You want to know the answers, well, you just have to continue ... good reading!
- Who is Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14/03/1879 - 18/04/1955) was a great scientist who lived between the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. German by birth, it was subsequently a US national. His genius ranged in different fields, in fact, besides being one of the most famous physicists in the history of science, he was moved by other passions such as music, philosophy and politics. For these reasons it is believed, without doubt, that he was one of the most important scholars and thinkers of the twentieth century.
In the course of his life Einstein moved to different cities in the world. 1905 marked a turning point in his life and in the world of Physics in general, in fact. In that year, which went down in history as annus mirabilis, within seven months he published six works on important topics with highly innovative content such as the photoelectric effect, the new determination of molecular dimensions, the Brownian motion , special relativity and so on. It was precisely the work done on the photoelectric effect that, in 1921, allowed him to win the Nobel Prize for Physics.
His fame grew enormously and in an ever increasing way after the awarding of the Nobel Prize but above all thanks to the great originality of his Theory of relativity, which left a mark in the collective imagination, which remained deeply fascinated and amazed.
Regarding the difficult historical context that marked the life of the scientist and not only, namely the First World Conflict, Einstein was one of the few German academics to publicly criticize the involvement of Germany in the war. He, of course, deeply despises violence and, once these terrible years are over, actively commits himself to the defense of his pacifist and anti-racist thinking.
- The origins of the Theory of Relativity
The origins of this principle refer to the very origins of modern science, in fact, in physics, when we talk about relativity theory we refer to the topic of mathematical transformations that must be applied to the descriptions of physical phenomena in the transition between two reference systems in relative motion between them, according to the principle of relativity.
The so-called Galilean principle of relativity, maintains that the laws of mechanics have the same mathematical form as any reference system in which the principle of inertia applies. This principle, which is due precisely to Galileo Galilei, dates back to 1609 and is still valid.
This type of study was taken up and reworked by many scientists throughout history, but it is with the arrival of Albert Einstein that the theory of relativity had an important and further development, so much so that today we tend to associate the aforementioned theory to its name.
- What the Relativity Theory says
This theory is, in fact, the fruit of two distinct mathematical models formulated by Albert Einstein, namely: the special relativity and the general relativity. The first, born from an article written in 1905, in accordance with the Galilean principle of relativity, which includes important principles including the composition of velocities, the equations of electromagnetic waves, in which the speed of light is expressed as constant or independent. from the reference system. Still in the context of special relativity, Einstein states the historical formula E=mc2, which explains how the kinetic energy (E) is proportional to the mass (m) and to the speed of light (c).
General relativity, in essence, states that the observer's speed influences the perception of the before and after, and therefore the passage of time is not universal. Published in 1916, and based on the assumption, known as the equivalence principle, according to which an acceleration is indistinguishable locally from the effects of a gravitational field, and therefore the inertial mass is equal to the gravitational mass. It must be said that, although it proved extremely accurate over time, general relativity developed independently of the quantum mechanics with which, to date, it is not reconciled. On the other hand, it is also true that quantum physics, although it may include the assumptions of special relativity, does not take into account aspects of general relativity.
This theory is not exempt the limits, these are essentially due to the treatment of singularities and the states of matter in which gravitational and quantum interactions come to have the same order of magnitude. Among the developments envisaged for this theory, the most known and investigated are the string theory and the loop quantum gravitation.
Time is not at all what it seems. It does not flow in one direction, and the future exists simultaneously with the past. Albert Einstein
Dear friends, I have gone very far, I recognize it, so I immediately leave with my usual but heartfelt thanks and with the good omen that you have enjoyed what you read. I embrace you all!
The ego says: "When everything goes right I will find peace"
The Spirit says: "Find peace and everything will fall into place"
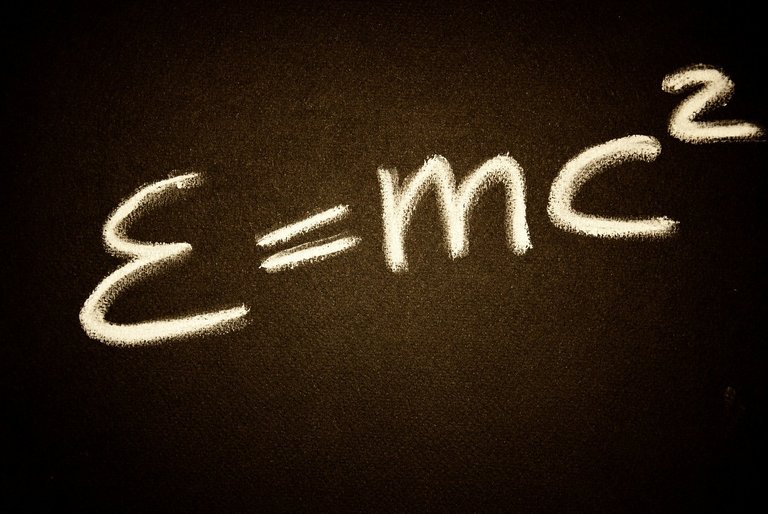


Tutti conoscono la formula, pochi ne capiscono il significato (me compreso). Grazie per averci ricordato l'anniversario 😀
Grazie a te per esser passato di qui! Non potevo non ricordare un genio così grande come quest'uomo... così come non potevo non mettere la sua iconica foto con la linguaccia!
102 anni? Sai che pensavo molti di piú. Sono cose che ho studiato tanti anni fa. Rileggerle con il tuo schema è stato più piacevole...
Effettivamente è vero, sembra di parlare di chissà quali epoche lontane ma in realtà non è passato poi così tanto tempo! Ti ringrazio! ;)