The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon. It traps part of the solar radiation and allows the temperature of the lower atmosphere to stay around 15 ° C on average, which has allowed the development of life. Without this greenhouse effect, mainly due to water vapor, the average temperature would be -18 ° C and life on Earth would not have developed in its current forms.

Mechanism of the greenhouse effect:
Solar radiation (which has wavelengths between 200 and 300 nm) passes through the atmosphere, transparent in the visible range. Part (about 28.3%) is returned directly to space by air, white clouds and the clear surface of the Earth (such as the Arctic and Antarctic), this is the albedo. Incident rays that have not been reflected back to space are absorbed by the atmosphere (20.7%) and / or the earth's surface (51%).
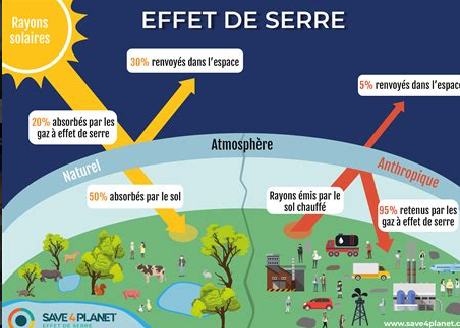
The part of the radiation absorbed by the Earth gives it heat (energy), which it in turn releases back to the atmosphere in the form of infrared rays, this is the black body radiation
The mechanism of the greenhouse effect This radiation is then partially absorbed by greenhouse gases, which then contribute to the warming of the lower layers of the atmosphere.
Then in a third step, this heat is re-emitted in all directions, in particular towards the Earth.
It is this radiation that returns to Earth and creates the greenhouse effect; it is the source of additional heat input to the Earth's surface. Without this phenomenon, the average temperature on Earth would first drop to -18 ° C. Then with the ice spreading over the globe, the Earth's albedo would increase and the temperature would likely stabilize at -100 ° C. Diagram of the structure of the Earth's atmosphere
On average, the energy from space received by Earth and the energy from Earth emitted to space are almost equal. Otherwise, the surface temperature of the Earth would evolve towards always colder or towards always hotter. Indeed, if the average energy exchanges with space are not balanced, there will be a storage or a release of energy by the Earth. This imbalance then causes the temperature of the atmosphere to change.
Article source:http://www.cndp.fr/crdp-reunion/node/169
L’effet de serre est un phénomène naturel. Il piège une partie du rayonnement solaire et permet à la température de la basse atmosphère de se maintenir autour de 15°C en moyenne ce qui a permis le développement de la vie. Sans cet effet de serre, principalement dû à la vapeur d’eau, la température moyenne serait de - 18°C et la vie sur Terre n’aurait pas connu un développement sous ses formes actuelles.

Mécanisme de l’effet de serre :
Le rayonnement solaire (qui a des longueurs d’onde comprises entre 200 et 300 nm), traverse l’atmosphère, transparent dans le domaine visible. Une partie (environ 28,3 %) est directement renvoyée vers l’espace par l’air, les nuages blancs et la surface claire de la Terre (comme l’Arctique et l’Antarctique), c’est l’albédo. Les rayons incidents qui n’ont pas été réfléchis vers l’espace sont absorbés par l’atmosphère (20,7%) et/ou la surface terrestre (51%).

La partie du rayonnement absorbée par la Terre lui apporte de la chaleur (énergie), qu’elle restitue à son tour en direction de l’atmosphère sous forme de rayons infrarouges, c’est le rayonnement du corps noir.
le mécanisme de l'effet de serreCe rayonnement est alors absorbé en partie par les gaz à effet de serre contribuant alors au réchauffement des basses couches de l’atmosphère.
Puis dans un troisième temps, cette chaleur est réémise dans toutes les directions, notamment vers la Terre.
C’est ce rayonnement qui retourne vers la Terre et qui crée l’effet de serre, il est à l’origine d’un apport supplémentaire de chaleur à la surface terrestre. Sans ce phénomène, la température moyenne sur Terre chuterait d’abord à - 18°C. Puis la glace s’étendant sur le globe, l’albédo terrestre augmenterait et la température se stabiliserait vraisemblablement à -100°C.
En moyenne, l’énergie venue de l’espace et reçue par la Terre et l’énergie de la Terre émise vers l’espace sont quasiment égales. Dans le cas contraire la température de surface de la Terre évoluerait vers toujours plus froid ou vers toujours plus chaud. En effet, si les échanges moyens d’énergie avec l’espace ne sont pas équilibrés, il y aura un stockage ou un déstockage d’énergie par la Terre. Ce déséquilibre provoque alors un changement de température de l’atmosphère.
Source de l'article:http://www.cndp.fr/crdp-reunion/node/169