
Hello Hivers. It's been a while. I hope you well. Today, I want to tell you about our first ever school experiment as a senior high school student. This experiment made me realize that there's a different world under the microscope.
Background
First of all, what is plant cell? Well, plant cell is the basic unit of all plants. Unlike animal cells, plant cell have cell wall which makes their body strong and upright structure. Aside that, plant cell also have specialize cell. Specialize cell has a structure that suits it's function. Example of these are root hair cell, palisade cell, guard cell and many more. But in this blog let's talk about the guard cell and stomata. Guard cells controls gas exchange and water loss in leaves, stems, and other organs. On the other hand, stomata allow plants to take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and release oxygen as a waste product. The stoma is an epidermal opening between guard cells, which are elongated cells. The opening may be adjusted when the guard cell's turgidity changed. When the guard cells become turgid, they bend outward to open the stoma; when they become flaccid, the stoma narrows and ultimately shuts.
Materials:
Compound microscope
Tap water
Rheo leaf (tradescantia spathacea)
Razor blade
Rubber dropper
Concentrated salt solution
Forceps
Procedure:
📍 Clean the Rhoes leaf surface and with the aid of a sharp razor blade, scrape a portion of the lower epidermis and lift a flap with forceps. You only need the violet part so if there's green attached to it, scrape it as well.
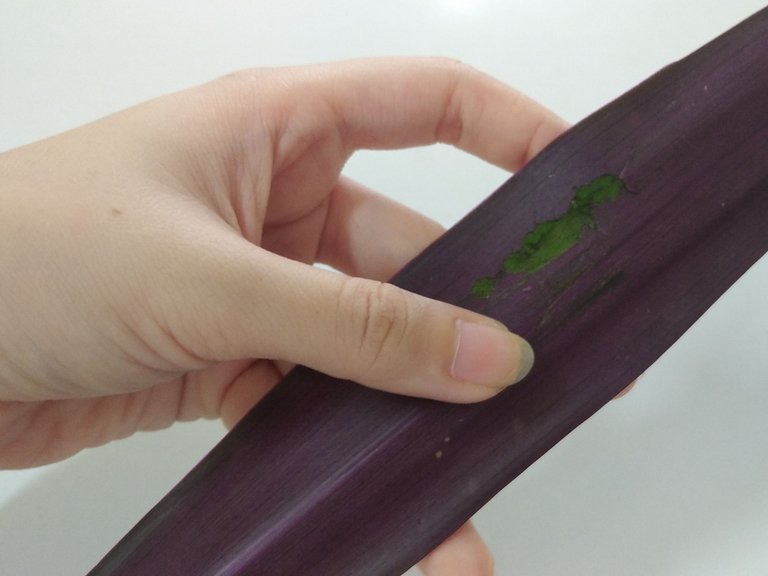

📍 Place a drop of water on a glass slide to mount this little flap tissue. Examine using a low power objective lens (LPO). You should be able to retrieve this picture.
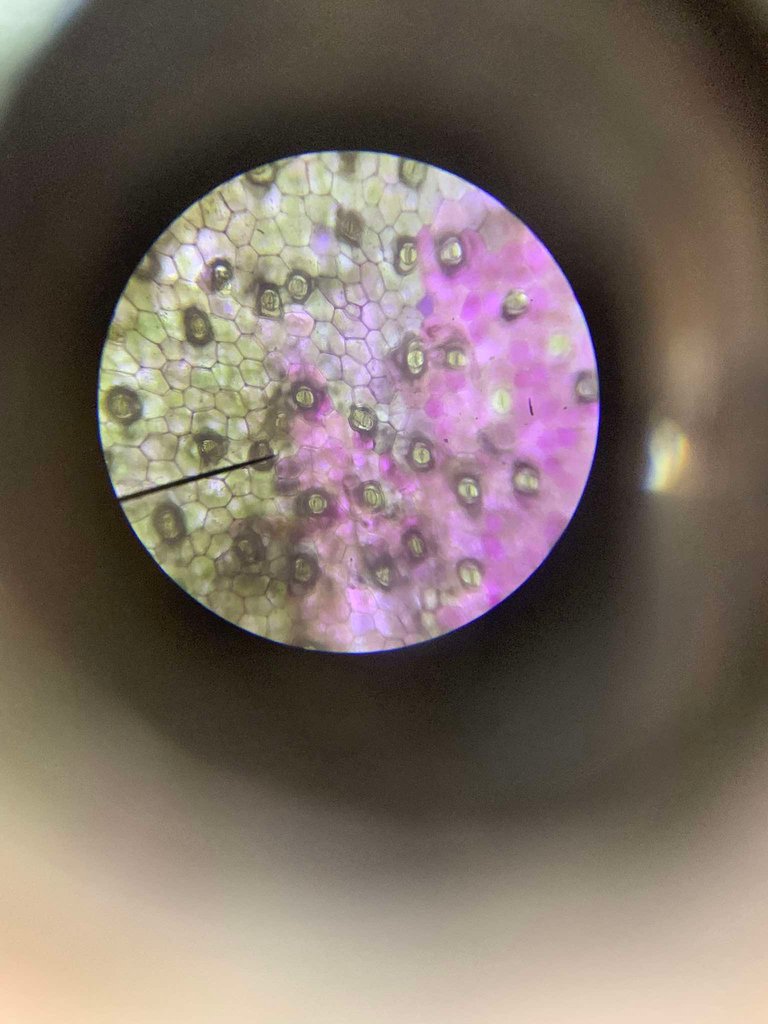
📍 Then proceed to high power objective lens (HPO). The guard cells are easy to locate because of their bright green color. The guard cells are epidermal cells containing chloroplasts and therefore capable for photosynthesis. Focus on a pale and locate the stoma, which is the opening
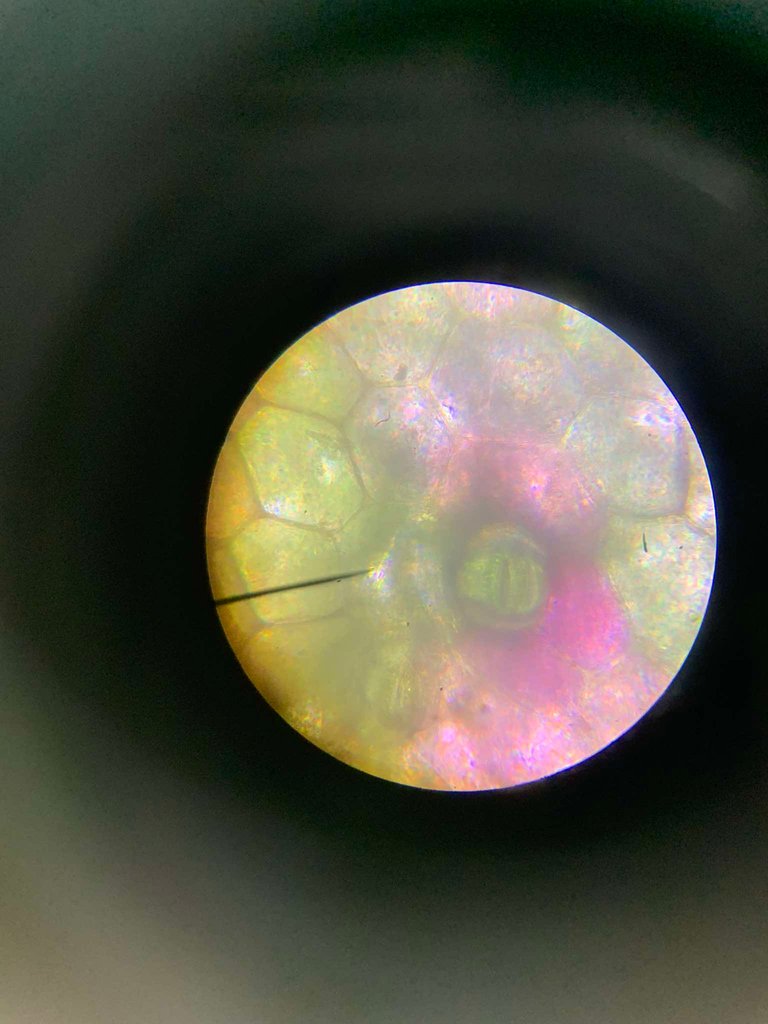
📍 Now, change the water with concentrated salt solution and examine the structures again. This time, are the cells turgid or flaccid? What happened to stomata?
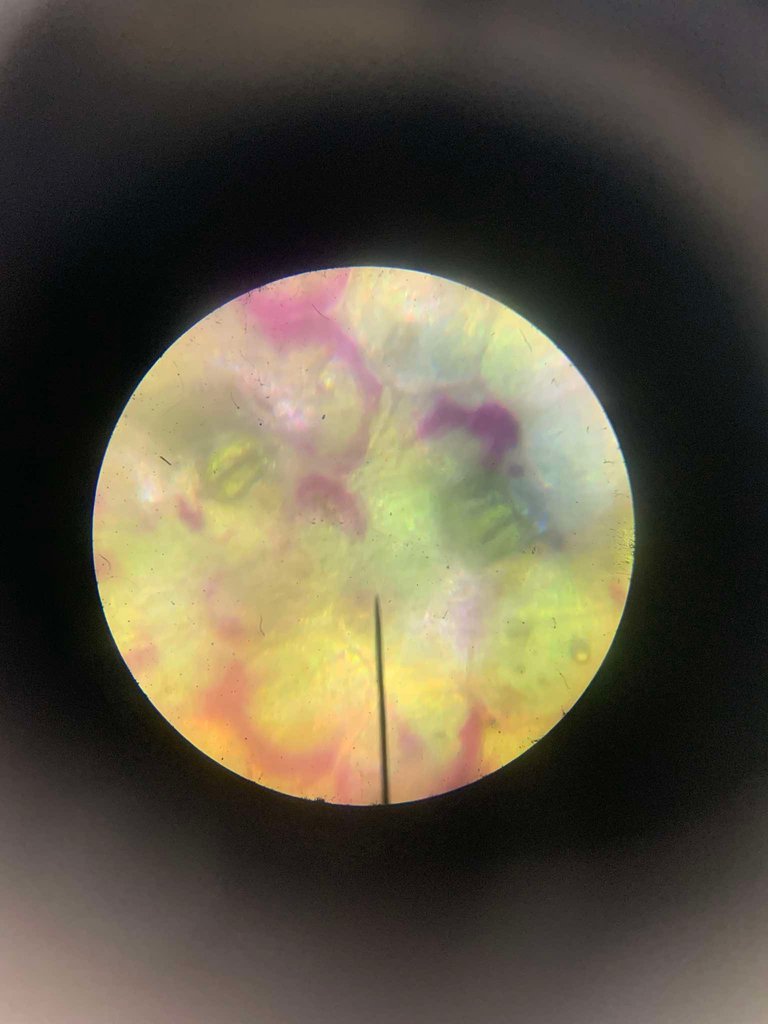
As you can see, the cell became flaccid and the guard cell closes due to lack of water. This is really essential to prevent excessive water loss, protects plant from dehydration,acts as a survival mechanism in high salinity, and most importantly maintains water balance in plant cells.
I hope you learnt something today! I was really thrilled to share this with you all since I felt the image we see of the structure of a plant cell was not correct, but to my amazement, it exceeded my expectations. Thank you for reading all the way through. I hope you find the material beneficial. Do not fear, there will be more to come, so stay tuned.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Congratulations @phoennix09! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 4500 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP