Here is the daily technology #threadcast for 10/19/24. We aim to educate people about this crucial area along with providing information of what is taking place.
Drop all question, comments, and articles relating to #technology and the future. The goal is make it a technology center.

Build details showcase incredible scale of Saudi Arabia's Line megacity
As the Line gigaproject continues to grow in the Saudi desert, some new construction details have been announced that highlight the mind-boggling challenge of turning a huge tract of rugged landscape into a futuristic megacity, including its reported use of one fifth of the entire world's currently available steel.
#nesonleo #saudiarabia #construction #megacity
The Line: A Futuristic City
The Line is a 170 km stretch of infrastructure designed to be a self-sustaining, futuristic city. The initial stage of the project, set to be completed by 2030, will span just 2.4 km and will serve as a precursor to the full-scale city. The Line will be a marvel of modern engineering, featuring:
Neom's Vision
Neom, the brainchild of Saudi Arabia's Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, is a massive project aimed at transforming the country's economy from a reliance on fossil fuels to a more sustainable, tourism-driven model. The project spans over 26,500 km² (10,230 sq mi) and will feature:
The Impact of The Line
The Line is expected to have a significant impact on the region, both economically and environmentally. Some of the expected benefits include:
The Construction Process
The construction of The Line and Neom's various projects is a complex and challenging process. Some of the key aspects include:
Challenges and Controversies
While The Line and Neom's project are ambitious and innovative, they are not without their challenges and controversies. Some of the key issues include:
Overall, The Line and Neom's project are a testament to Saudi Arabia's vision for a sustainable, futuristic future. While challenges and controversies surround the project, its potential to stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and provide a model for sustainable urban development make it an exciting and ambitious project.
Article
It was an excellent day! We exceeded 400 comments.
Congratulations to everyone!
This is becoming a nice place to post and find news. It is really something that can grow into something bigger. I will be talking about this.
Without a doubt, it is becoming a good place to gather all the possible news about #technology.
We will continue to maintain a good pace and have a good average.
So, I've tried installing KolibiriOS on a USB drive and it won't boot... Not sure if it's my laptop, or I made the boot drive incorrectly... Will have to try it on another device.
I enjoyed watching this, and it counts for a technology content, so here you go guys:
Nigeria is a case
Breaking:National Grid Collapses, Third Time In A Week |
READ FULL STORY
#newsonleo #technology #nigeria
Netflix beats Q3 forecasts with strong subscriber growth
#technology #netflix
Netflix reported an impressive performance for the third quarter of the year, surpassing Wall Street estimates when it comes to subscriber growth, revenue, and profit margins for the period.
For the three months ended September 30, the streaming service giant reported earnings per share (EPS) of $5.40, blowing past analysts’ forecasts of $5.12.
For the same period, its revenue also exceeded market expectations, reaching $9.83 billion, compared to the predicted $9.77 billion.
This marks an annual growth of 15% compared to the revenue in the corresponding period last year. Furthermore, Netflix’s net income rose to $2.36 billion from $1.68 billion a year earlier, clocking a YoY growth of 41%. Going forwards
clocking a YoY growth of 41%. Going forwards, Netflix aims to secure $10.13 billion in revenue and $4.23 in EPS for the current quarter.
Netflix’s operating margin for Q3 2024 also amounted to 30%, while its operating income rose to $2.9 billion for the same period. Its free cash flow surged to $2.19 billion as well.
“We’ve delivered on our plan to reaccelerate our business, and we’re excited to finish the year strong with a great Q4 slate,” Netflix said in a letter to shareholders.
For the full year (2025), Netflix expects its revenue to range between $43-44 billion. Netflix’s shares rose 3.5% in after-hours trading, and are currently priced at $687.65.
OpenAI secures $6.6Bn in latest fundraise to reach $157B in valuation
#technology #ai #openai
OpenAI’s $6.5 billion funding round has been the cause of speculation for weeks, and now, the AI firm has confirmed the development.
OpenAI confirmed that it has closed its latest (and successful) funding round, wherein it raised $6.6 billion and elevated its valuation to an impressive $157 billion. For comparison, OpenAI was valued at $80 billion earlier this year.
We are making progress on our mission to ensure that artificial general intelligence benefits all of humanity. Every week, over 250 million people around the world use ChatGPT to enhance their work, creativity, and learning.
Across industries, businesses are improving productivity and operations, and developers are leveraging our platform to create a new generation of applications. And we’re only getting started,” OpenAI noted.
This round of funding is one of the largest private investments so far.
The new round of funding was led by venture capital firm Thrive Capital (which confirms prior reports on the matter).
The funding round also included the participation from several other prominent investors, including Microsoft, Nvidia, SoftBank, Khosla Ventures, Altimeter Capital, Fidelity, and MGX.
With this, OpenAI has raised a total of $17.9 billion across funding rounds ever since it was founded.
Microsoft could end up with substantial equity in the restructured, for-profit OpenAI
Microsoft and OpenAI are reportedly negotiating over how much equity the former will get in OpenAI once OpenAI converts to a for-profit.
How much equity in OpenAI will Microsoft get once the former becomes a for-profit company? That’s the multibillion-dollar question — one the two parties are racing to answer ahead of a two-year deadline.
#microsoft #openai #technology #newsonleo
The Wall Street Journal reports that both Microsoft and OpenAI have hired investment banks to negotiate Microsoft’s equity — which could be substantial. The tech giant is said to have sunk nearly $14 billion into OpenAI. As of October, OpenAI is the second-most valuable startup in the U.S. behind SpaceX.
Among other issues, Microsoft and OpenAI must resolve how much equity will go to CEO Sam Altman and OpenAI employees, as well as which specific governance rights Microsoft will have. Once OpenAI converts to a for-profit, it’ll become a public-benefit corporation, but with a nonprofit component that’ll own equity in the restructured company.
Article
Hi, @taskmaster4450le,
This post has been voted on by @darkcloaks because you are an active member of the Darkcloaks gaming community.
Get started with Darkcloaks today, and follow us on Inleo for the latest updates.
SpaceX wins $733M Space Force launch contract
SpaceX was awarded an eight-launch, $733 million contract by the U.S. Space Force on Friday, as part of an ongoing program intended to foster competition
SpaceX was awarded an eight-launch, $733 million contract by the U.S. Space Force on Friday, as part of an ongoing program intended to foster competition among launch providers.
#newsonleo #spacex #technology #spaceforce
The United States Space Force has awarded a massive contract to SpaceX, valued at $5.6 billion over five years, for the launch of national security space missions. This significant development is part of the National security Space Launch Phase 3 Lane 1 program, which will see SpaceX launching seven missions for the Space Development Agency and one for the National Reconnaissance Office. These missions are expected to utilize Falcon 9 rockets and take place no earlier than 2026.
The contract is the result of a competitive bidding process, which saw SpaceX, United Launch Alliance, and Blue Origin competing for the opportunity to launch missions under Lane 1. Despite Blue Origin not yet having achieved orbit, the company was still selected to compete for launches under the program. The Space Force has acknowledged that the pool of awardees is small, but has stated its intention to allow companies to bid on Lane 1 on an annual basis, with the next opportunity to join the program set to take place later in 2024.
The Phase 3 Lane 1 award period will run from fiscal year 2025 to fiscal year 2029, with the potential for a five-year extension. The Space Force anticipates awarding at least 30 missions over this period, providing a significant boost to the company's launch capabilities. This contract is a significant win for SpaceX, which has been a major player in the launch industry for several years. However, the company may face increased competition in the future as new launch companies and vehicles come online.
The Space Force has stated its intention to see "increasing competition and diversity" in the launch market, and the ability to on-ramp new providers will likely lead to a more competitive landscape in the years to come. The contract is part of the Space Force's efforts to modernize its launch capabilities and provide a more reliable and cost-effective way of launching national security space missions. The Phase 3 Lane 1 program is designed to provide a more flexible and responsive launch capability, allowing the Space Force to quickly and efficiently launch missions as needed.
In a statement announcing the contract, Lt. Col. Douglas Downs, the Space Force's materiel leader for space launch procurement, said: "We expect to see increasing competition and diversity with the ability to on-ramp new providers. This contract will provide a stable and reliable launch capability for our national security space missions."
The contract is a significant development for the launch industry, and will likely have a major impact on the market in the years to come. As the Space Force continues to modernize its launch capabilities, it will be interesting to see how the competitive landscape evolves and which companies emerge as major players in the industry.
The contract is also a testament to SpaceX's capabilities and its ability to deliver reliable and cost-effective launch services. With this contract, SpaceX will be able to further expand its launch capabilities and provide a more comprehensive range of services to its customers. The contract is also a significant win for the Space Force, as it will provide a more reliable and cost-effective way of launching national security space missions.
Overall, the contract is a significant development for the launch industry, and will likely have a major impact on the market in the years to come. As the Space Force continues to modernize its launch capabilities, it will be interesting to see how the competitive landscape evolves and which companies emerge as major players in the industry.
Article
Eric Schmidt's SandboxAQ aims for $5B valuation for its AI/quantum Google moonshot
SandboxAQ began as Alphabet’s moonshot AI and quantum computing and now has an impressive roster of projects.
VCs are spending gobs of money on AI startups — especially those run by big names in tech — so SandboxAQ is putting its hand out again, even though it raised a whopping $500 million in early 2023.
#newsonleo #erocschmidt #sandboxaq #google #technology
SandboxAQ, a cutting-edge AI quantum computing startup spun out of Alphabet, is reportedly seeking to raise a staggering $5 billion in its latest funding round, valuing the company at a whopping $5 billion. This significant increase in valuation comes just a few months after its last funding round in February 2023, which valued the company at $4 billion.
ndustry.
Founded in March 2022 by Jack Hidary, a longtime X Prize board member, SandboxAQ is revolutionizing the intersection of quantum computing and AI. Unlike other companies that focus on building quantum computers, SandboxAQ is developing software based on quantum physics that can model molecules and make predictions about their behavior. This innovative approach has already led to a wide range of products across life science, materials science, navigation, encryption, and cybersecurity.
The company has already secured several developmental contracts, showcasing its impressive capabilities. For instance, it is working with battery company Novonix to extend lithium-ion battery life, and has a contract with the U.S. Air Force to develop magnetic navigation systems that don't rely on GPS. These contracts demonstrate SandboxAQ's ability to apply its technology to real-world problems and its potential for significant impact.
SandboxAQ's AI technology is centered around using large modeling AI techniques on equations, rather than predicting language like generative AI chatbots. This approach enables the company to generate data more efficiently and accurately, leading to several impressive developments. The company's chairman, billionaire and former Google CEO Eric Schmidt, has been instrumental in guiding SandboxAQ's development, providing valuable insights and expertise.
The company's impressive track record has caught the attention of investors, who are eager to get a piece of the action. Throughout the year, several investors have set up special purpose vehicles (SPVs) for SandboxAQ's shares, a hot financial tool that allows investors to buy into big-name AI startups. With its growing list of contracts and impressive technology, SandboxAQ is poised to become one of the leading AI companies in the industry.
The upcoming funding round is expected to be a significant one, with a valuation of $5 billion. This would be a major milestone for SandboxAQ, likely attracting even more attention from investors and the tech community. As the company continues to grow and develop its technology, it will be interesting to see how it uses its funding to further its mission and expand its reach.
With its impressive track record and growing list of contracts, SandboxAQ is well-positioned to become a major player in the AI industry. The company's ability to apply its technology to real-world problems and its potential for significant impact make it an exciting and promising development in the world of AI. As SandboxAQ continues to push the boundaries of what is possible, it will be exciting to see the company's future developments and the impact it will have on the industry.
Article
Fluid Truck files for Chapter 11 bankruptcy and pursues sale after leadership shakeup
Less than two months after Fluid Truck’s board ousted its sibling co-founders from their executive positions, the company has laid off 30% of its staff,
Less than two months after Fluid Truck’s board ousted its sibling co-founders from their executive positions, the company has laid off 30% of its staff, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection, and found a potential buyer to take on the business, pending court approval, according to bankruptcy filings and information from a former employee.
#newsonleo #fluidtruck #bankruptcy #technology
Fluid Truck, a startup that allows individuals and small business owners to purchase fleets of vans and trucks to be rented out on its platform, has filed for bankruptcy in a Delaware court. The company, which has been referred to as the "Zipcar of commercial vehicles," has been struggling financially and faces several lawsuits, including a class action filed in Colorado.
According to the bankruptcy filing, Fluid Truck has estimated that the number of creditors awaiting payment is at around 5,500. The company owes FVIP members $12 million, and owes vendors $26 million. Additionally, Fluid Truck suffered cash losses of $20.6 million in 2023. The company's financial struggles began under the leadership of its co-founders and former CEO and chief legal counsel, James Eberhard and Jenifer Snyder. Despite raising over $80 million in venture funds and expanding to 400 cities in 32 states across the U.S., Fluid Truck found itself in a deep financial hole due to a combination of macroeconomic factors and mismanaged insurance claims.
The company's deficits accumulated, and bad blood started festering between Eberhard and two minority shareholders on the board. In July, the board voted to remove Eberhard and Snyder from their roles, and Eberhard's replacement, Scott Avila from Paladin Management, began exploring liquidation options in August. However, Fluid Truck received a large, long-awaited payment from a customer, and decided to use that momentum to try to sell the company.
Kingbee Rentals, a van rental agency in West Valley City, Utah, came forward unexpectedly as a potential buyer. However, Kingbee couldn't afford to acquire all of Fluid Truck's assets on its own, and Fluid Truck couldn't afford to keep the lights on for much longer. To address this, Fluid Truck has asked the courts to approve emergency funding in the form of a $7 million debtor-in-possession (DIP) loan from Kingbee and some existing investors.
The court approved the loan on an interim basis on Friday, but with a caveat: if the sale doesn't close by December 31, Fluid Truck will be in default, and the lenders can liquidate the business. "This gives them a hammer to do something if [Fluid] blows past that deadline," said Adam Stein-Sapir, a bankruptcy expert at Pioneer Funding Group. It's unclear how much Fluid Truck will be able to sell its assets for, but Stein-Sapir says it could be around the $7 million mark. This is bad news for any unsecured lenders, like FVIP members, who will be among those last in line to be paid back.
"For people who are just unsecured here, it's looking pretty grim in terms of recovery," Stein-Sapir said. "Unless they filed a lien or have some kind of security in those funds, they are in some trouble." Fluid Truck did not immediately respond to a request for comment. The company's bankruptcy filing and the uncertainty surrounding its future make it difficult to predict what will happen next. However, one thing is clear: Fluid Truck's financial struggles have left many creditors in a precarious position, and it's unclear how much they will be able to recover.
The bankruptcy filing and the uncertainty surrounding Fluid Truck's future have left many creditors in a state of limbo. The company's creditors, including FVIP members and vendors, are waiting to see what will happen next and how much they will be able to recover. The bankruptcy expert, Adam Stein-Sapir, believes that the company's assets could be sold for around $7 million, but this is a worst-case scenario for unsecured lenders, who will be among the last to be paid back. The future of Fluid Truck is uncertain, and it remains to be seen what will happen to the company and its creditors in the coming months.
Article
Crypto's $130 million congressional election binge has candidates like Utah's John Curtis poised for big wins
In running to take Mitt Romney's Senate seat, Republican John Curtis has benefited by being a friend to the crypto industry.
#politics #newsonleo #crypto #utah #technology
As the midterm elections draw near, the cryptocurrency industry is making a significant impact on the political landscape by backing candidates who are friendly to its interests. One of the most notable beneficiaries of this support is Utah Senate candidate John Curtis, a Republican congressman who is running to fill the seat being vacated by Mitt Romney. Curtis has gained the favor of the crypto industry due to his pro-crypto stance and willingness to listen to industry leaders.
As the midterm elections draw near, the cryptocurrency industry is making a significant impact on the political landscape by backing candidates who are friendly to its interests. One of the most notable beneficiaries of this support is Utah Senate candidate John Curtis, a Republican congressman who is running to fill the seat being vacated by Mitt Romney. Curtis has gained the favor of the crypto industry due to his pro-crypto stance and willingness to listen to industry leaders.
At a recent event in Salt Lake City, Curtis spoke to a crowd of crypto enthusiasts about the importance of understanding the technology and its potential applications. He shared a personal anecdote about a conversation he had with fellow lawmakers about Internet service providers and how to incentivize them to improve their offerings. However, when he asked whether they had ever run a speed test, he was met with puzzled responses. This experience has given him a unique perspective on the importance of government involvement in the crypto space.
Curtis' pro-crypto stance has earned him significant financial support from the industry. The Defend American jobs PAC, a single-issue committee focused on cryptocurrency and blockchain policy, has contributed over $1.9 million to his campaign, according to Federal election commission data. This is just one example of the crypto industry's financial backing, which has also targeted other candidates across the country who are publicly adopting a pro-crypto policy within their campaigns.
The crypto industry's financial muscle is not limited to Utah. It has also spent over $130 million in congressional races across the country, including the primaries. The industry is targeting competitive Senate and House races in Arizona, Michigan, Indiana, West Virginia, and Massachusetts, among other states. One of the biggest targets is Ohio Democratic Sen. Sherrod Brown, the chair of the banking committee, who is a strong critic of the industry. The industry has directed over $40 million towards defeating Brown, who is currently in a close race that will determine which party will control the Senate.
The crypto industry is not just focused on battleground districts, but is also supporting lawmakers who embrace regulation that favors the technology rather than getting in its way. When asked about the industry's efforts, House Majority Whip Rep. Tom Emmer (R-Minn.) said, "When we talk about digital assets, when we talk about crypto, that is not about Republicans and Democrats. That's about Americans, that's about decentralization of a system that has been, literally, consolidated at the tOP."
As the midterm elections approach, it remains to be seen how much of an impact the crypto industry's financial backing will have on the outcome of races. However, one thing is clear: the industry is flexing its financial muscle and is determined to have a say in the outcome of the election.
Article
BlackRock's ETF chief says 75% of its bitcoin buyers are crypto fans new to Wall Street
Bitcoin ETF inflows surpass $2.1 billion in a week as bitcoin touches highest price level since July.
A year ago, Samara Cohen believed there was so much pent-up demand for bitcoin that she and her team at BlackRock launched one of the first-ever spot bitcoin exchange-traded products in the U.S. Now investors are flocking in, and a lot of them are crypto enthusiasts who are new to Wall Street.
#newsonleo #bitcoin #blackrock #technology
The Rise of Spot Bitcoin ETFs: A Game-Changer for Investors
The financial landscape has undergone a significant shift with the rapid growth of spot bitcoin exchange-traded products (ETPs), boasting a total market capitalization of over $63 billion and total flows of nearly $20 billion. As bitcoin reaches its highest level since July, trading above $68,300, the surge in trading volume is a testament to the popularity of spot bitcoin ETFs. This article delves into the world of spot bitcoin ETFs, exploring the reasons behind their widespread adoption and the impact on investors.
A Year of Pent-Up Demand
Samara Cohen, Chief Investment Officer at BlackRock, launched one of the first-ever spot bitcoin ETFs in the US a year ago, anticipating a surge in demand. Her prediction has come true, with investors flocking to the market. Cohen attributes the demand to a better way to access bitcoin, specifically the ETF wrapper. The ETF wrapper provides a more accessible and transparent way for investors to gain exposure to bitcoin, making it an attractive option for those new to Wall Street. The wrapper allows investors to buy and sell shares of the ETF, which in turn holds a basket of underlying assets, such as bitcoin, providing a more liquid and tradable instrument.
A New Breed of Investor
The majority of buyers of these new spot bitcoin products are direct investors, with 75% of them having never owned an iShare before. This influx of new investors is a significant departure from the traditional Wall Street crowd. Cohen notes that part of the strategy was to educate crypto investors about the benefits of ETPs, and it appears that this effort has been successful. The rise of spot bitcoin ETFs has attracted a new breed of investor, one that is more comfortable with the decentralized nature of crypto and is seeking a more accessible and transparent way to gain exposure to the asset class.
The Power of ETFs
ETFs have been a game-changer in traditional finance markets, providing transparency, access, and accelerated growth. Cohen believes that ETFs and blockchain technology are solving for similar goals, including decentralization and transparency. The use of counterparty clearing and multilateral trading has reduced risk and created huge tailwinds for ETFs. The combination of ETFs and blockchain technology has enabled the creation of spot bitcoin ETFs, which provide a more accessible and transparent way for investors to gain exposure to bitcoin.
A Win for Investors
Cohen sees the rise of spot bitcoin ETFs as a win for investors, as it allows them to effectively marry the ecosystems of traditional finance and decentralized finance (DeFi). This marriage enables investors to access the benefits of both worlds, including the transparency and accessibility of ETFs and the decentralized nature of DeFi. The rise of spot bitcoin ETFs has opened up new investment opportunities for investors, providing a more accessible and transparent way to gain exposure to bitcoin and other crypto assets.
The Future of Crypto
The rise of spot bitcoin ETFs is a significant development in the world of crypto, with the US market playing a crucial role. The country remains the biggest crypto market globally, accounting for nearly 23% of all crypto trading volume. With more than 40 million Americans holding crypto, the potential for growth is vast. As the market continues to evolve, the rise of spot bitcoin ETFs is likely to play a key role in driving adoption and growth.
Regulatory Clarity Needed
While the rise of spot bitcoin ETFs is a positive development, regulatory clarity is still needed to unlock further growth. The lack of clear guidelines from lawmakers on Capitol Hill is hindering the adoption of crypto products by wealth managers and financial advisors. Regulatory clarity will be crucial in providing a framework for the development of spot bitcoin ETFs and other crypto products, enabling the industry to grow and thrive.
Conclusion
The rise of spot bitcoin ETFs has been a game-changer for investors, providing a more accessible and transparent way to gain exposure to bitcoin. The influx of new investors and the growth of the market are a testament to the power of ETFs and blockchain technology. As the market continues to evolve, regulatory clarity will be crucial in unlocking further growth and adoption. The rise of spot bitcoin ETFs is a significant development in the world of crypto, and its impact on investors is likely to be profound.
Article
The government is getting fed up with ransomware payments fueling endless cycle of cyberattacks
As ransomware cyberattacks escalate, government officials say companies are making bad decisions on the 'pay or not pay' dilemma, especially cyber insurers.
With ransomware attacks surging and 2024 on track to be one of the worst years on record, U.S. officials are seeking ways to counter the threat, in some cases, urging a new approach to ransom payments.
#technology #newsonleo #cyberattack #ransomware #government
The Ransomware Dilemma: To Pay or Not to Pay
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, ransomware attacks continue to pose a significant threat to organizations worldwide. As businesses grapple with the decision of whether to pay ransoms, government officials, cybersecurity experts, and industry leaders are divided on the best course of action. This article examines the complex factors influencing these decisions and the broader implications for cybersecurity policy.
The Growing Threat of Ransomware
According to the Office of the director of National Intelligence, by mid-2024, over 2,300 ransomware incidents had been recorded globally, with nearly half targeting U.S. organizations. This trend suggests that 2024 could surpass the 4,506 attacks recorded in 2023, highlighting the urgent need for effective countermeasures.
The Role of Cyber Insurance
Ann Neuberger, U.S. deputy national security adviser for cyber and emerging technologies, has criticized the practice of insurance policies covering ransomware payment reimbursements. She argues that this fuels criminal ecosystems and advocates for stricter cybersecurity requirements as a condition for coverage to discourage ransom payments.
The Dilemma: To Pay or Not to Pay
Organizations face a difficult decision when hit by ransomware:
Factors influencing this decision include:
Case Studies
Lehigh Valley Health Network (LVHN)
National Public Data (NPD)
UnitedHealth Group (Change Healthcare)
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
New SEC reporting requirements mandate disclosures about cyber incidents, ransom payments, and recovery efforts. The upcoming Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical infrastructure Act will extend similar obligations to non-SEC regulated organizations in critical infrastructure sectors.
Evolving Tactics of Cybercriminals
Hackers are adapting to improved cyber defenses by:
Prevention and Best Practices
Experts recommend:
Conclusion
As ransomware attacks continue to evolve and pose significant threats to organizations of all sizes, the debate over whether to pay ransoms remains contentious. While prevention and preparedness are universally acknowledged as the best defenses, businesses must navigate complex decisions when faced with attacks. As regulatory scrutiny increases and cybercriminals adapt their tactics, organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in their approach to cybersecurity.
Article
Gallery: Nikon Small World celebrates 50 years of photomicrography
For 50 years now, camera company Nikon has been highlighting microscopic marvels with the annual Nikon Small World photomicrography competition. Headlining this year’s winners is a groundbreaking view of mouse brain tumor cells.
#newsonleo #technology
The Nikon Small World competition celebrates the art of science, bringing our attention to the minute details we all too often overlook. As such, common subjects include human, animal and plant cells, slime mold, extreme close-ups of insects, and physical processes frozen in time. Entries aren’t just prized on their aesthetics, but also their scientific value.
That’s clear in this year’s overall winner, which was awarded to Dr. Bruno Cisterna and Dr. Eric Vitriol. Their photo shows differentiated mouse brain tumor cells, specifically highlighting components like the actin cytoskeleton, microtubules and nuclei. Importantly, it shows how disruptions to those components can lead to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and ALS.
World's largest carbon fiber composite Neutron rocket is AFP-laid
Rocket Lab's Neutron is the largest composite rocket ever made.
Rocket Lab is making innovative strides in space travel with the Neutron medium payload rocket – namely, it's the largest composite rocket ever made. Initially, hundreds of layers and thousands of square feet of carbon fiber were laid onto a mold by hand, taking a large team several weeks to complete.
#neutron #carbonfiber #rocketlabs #technology #newsonleo
What is Automated Fiber Placement (AFP)?
Automated Fiber Placement (AFP) is a manufacturing process used to create composite structures, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP). It involves the automated laying down of carbon fiber sheets or layers to build the desired structure. AFP is similar to a 3D printer, but instead of printing with plastic or other materials, it uses carbon fibers to create complex shapes and structures.
How does AFP work?
The AFP machine consists of a large, rotating head that is equipped with a high-speed cutting tool. The head is capable of rotating 360 degrees, allowing it to lay down carbon fibers from any direction. The machine is also equipped with a sophisticated control system that ensures precise placement and alignment of the carbon fibers.
Here's a step-by-step overview of the AFP process:
Benefits of AFP
The AFP technology offers several benefits over traditional manufacturing methods, including:
Applications of AFP
The AFP technology has a wide range of applications in the space industry, including:
Comparison to traditional manufacturing methods
The AFP machine offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods, including:
Challenges and limitations
While the AFP technology offers several benefits, there are also challenges and limitations to its use, including:
Overall, the AFP technology is a game-changer for the space industry, offering a faster, more efficient, and more cost-effective way to produce complex composite structures.
Article
The next winner of the AI boom is also one of its biggest problems
Data centers could consume up to 9% of electricity in the U.S. by the end of the decade
Earlier this year, Google (GOOGL) and Microsoft (MSFT) released separate reports showing that neither company is on track to meet its climate goals by the end of the decade. They both blamed the same culprit: data centers.
#ai #technology #energy #electricity #newsonleo
The Future of AI Infrastructure: Data Centers Take Center Stage
As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to evolve, the focus is shifting from chip development to the broader data center industry. Experts predict that data and AI infrastructure will be the key beneficiaries in the next phase of AI expansion, despite growing environmental concerns.
The Rise of Data Centers
Key Players and Strategies
Environmental Concerns and Energy Consumption
Nuclear Power as a Potential Solution
Looking Ahead
As AI continues to advance, the industry faces a dual challenge: meeting the growing demand for computational power while addressing environmental concerns. The shift towards nuclear energy and the development of more efficient data center technologies will likely play crucial roles in shaping the future of AI infrastructure.
The summary is organized into several main sections:
Article
What is a data center and what is the history?
Certainly, I'd be happy to provide an in-depth article on data centers and their history. Given the length you've requested, I'll break this down into several sections for better organization. Let me know if you'd like me to explain or elaborate on any part as we go through this.
Data Centers: A Comprehensive History and Overview
Table of Contents
3.1 The Mainframe Era (1940s-1970s)
3.2 The Microcomputer Revolution (1980s-1990s)
3.3 The Internet Boom (Late 1990s-Early 2000s)
3.4 The cloud computing Era (Mid 2000s-Present)
4.1 Physical infrastructure
4.2 Network infrastructure
4.3 Computing Resources
4.4 Storage Systems
4.5 Power and Cooling
1. Introduction
In our increasingly digital world, data centers have become the backbone of modern information technology infrastructure. These facilities, often operating behind the scenes, play a crucial role in powering the internet, supporting business operations, and enabling the myriad of digital services we rely on daily. From streaming your favorite TV shows to processing financial transactions, data centers are at the heart of it all.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of data centers, delving into their definition, history, components, and significance in today's digital landscape. We'll explore how these technological marvels have evolved over the decades, examine their current state, and look ahead to future trends that will shape their development.
2. What is a Data Center?
At its core, a data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. It generally includes redundant or backup power supplies, redundant data communications connections, environmental controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire suppression), and various security devices.
However, this simple definition barely scratches the surface of what modern data centers represent. Today's data centers are complex ecosystems that integrate cutting-edge hardware, software, and networking technologies to provide a wide range of services:
Data Storage and Management: Data centers store and manage vast amounts of data for organizations and individuals.
Cloud Computing: They provide the infrastructure for cloud services, allowing users to access computing resources on-demand.
Content Delivery: Many data centers serve as content ⇪ networks× (CDNs), ensuring fast and reliable access to web content worldwide.
Big Data Analytics: Data centers power the processing and analysis of enormous datasets, enabling insights and decision-making for businesses and researchers.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: They provide the computational power necessary for training and running sophisticated AI models.
Internet of Things (IoT) Support: Data centers process and store data from millions of connected devices, enabling the IoT ecosystem.
The scale of modern data centers can be staggering. Some of the largest facilities occupy millions of square feet and consume as much electricity as small towns. They represent significant investments for companies and are critical to the functioning of the global digital economy.
3. The Evolution of Data Centers
The history of data centers is intimately tied to the history of computing itself. To understand how we arrived at today's massive, highly efficient facilities, we need to trace the evolution of data processing from the earliest days of electronic computing.
3.1 The Mainframe Era (1940s-1970s)
The concept of a data center has its roots in the early computer rooms of the 1940s and 1950s. These rooms housed massive mainframe computers, which were the first general-purpose electronic computing machines.
ENIAC and Early Mainframes
The ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), completed in 1945, is often considered the first general-purpose electronic computer. It filled a 30-by-50-foot room and weighed 30 tons. The ENIAC and its contemporaries required specially designed rooms with raised floors for cooling, complex wiring systems, and substantial power supplies.
These early mainframes were primarily used by government agencies, universities, and large corporations for scientific calculations, data processing, and business operations. The rooms that housed these machines can be considered the first data centers, though they were a far cry from today's facilities.
IBM and the Mainframe Revolution
In the 1960s and 1970s, IBM dominated the mainframe market with its System/360 and subsequent models. These machines were more reliable and versatile than their predecessors, leading to wider adoption in the business world. As organizations increasingly relied on these computers for critical operations, the concept of the computer room evolved.
Key developments during this era included:
3.2 The Microcomputer Revolution (1980s-1990s)
The 1980s saw a significant shift in computing with the rise of personal computers and client-server architectures. This era marked the beginning of the transition from centralized mainframe computing to more distributed models.
The Rise of Client-Server Computing
As PCs became more powerful and networked computing became feasible, organizations began adopting client-server architectures. This approach distributed computing tasks between centralized servers and individual client computers.
The shift had profound implications for data centers:
The Birth of the Modern Data Center
By the late 1980s and early 1990s, the term "data center" came into common use. These facilities were purpose-built to house computer systems and related equipment. Key features of data centers during this period included:
3.3 The Internet Boom (Late 1990s-Early 2000s)
The rapid growth of the internet in the late 1990s led to an explosion in demand for data center services. This period saw the emergence of large-scale commercial data centers and the beginning of the dotcom boom.
Web Hosting and Colocation
As businesses rushed to establish an online presence, the need for reliable web hosting services grew exponentially. This led to the rise of colocation facilities, where multiple organizations could rent space for their servers in a professionally managed data center.
Key developments during this period included:
The Dotcom bubble and Its Aftermath
The late 1990s saw massive investments in internet-related companies and infrastructure. This led to the rapid construction of numerous data centers to meet anticipated demand. However, when the dotcom bubble burst in 2000-2001, many of these facilities were left underutilized.
Despite the economic setback, this period laid the groundwork for future growth:
3.4 The Cloud Computing Era (Mid 2000s-Present)
The mid-2000s marked the beginning of the cloud computing era, which has dramatically reshaped the data center landscape. This period has seen unprecedented growth in data center capacity and capabilities.
The Rise of Cloud Giants
Companies like Amazon (with AWS), Google, and Microsoft began offering cloud computing services, allowing organizations to rent computing resources on-demand. This led to the construction of massive-scale data centers, often called "hyperscale" facilities.
Key features of this era include:
Edge computing and Micro Data Centers
While hyperscale facilities have dominated headlines, there's also been a trend towards smaller, more distributed data centers. Edge computing, which brings data processing closer to the end-user, has led to the development of micro data centers.
These smaller facilities are crucial for applications requiring low latency, such as autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
4. Anatomy of a Modern Data Center
Modern data centers are complex facilities that integrate various systems to provide reliable, efficient, and secure computing resources. Let's examine the key components that make up a typical data center.
4.1 Physical Infrastructure
The physical infrastructure of a data center forms the foundation upon which all other systems are built. Key elements include:
4.2 network Infrastructure
The network is the lifeblood of a data center, connecting servers, storage systems, and external users. Key components include:
4.3 Computing Resources
The core purpose of a data center is to provide computing power. This is typically delivered through:
4.4 Storage Systems
Data storage is a critical function of any data center. Modern facilities use a variety of storage technologies:
4.5 Power and Cooling
Ensuring a reliable power supply and maintaining optimal environmental conditions are crucial for data center operations:
Edge Data Centers: Smaller facilities located closer to end-users to reduce latency for specific applications.
Cloud Data Centers: These power public cloud services, offering computing resources on-demand.
Micro Data Centers: Small, self-contained units that can be deployed quickly in various locations.
Mobile Data Centers: Containerized data centers that can be easily transported to different locations.
Each type of data center has its own advantages and is suited to different use cases. The choice depends on factors such as the organization's size, IT needs, budget, and geographical requirements.
6. The Role of Data Centers in Modern Society
Data centers have become integral to nearly every aspect of modern life. Their importance extends far beyond the tech industry, touching virtually every sector of the economy and society. Here are some key areas where data centers play a crucial role:
Business Operations
In the business world, data centers are the engines that power day-to-day operations. They host critical applications, store valuable data, and enable communication and collaboration. From small startups to multinational corporations, businesses rely on data centers for:
E-commerce
The explosive growth of online shopping has been made possible by robust data center infrastructure. Data centers support e-commerce by:
Financial services
The financial sector is heavily dependent on data centers for its operations. They are crucial for:
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, data centers play a vital role in improving patient care and advancing medical research:
Entertainment and Media
The digital transformation of the entertainment industry has been powered by data centers:
Government and Public Services
governments at all levels rely on data centers to provide services to citizens:
Education
In the education sector, data centers support:
Smart Cities and IoT
As cities become "smarter" and more connected, data centers play a crucial role in:
The Internet of Things (IoT) relies heavily on data centers to process and store the vast amounts of data generated by connected devices. From smart homes to industrial IoT applications, data centers are the backbone that makes these technologies possible.
7. Environmental Impact and sustainability
As data centers have grown in size and number, their environmental impact has become a significant concern. The industry has responded with various initiatives to improve sustainability:
Energy Consumption
Data centers are major energy consumers, accounting for about 1% of global electricity use. Efforts to reduce this impact include:
Water Usage
Cooling systems in data centers can consume significant amounts of water. Strategies to reduce water usage include:
E-waste
The frequent upgrading of IT equipment in data centers generates substantial electronic waste. Responsible practices include:
Carbon Footprint
Beyond energy consumption, data centers contribute to carbon emissions through construction, manufacturing of equipment, and transportation. Efforts to reduce this impact include:
8. Security and Data Protection
As data centers store and process increasingly valuable and sensitive information, security has become a top priority. Modern data centers employ multiple layers of security:
Physical Security
Network Security
Data Protection
Cybersecurity
9. Future Trends in Data Center technology
The data center industry continues to evolve rapidly. Some key trends shaping the future of data centers include:
Edge computing
As IoT devices proliferate and applications require lower latency, edge computing is becoming increasingly important. This involves deploying smaller data centers closer to end-users, complementing larger centralized facilities.
Artificial intelligence and Machine learning
AI is being incorporated into data center operations to optimize performance, predict failures, and enhance security. At the same time, data centers are being designed to support the intensive computational requirements of AI and ML workloads.
Quantum computing
While still in its early stages, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize certain types of data processing. Some data centers are already preparing to incorporate quantum computers alongside classical systems.
Sustainable Design
Future data centers will likely place even greater emphasis on sustainability, with designs that minimize environmental impact and potentially even benefit local ecosystems.
Automation and Lights-Out Operations
Increased automation and remote management capabilities are enabling "lights-out" data centers that can operate with minimal on-site staff.
Liquid Cooling
As computing densities increase, more data centers are likely to adopt liquid cooling technologies, which can handle higher heat loads more efficiently than air cooling.
Software-Defined Everything
The trend towards software-defined networking, storage, and data centers is likely to continue, offering greater flexibility and efficiency in resource management.
10. Conclusion
Data centers have come a long way from the early days of mainframe computers. Today, they are the backbone of our digital world, powering everything from social media to scientific research. As we've seen, the evolution of data centers reflects the broader trends in computing and society's increasing reliance on digital technology.
Looking ahead, data centers will continue to play a crucial role in shaping our digital future. The challenges they face – from energy efficiency to security – are significant, but so too are the opportunities for innovation. As edge computing, AI, and new cooling technologies come to the fore, we can expect data centers to become even more sophisticated and integral to our daily lives.
The history of data centers is, in many ways, the history of our digital age. As we look to the future, it's clear that these facilities will continue to evolve, adapt, and underpin the technologies that drive our world forward. Understanding data centers – their past, present, and future – is key to comprehending the infrastructure that makes our digital lives possible.
Amazon has made a big change to how it ships packages
The inflatable plastic pillows are officially a thing of the past, replaced by paper-based padding that can be recycled
#amazon #newsonleo #technology
Amazon's Commitment to Reducing Plastic Packaging
In recent years, Amazon has made a commitment to reduce its plastic packaging and increase its use of sustainable materials. The company has set ambitious goals to reduce its plastic use and has taken steps to achieve these goals.
In 2020, Amazon announced that it would eliminate plastic air pillows from its global network of fulfillment centers. The company had already replaced 95% of its air pillows across North America with paper filler, and had eliminated plastic air pillows in Australia and Europe.
In June 2022, Amazon announced that it would work "toward full removal" of plastic air pillows from North America by the end of the year. The company stated that it had already replaced 95% of its air pillows across the continent with paper filler.
Challenges in Reducing Plastic Packaging
Despite Amazon's efforts to reduce plastic packaging, the company still faces significant challenges in doing so. One of the main challenges is the scale of its operations. Amazon operates in 21 countries and ships to many more, which means that it uses a vast amount of packaging materials.
Amazon also faces significant costs associated with reducing its plastic use. The company has stated that it will need to invest in new equipment and processes to replace its current plastic packaging with sustainable alternatives.
Additionally, Amazon's packaging materials are often not recyclable, which makes it difficult for the company to recycle its waste. The company's plastic film, for example, is not recyclable and is often sent to landfills and incinerators.
Oceana's Criticism of Amazon's Plastic Use
Oceana, a nonprofit ocean advocacy group, has been critical of Amazon's plastic use. The group has estimated that Amazon generates 208 million pounds of plastic packaging trash in the United States each year, which is about 10% more than the previous year.
Oceana has also criticized Amazon's use of plastic film, which is not recyclable and is often sent to landfills and incinerators. The group has called on Amazon to strengthen its plastic-reduction promises and to scale up its use of reusable alternatives.
Amazon's Response to Criticism
Amazon has responded to criticism of its plastic use by pointing to its efforts to reduce its plastic packaging. The company has stated that it is committed to reducing its plastic use and is working to develop new sustainable packaging materials.
However, Amazon's response has been criticized by Oceana and other environmental groups. The company's efforts to reduce its plastic packaging have been seen as too slow and too little, and have not gone far enough to address the scale and scope of its plastic use.
What's Next for Amazon's Plastic Reduction Efforts?
In the coming months, Amazon is expected to take further steps to reduce its plastic packaging. The company has hinted at phasing out padded bags containing plastics, which are a common type of plastic packaging used by the company.
Amazon has also stated that it is working to reduce its use of single-use plastic packaging in favor of household-recyclable alternatives. However, it is unclear what this means in practice, and whether the company will be able to achieve its goals.
Overall, Amazon's efforts to reduce plastic packaging are significant, but the company still faces significant challenges in doing so. It remains to be seen whether Amazon will be able to achieve its goals and reduce its plastic packaging to the extent that it needs to.
Article
Plug-in hybrids aren't quite working as a transition to electric cars
Consumers aren't too happy with their plug-in hybrids, despite the fact they're billed as a bridge between gas-powered cars and electric vehicles
Plug-in hybrids are proving to not be the transitional bridge between gas-powered cars and electric vehicles many folks were hoping for. That’s a shame because when used properly, PHEVs are absolutely fantastic. A study from JD Power is shedding new light on how and why customers are unsatisfied with their plug-in hybrids.
#nesonleo #evs #plugins #automotive
Why Plug-in Hybrids are Declining in Sales
Why Consumers Are Not Adopting Plug-in Hybrids
What Manufacturers Need to Do
Conclusion
The decline of plug-in hybrids as a transition to electric cars is a clear indication that the industry needs to rethink its strategy. While PHEVs have their merits, they are not as favorable as battery-electric vehicles in terms of satisfaction and adoption. As the market continues to evolve, it's essential for manufacturers to prioritize education and marketing, as well as to continue improving the ownership experience of electric vehicles.
What Can Consumers Do
Article
A detailed overview of the history of plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs).
Early Experimentations (1900s-1920s)
The first electric vehicles were developed in the early 20th century, with many pioneers experimenting with electric motors and batteries. In 1901, Robert Anderson, a Scottish inventor, created a crude electric carriage that could travel at a speed of about 7 mph (11 km/h). In the early 1900s, electric vehicles became popular in the United States, particularly in urban areas, due to their quiet operation and zero emissions.
However, the early electric vehicles had several limitations. They were often heavy, had limited range, and required frequent recharging. The batteries were also expensive and not very efficient, which made electric vehicles less competitive with gasoline-powered vehicles.
Post-WWII (1940s-1960s)
Following World ⇪ II×, the United States saw a resurgence of interest in electric vehicles, particularly in the automotive industry. In 1948, General Motors (GM) introduced the first production electric vehicle, the GM Electric Dream, which was a modified version of the Chevrolet Styleline sedan. The vehicle had a range of about 80 miles (130 km) on a single charge.
In the 1950s and 1960s, GM and other automakers continued to develop electric vehicles, but they were often limited to short-range capabilities and high costs. The vehicles were also often marketed as "electric taxis" or "electric delivery vans" rather than as personal vehicles.
1970s-1980s
The 1970s saw a renewed focus on alternative energy sources, including electric vehicles, due to the oil crisis. In 1979, the U.S. government set a goal of having 1 million electric vehicles on the road by 1985. However, the industry struggled to meet this goal, and the number of electric vehicles on the road remained relatively small.
In the 1980s, companies like General Motors and Chrysler produced electric vehicles with rechargeable batteries, but they were often expensive and had limited range. The vehicles were also often criticized for their performance and handling.
1990s-2000s
The modern electric vehicle era began in the 1990s, with the introduction of the Toyota RAV4 EV and the General Motors EV1. The Toyota RAV4 EV, introduced in 1997, was a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) that had a range of about 100 miles (160 km) on a single charge. The General Motors EV1, introduced in 1996, was a battery electric vehicle that could travel up to 80 miles (130 km) on a single charge.
The EV1 was a significant step forward for electric vehicles, but it was not without controversy. GM leased the EV1 to customers, but it eventually recalled the vehicle due to concerns about its performance and range.
2000s-2010s
In the 2000s, the electric vehicle industry began to gain momentum, with the introduction of new models and technologies. In 2008, the U.S. government set a goal of having 500,000 electric vehicles on the road by 2015.
The Nissan Leaf, introduced in 2010, was one of the first mass-produced electric vehicles with a range of over 100 miles. The Leaf was a significant success, with over 500,000 units sold worldwide by 2015.
In 2013, Tesla Motors introduced the Model S, a luxury electric sedan with a range of over 300 miles. The Model S was a game-changer for the electric vehicle industry, demonstrating that electric vehicles could be both practical and desirable.
Key Milestones
Here are some key milestones in the history of plug-in electric vehicles:
SpaceX Starship Ocean Landing is Promising for a Tower Catch Attempt
Elon Musk said the SpaceX starship achieved a precise, soft landing in the ocean, paving the way for return to launch site and being caught by the tower arms
Elon Musk said the SpaceX starship achieved a precise, soft landing in the ocean, paving the way for return to launch site and being caught by the tower arms, like the booster.
#space #spacex #rocket #technology #newsonleo
Full and rapid reusability improves the cost of access to orbit and beyond by over 10,000%. The cost per kilogram to space will go from $1000 per kilogram to $10 per kilogram. The amount of material launched to space will increase by thousands of times.
It is the fundamental technology breakthrough needed to make life multiplanetary and for us to become a true spacefaring civilization.
SpaceX Starship made the flip maneuver and landing burn on its fifth flight test. Vehicle improvements ensured flaps were protected from high heating, resulting in a controlled entry and high accuracy splashdown at the targeted area in the Indian Ocean.
SpaceX is working towards a November 10-15, 2024 launch date for flight 6.
Article
Meta, Microsoft and OpenAI Were Getting Nvidia Chips Sooner But xAI Completed Faster
xAI completed its 100,000 Nvidia H100 AI data center before Meta and OpenAI despite the Meta and OpenAI getting chips delivered first. xAi completed the main
#technology #nvidia #openai #microsoft #meta #xai
xAI completed its 100,000 Nvidia H100 AI data center before Meta and OpenAI despite the Meta and OpenAI getting chips delivered first. xAi completed the main chip installation and build in 19 days and the overall project in 122 days. Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang says this scale of build can take a year for many companies. The time xAI has saved has already allowed it to catch up for Grok 3 to be trained and ready by the time GPT5 is release and before Llama 4 is released.
The larger 200,000 H100/H200 xAI system should be ready in December or January and would enable a faster training for Grok 4 than GPT6.
If xAI gets even faster then the 300K B200 Chip system could be 6-18 months ahead of rivals and this would be used for Grok 5.
Article
China speed is something to watch out for with #Tesla.
This is especially true for the Metapacks.
SpaceX Starlink Upgrading to Gigabit Per Second Speeds
SpaceX has applied to the FCC to make changes to Starlink to increase communication speed from 200-300 Mbps to about 1 gigabit per second or more.
SpaceX has applied to the FCC to make changes to Starlink to increase communication speed from 200-300 Mbps to about 1 gigabit per second or more.
#spacex #internet #fcc #newsonleo
SpaceX will get the Starship flying and will launch new Starlink satellites that are about three times bigger than the Starlink version 2 mini.
SpaceX wants to lower the altitudes of satellites by about 10% (530 to about 480 km). SpaceX wants to get the satellites even closer (to less than 400 km.)
Article
22 Bit Military Grade Decryption Using DWave Systems Quantum Computers
A paper by Chinese researchers, “Quantum Annealing Public Key Cryptographic Attack Algorithm Based on D-Wave Advantage”, described how D-Wave’s machines can optimize problem-solving in ways that made it possible to decode tiny version of a military grade public key cryptography.
#newsonleo #quantum #dwave #military #technology
Wang Chao from Shanghai University, used a D-Wave machine to attack Substitution-Permutation Network (SPN) structured algorithms that perform a series of mathematical operations to encrypt info. SPN techniques are at the heart of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) – one of the most widely used encryption standards.
The techniques used were applied to a 22-bit key but usually 2048 to 4096 bit keys are used. Breaking the longer keys is many billion trillions of times more difficult.
Article
Google granted request to pause 'dangerous remedies' to Play store in blow to Epic Games
In the Epic Games lawsuit, a jury last year found that Google illegally monopolized how consumers download apps on Android devices and how they pay for in-app transactions.
Google said Friday that a federal judge in California granted its request to pause his order directing the Alphabet unit to overhaul its Android app store Play by Nov. 1 to give consumers more choice over how they download software.
#bigtech #newsonleo #epicgames #google #technology
San Francisco-based US District Judge James Donato made the decision on Friday as part of an antitrust lawsuit against Google brought by “Fortnite” maker Epic Games. Google argued that Donato’s Oct. 7 injunction would harm the company and introduce “serious safety, security and privacy risks into the Android ecosystem.”
Donato delayed the injunction to allow the San Francisco-based 9th US Circuit Court of Appeals to consider Google’s separate request to pause the judge’s order. Donato denied Google’s separate request to pause the order for the duration of its broader appeal in the case.
Article
Meta fires staffers who misused $25 meal credits to buy wine glasses, acne pads: report
Meta has reportedly fired Los Angeles staffers for abusing a $25 meal credit perk to stock up on household supplies like wine glasses, acne pads and laundry detergent.
Facebook and Instagram parent Meta has reportedly fired about two dozen staffers in Los Angeles for abusing a $25 daily meal perk to stock up on household supplies like wine glasses, acne pads and laundry detergent.
#newsonleo #meta #technology
The fired workers were found to have misused the delivery credit – which workers can use on services like GrubHub or UberEats if they stay at the office late or are based in offices that lack a kitchen – over a long period of time, the Financial Times reported, citing a person familiar with the matter.
The firings were part of a broader restructuring at Mark Zuckerberg’s social media giant that sparked job cuts across multiple business segments on Tuesday, including its Instagram, WhatsApp and Reality Labs teams.
Employees axed over meal program shenanigans were reportedly informed last week.
Some Meta staffers grumbled about the clampdown on Blind, an app verifies that its users work at the companies they claim but allows them to remain anonymous.
Article
Hacked robot vacuums hurl racial slurs at shocked owners, who react with 'fear, disgust'
These vacuums had no filter.
U.S. homeowners were shocked when their Chinese-made robot vacuums were hijacked and rewired to bombard them with racial slurs.
#technology #hack #vacuum #robots #newsonleo
The racist hack attack affected Ecovacs Deebot X2s — a brand that’s manufactured in China — across several American cities, per ABC News Australia.
Minnesota lawyer Daniel Swenson said he was watching TV in May when his robo-vacuum started to emit sounds that initially “sounded like a broken-up radio signal or something,” he told the outlet.
Article
Elon Musk responds to calls for Tesla to buy Rivian
Tesla CEO Elon Musk responded to calls for his EV maker to buy competing startup Rivian, in what would be a monumental merger between two industry-leading companies.
Musk was in Philadelphia on Friday night for an event ahead of the U.S. presidential election as he was attempting to help former U.S. President Donald Trump swing Pennsylvania. The stop is one of several Musk has planned in the Keystone State.
#newsonleo #tesla #rivian
The event, while more focused on politics, was also met with questions about Tesla, Musk’s electric vehicle company.
One attendee who was there to ask Musk a question pushed the CEO on why Tesla had not sought to buy Rivian, a competing automaker that has a solid consumer base, strong products, and an innovative CEO running the company but a shaky financial platform.
Musk said:
Article
Starlink services bound for South Korea by 2025
Starlink services might be bound for South Korea by early 2025. Starlink’s availability in South Korea will depend on the local government’s moves regarding regulatory updates that will ensure a stable connection to SpaceX’s internet services without interfering with the providers already operating in the country.
On Wednesday, October 16, 2024, South Korea’s Ministry of Science and ICT reportedly issued a 60-day public notice informing the public about amendments to technical standards. The changes aim to prevent frequency interference, ensuring smooth service for internet users.
#nesonleo #starlink #spacex #southkorea
BYD Shark 6 falls short on payload & towing capacity in Australia
The BYD Shark 6 falls short on payload and towing, compared to other Australian competitors like the Ford Ranger and Toyota HiLux. However, the Chinese automaker doesn’t believe it will affect sales in Australia.
#newsonleo #technology #byd #shark #australia
BYD’s plug-in ute falls short of the segment standard 3500 kg braked towing capacity, reported Drive. Australian car sales in 2022 revealed that the average ute had a payload of 900+kg. Pickup trucks from the United States usually claimed higher towing and payload capacity. The BYD Shark features a payload capacity of 790 kg and a towing capacity of 2,500 kg.
“We’re going to have a range of 800 km (combined), 100 km on EV, you can see the design elements, you can see the payload is 790 kg. Yes, (3500 kg braked towing capacity) that’s a number, but our number’s 2500 kg, and we’re entirely comfortable with that. We think that will meet the majority of Aussie motorist’s needs and we’re super happy with that,” David Smiterhman, the CEO of EVDirect—BYD’s Australian importer.
Article
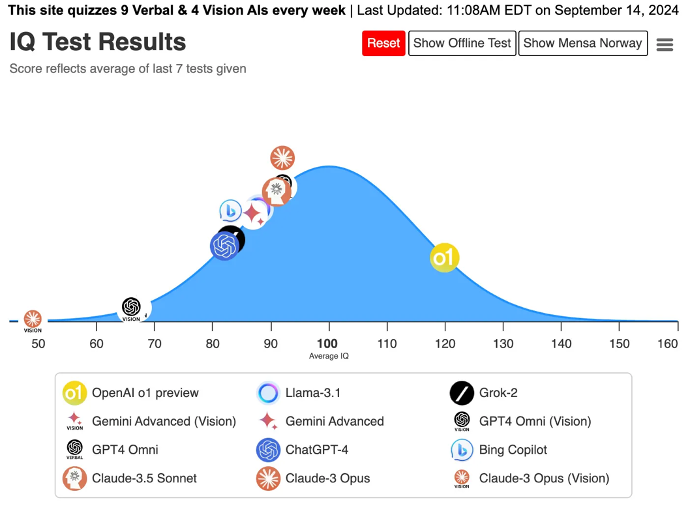
#ai #llm #technology #iq
According to new estimates from Kelley Blue Book, electric vehicle (EV) sales in the U.S. grew by 11% year over year in the third quarter and reached record highs for both volume and market share. According to the latest counts, an estimated 346,3091 EVs were sold in Q3 2024, a 5% increase from Q2. The EV share of sales in Q3 hit 8.9%, the highest level recorded and an increase from 7.8% in Q3 2023.
#newsonleo #coxautomotive #evs #unitedstates
Lott's analysis of Anthropic's Claude model progression is enlightening:
Claude-2 (July 2023, 4 months later): ~82 IQ
Claude-3 (March 2024, 8 months later): ~101 IQ
Based on this trend, Lott projects:
Claude-4 (expected in 12-16 months): ~120 IQ
Claude-5 (16-32 months after Claude-4): ~140 IQ
Claude-6 (20-64 months after Claude-5): Smarter than everyone
"I now think that timeline is holding up, and that OpenAI has always been about 6 months ahead of Anthropic/Claude, behind the scenes. If so, then we should start seeing AIs breaking 140 IQ in 2026."
China has not cracked encryption, at least not yet
Popular YouTuber Mental Outlaw explains why the recent quantum computing breakthrough by researchers in China does not currently threaten encryption standards.
#china #encryption #technology
According to the research paper, the quantum computer used in the experiment factorized the integer 2,269,753. Mental Outlaw noted that this surpassed records set by other quantum computers but failed to surpass the record set by classical computers.
The YouTuber clarified that the quantum computer only broke a 22-bit key. For context, the record set by classical computers was cracking an 892-bit key, which required a whopping 2,700 physical core years to break.
For perspective, early RSA encryption used 512-bit keys, with modern standards adopted around 2015 ranging from 2048 to 4096 bits. Moreover, quantum computers cannot be combined to achieve greater processing power and overcome this limitation.
Quantum bits also require near-absolute zero temperatures to remain stable enough to function as viable information processors, which requires significant cooling infrastructure.
Another issue highlighted in the YouTube video is that most of the quantum bits in a quantum computing system are dedicated to error correction. This means the vast majority of the potential processing power in a quantum computer is used to correct outputs rather than solving the main problem fed to the computer.
The popular YouTuber concluded that quantum computers do not yet pose a significant threat to modern encryption standards but warned that this may change due to faster-than-expected technological progress.
Article
#technology raises the standard of living because it is inherently deflationary. This means prices come down over time. Just think of what ChatGPT did for the cost of garnering information. That is only going to expand as the cost for compute comes down.
23andMe faces an uncertain future — so does your genetic data
Financial and security chaos at the once-pioneering genetic testing firm has intensified concerns about user data. Here's how to take action.
#23andme #technology #genetic #data #newsonleo
23andMe's Data Privacy Dilemma: Navigating Uncertain Waters
In the rapidly evolving landscape of personal genomics, few companies have garnered as much attention - or controversy - as 23andMe. Once hailed as a pioneer in direct-to-consumer genetic testing, the company nOW finds itself at a critical juncture, facing financial struggles, data breaches, and mounting concerns over the privacy and security of its vast genetic database. This article delves deep into the current state of 23andMe, exploring the challenges it faces and the potential implications for millions of customers who have entrusted the company with their most personal biological information.
The Rise and Fall of a Genetic Testing Giant
From Pioneering Start-up to Public Company
23andMe burst onto the scene in 2006 with a revolutionary promise: to unlock the secrets of your DNA through a simple saliva test. Co-founded by Anne Wojcicki, the company quickly captured the public's imagination, offering insights into ancestry, traits, and potential health risks. As one of the first companies to make genetic testing accessible to the masses, 23andMe rode a wave of enthusiasm for personalized medicine and consumer genomics.
The company's growth was meteoric. By 2018, it had attracted millions of customers and secured partnerships with pharmaceutical giants like GlaxoSmithKline. The crowning achievement came in June 2021 when 23andMe went public through a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC) merger, valuing the company at a staggering $6 billion.
The Steep Decline
However, the euphoria surrounding 23andMe's public debut was short-lived. In the years since going public, the company has experienced a dramatic reversal of fortunes. Several factors have contributed to this decline:
Limited Repeat Business: Unlike many successful tech companies that rely on recurring revenue, 23andMe's core product - the DNA test kit - is typically a one-time purchase. This has made it challenging for the company to sustain growth.
Subscription Model Struggles: Attempts to pivot towards a subscription-based model, offering ongoing health insights and reports, have not gained significant traction among consumers.
Regulatory Hurdles: The company has faced ongoing scrutiny from regulators, particularly the FDA, regarding health-related claims and the accuracy of its tests.
These factors have culminated in a stark financial reality: 23andMe has yet to turn a profit since going public. The company's stock price has plummeted, with its market value dropping by over 99% from its peak. This financial decline has forced the company to reevaluate its strategies and explore new avenues for monetization.
The Data Breach: A Crisis of Trust
In a devastating blow to both its reputation and financial stability, 23andMe suffered a major data breach in 2023. The scale and nature of this breach sent shockwaves through the genetic testing industry and raised alarm bells for privacy advocates worldwide.
The Anatomy of the Breach
The breach, which occurred over several months in 2023, resulted in hackers gaining access to the sensitive genetic information of nearly 7 million 23andMe users. The stolen data included:
This wasn't just a typical data breach involving names and email addresses; it was a theft of the most personal biological information of millions of individuals. The implications of such data falling into the wrong hands are far-reaching and potentially life-altering for those affected.
The Fallout
The immediate consequences of the breach were severe:
Legal Repercussions: 23andMe faced a barrage of lawsuits from affected customers. In September 2023, the company agreed to pay $30 million to settle these legal claims.
Reputational Damage: The breach severely undermined public trust in 23andMe's ability to safeguard sensitive genetic information.
Regulatory Scrutiny: The incident drew increased attention from regulators and lawmakers, potentially paving the way for stricter oversight of the genetic testing industry.
Financial Impact: The costs associated with the breach, including the settlement and potential loss of customers, further strained the company's already precarious financial position.
Lessons and Implications
The 23andMe data breach serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in storing large amounts of sensitive genetic data. It raises critical questions about:
Moreover, the breach highlights the unique risks associated with genetic information. Unlike a credit card number or password, a person's genetic code cannot be changed. Once compromised, it remains vulnerable to potential misuse for life.
The Privatization Dilemma
In the wake of the data breach and amid ongoing financial struggles, 23andMe finds itself at a crossroads. The company's leadership, particularly CEO Anne Wojcicki, has begun exploring options that could fundamentally alter the future of the company and, by extension, the fate of millions of genetic profiles in its possession.
The Takeover Speculation
In September 2023, shortly after announcing the settlement related to the data breach, Wojcicki made a startling statement. She revealed that the company was "considering third-party takeover proposals." This announcement sent ripples through the tech and biotech industries, raising questions about who might be interested in acquiring 23andMe and, more importantly, what they might do with its vast trove of genetic data.
The Quick Reversal
Almost as quickly as the takeover speculation began, Wojcicki attempted to quell it. She walked back her initial statement, clarifying that her intention was to take the company private rather than sell it to a third party. However, the damage was already done. The mere suggestion of a potential sale had ignited a firestorm of concern among privacy advocates, customers, and industry observers.
Board Exodus
In a dramatic turn of events following Wojcicki's statements, aLL of 23andMe's independent board members resigned with immediate effect. This mass exodus raised eyebrows and fueled further speculation about the company's future direction and governance.
The resignation of independent board members is particularly significant because these individuals typically serve as a check on management and represent the interests of shareholders. Their departure en masse suggests deep disagreements about the company's path forward or concerns about its governance.
The Privatization Plan
Wojcicki's revised plan to take 23andMe private presents its own set of challenges and implications:
Financing: Given the company's financial struggles, securing the necessary funding to buy out public shareholders could be difficult.
Valuation: Determining a fair price for the company in its current state is likely to be contentious.
Regulatory Scrutiny: Any attempt to take the company private would likely face intense scrutiny from regulators, given the sensitive nature of the data involved.
Customer Trust: The process of going private might further erode customer confidence, particularly if it's perceived as a move to avoid public accountability.
The Data Monetization Dilemma
Amidst these upheavals, a key question has emerged: How does 23andMe plan to achieve profitability? Wojcicki has reportedly indicated to investors that the company will shift its focus away from costly drug development programs. Instead, 23andMe aims to concentrate on marketing its vast database of customer genetic information to pharmaceutical companies and researchers.
This pivot towards data monetization raises significant ethical and privacy concerns:
The tension between the potential scientific and medical advancements that could come from analyzing this genetic goldmine and the privacy rights of individuals is at the heart of the debate surrounding 23andMe's future.
The Regulatory Vacuum
One of the most critical aspects of the 23andMe situation is the regulatory environment - or lack thereof - in which the company operates. Unlike many health-related companies, 23andMe is not bound by the strict regulations of HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), which sets standards for protecting sensitive patient health information.
The HIPAA Exception
23andMe's exemption from HIPAA regulations may come as a surprise to many customers who assume their genetic information is protected under the same laws that govern medical records. However, as a direct-to-consumer genetic testing company, 23andMe falls into a regulatory gray area.
The company argues that this exemption allows for a "more appropriate and transparent model for the data we handle, rather than the HIPAA model employed by the traditional healthcare industry." However, critics contend that this lack of regulatory oversight leaves customers vulnerable.
The Patchwork of State Laws
In the absence of comprehensive federal regulation, the protection of genetic data is largely governed by a patchwork of state laws. This inconsistent regulatory landscape creates challenges for both companies and consumers:
The Need for Federal Action
The current situation highlights the urgent need for comprehensive federal legislation governing genetic privacy. Such legislation could:
Until such legislation is enacted, companies like 23andMe will continue to operate in a regulatory environment that many consider inadequate given the sensitive nature of the data they handle.
The Data Ownership Conundrum
At the heart of the 23andMe controversy lies a fundamental question: Who owns your genetic data? This question becomes particularly pertinent in the context of potential company sales or restructuring.
The Fine Print
23andMe's privacy policy, which many customers may not have read closely, contains some concerning provisions:
These clauses effectively mean that in the event of a sale or major restructuring, customer genetic data could be transferred to new ownership with potentially different priorities or ethical standards.
The Research Dilemma
A significant portion of 23andMe's value proposition to both customers and potential investors lies in its research capabilities. The company reports that approximately 80% of its customers - roughly 12 million people - have consented to participate in its research program.
This high participation rate is a double-edged sword:
The Irreversibility of Genetic Information
Unlike other forms of personal data, genetic information is uniquely permanent and shared. Your DNA not only reveals information about you but also about your biological relatives. This creates complex ethical considerations:
These questions remain largely unresolved in both ethical and legal frameworks.
The Law Enforcement Quandary
Another contentious issue surrounding genetic databases like 23andMe's is their potential use by law enforcement agencies. While 23andMe has thus far resisted all U.S. law enforcement requests for genetic data, the company's policies could change under new ownership or different management.
Current Stance
23andMe's current policy states that it will not share users' information with law enforcement without a warrant. The company maintains a transparency report detailing the number and nature of law enforcement requests it receives.
The Golden State Killer Case
The use of genetic databases for criminal investigations gained widespread attention with the arrest of the Golden State Killer in 2018. While that case involved a different genetic database (GEDmatch), it highlighted the potential for law enforcement to use these resources in ways that many customers never anticipated.
Privacy Advocates' Concerns
Organizations like the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) have expressed strong concerns about the potential for genetic databases to be used for indiscriminate searches by law enforcement. They argue that such use could violate Fourth Amendment protections against unreasonable searches and could lead to false accusations based on partial genetic matches.
The Slippery Slope
Critics worry that even if 23andMe maintains its current stance, the mere existence of large genetic databases creates pressure for their use in criminal investigations. This could lead to:
The potential for mission creep in the use of genetic data by law enforcement remains a significant concern for privacy advocates and ethicists.
Protecting Your Genetic Privacy
Given the uncertainties surrounding 23andMe's future and the broader issues of genetic data privacy, many customers and privacy advocates are calling for proactive measures to protect personal genetic information.
Deleting Your Account
One of the most straightforward steps 23andMe customers can take is to request the deletion of their account and data. The process involves:
However, it's crucial to note that this process comes with significant caveats:
The Research Data Conundrum
For the approximately 12 million customers who consented to participate in 23andMe's research program, the situation is even more complex. While customers can revoke their consent for future research, there's no way to delete information that has already been shared or used in research studies.
This highlights the importance of carefully considering consent for research participation before submitting genetic samples to companies like 23andMe.
Broader Privacy Measures
Beyond account deletion, individuals concerned about genetic privacy should consider:
Family discussions: Have conversations with family members about genetic privacy, as their decisions can impact your genetic privacy and vice versa.
Stay informed: Keep up with developments in genetic privacy laws and company policies.
Consider alternatives: For those interested in genetic testing for health reasons, consider discussing options with healthcare providers that may offer greater privacy protections.
Advocate for stronger protections: support efforts to create comprehensive genetic privacy laws at both the state and federal levels.
The Future of Personal Genomics
The challenges facing 23andMe are not unique to the company but reflect broader issues in the personal genomics industry. As we look to the future, several key trends and questions emerge:
Balancing Innovation and Privacy
The promise of personalized medicine based on genetic information remains compelling. However, realizing this potential while adequately protecting individual privacy will require careful balancing:
The Role of Big Tech
As traditional tech giants like Google and Amazon increasingly enter the healthcare space, questions arise about their potential interest in genetic data:
Decentralized and Blockchain-Based Solutions
Some technologists and privacy advocates are exploring decentralized models for genetic data storage and sharing:
The Global Perspective
As genetic testing becomes more widespread globally, international considerations come into play:
Conclusion: A Pivotal Moment for Genetic Privacy
The current situation at 23andMe represents a pivotal moment not just for the company, but for the entire field of personal genomics and the broader conversation about data privacy in the digital age. The challenges facing 23andMe encapsulate many of the most pressing issues at the intersection of technology, healthcare, and privacy:
The Value and Vulnerability of Genetic Data
The 23andMe saga underscores both the immense potential and the significant risks associated with large-scale genetic data collection. On one hand, the company's vast database offers unprecedented opportunities for medical research and personalized healthcare. The insights gleaned from analyzing millions of genetic profiles could lead to breakthroughs in disease prevention, treatment, and our understanding of human biology.
On the other hand, the recent data breach and the company's financial struggles highlight the vulnerabilities inherent in centralizing such sensitive information. Genetic data is uniquely personal and immutable – unlike a password or credit card number, it cannot be changed if compromised. The potential for misuse, whether by malicious actors, overzealous law enforcement, or profit-driven corporations, is a serious concern that cannot be overlooked.
The Need for Robust Regulation
The regulatory vacuum in which companies like 23andMe operate is becoming increasingly untenable. The patchwork of state laws and the inapplicability of HIPAA to direct-to-consumer genetic testing companies leave consumers vulnerable and companies without clear guidelines. This situation calls for comprehensive federal legislation that addresses:
Such legislation would not only protect consumers but also provide a stable regulatory environment in which ethical companies can innovate and thrive.
The Ethics of Data Monetization
23andMe's pivot towards monetizing its genetic database raises profound ethical questions. While the company argues that this approach could lead to valuable medical discoveries, it also turns customers' most personal information into a commodity. This shift challenges us to consider:
The Future of Personal Genomics
Despite the current challenges, the field of personal genomics is likely to continue growing and evolving. The insights offered by genetic testing remain compelling for many individuals, and the potential for medical advancements is too significant to ignore. However, the 23andMe situation may serve as a catalyst for changes in how the industry operates:
Decentralized models: We may see a shift towards more decentralized approaches to genetic data storage and analysis, giving individuals greater control over their information.
Transparent research partnerships: Companies might adopt more transparent models for research partnerships, clearly communicating how data will be used and sharing benefits with participants.
Privacy-centric innovation: New technologies and methodologies that allow for genetic analysis while preserving privacy could emerge as a focus of innovation in the field.
Integration with healthcare systems: Closer integration of personal genomics with traditional healthcare systems could provide a framework for more regulated and secure handling of genetic information.
A Call to Action
The challenges facing 23andMe serve as a wake-up call for consumers, regulators, and the tech industry at large. They highlight the urgent need for:
Individual awareness: Consumers must educate themselves about the implications of sharing their genetic data and make informed decisions about participation in genetic testing services.
Corporate responsibility: Companies handling genetic information must prioritize ethics and privacy, even at the expense of short-term profits.
Regulatory action: Policymakers need to act swiftly to create comprehensive frameworks for genetic data protection.
Ethical innovation: The tech and biotech industries must focus on developing technologies and business models that respect individual privacy while advancing scientific knowledge.
Public discourse: A broader societal conversation about the value, risks, and ethical implications of genetic data collection and analysis is crucial.
As we stand at this crossroads, the decisions made by 23andMe, regulators, and consumers will have far-reaching implications. They will shape not only the future of personal genomics but also set precedents for how we handle sensitive personal data in an increasingly data-driven world.
The story of 23andMe is more than just a cautionary tale about a company's financial struggles or a data breach. It is a microcosm of the challenges we face as we navigate the complex interplay between technological advancement, scientific discovery, personal privacy, and corporate responsibility. How we respond to these challenges will play a significant role in determining the kind of digital future we create – one where the immense potential of genetic information can be realized without compromising the fundamental right to privacy.
In the end, the 23andMe situation reminds us that in the realm of genetic data, the stakes are incredibly high. Our DNA is not just information – it's the most personal blueprint of who we are. As we move forward, we must ensure that the guardianship of this information is treated with the utmost care, respect, and ethical consideration it deserves.
Article
Midjourney plans to let anyone on the web edit images with AI
Midjourney is planning to release an upgraded web tool that’ll let users edit any uploaded images from the web using Midjourney’s generative AI.
#ai #technology #midjourney #generativeai #newsonleo
Deepfakes and Misinformation
Deepfakes are AI-generated images or videos designed to deceive viewers into believing they are real. They can be used to spread misinformation, disinformation, and propaganda, which can have serious consequences, particularly in the context of politics, elections, and social unrest.
The rise of deepfakes has become a major concern, with 900% more deepfakes being created and published this year compared to the same time frame last year, according to data from Clarity, a deepfake detection firm. This trend is alarming, as it highlights the ease with which AI-powered tools can be used to create convincing but fake content.
Copyright Infringement and Ownership
The release of Midjourney's AI-powered image editing tool raises concerns about copyright infringement and ownership. If users are able to edit existing images using AI, it raises questions about who owns the original content and who benefits from the edits.
Midjourney has committed to using the IPTC's digital Source Type property, which embeds metadata in images denoting that they've been AI-generated. However, this standard does not provide a clear framework for determining ownership or copyright infringement in cases where AI is used to edit images.
Lack of Regulation and Oversight
The lack of regulation and oversight in the AI industry is a major concern. While some states have enacted laws against AI-aided impersonation, there is a need for greater federal regulation to address the broader implications of AI-powered image editing tools.
Midjourney's decision to release this tool without adequate safeguards in place has raised concerns among experts and lawmakers. The company's approach to moderation and content control is limited, and it is unclear how it will prevent the misuse of its tool.
Mitigating the Risks
To mitigate the risks associated with its tool, Midjourney is taking steps to:
However, these measures are insufficient, and Midjourney must do more to prevent the misuse of its tool.
Potential Consequences
The release of Midjourney's AI-powered image editing tool has the potential to:
What's Being Done to Address the Concerns
Several organizations and governments are taking steps to address the concerns surrounding AI-powered image editing tools:
What's Next
As the AI landscape continues to evolve, it is clear that responsible AI deployment is becoming an increasingly pressing concern. Midjourney's decision to release this tool highlights the need for greater oversight and regulation of AI-powered technologies, particularly those that have the potential to spread misinformation and disinformation.
In the coming months and years, we can expect to see more regulations, laws, and industry standards emerge to address the concerns surrounding AI-powered image editing tools. As the AI industry continues to grow and evolve, it is essential that we prioritize responsible AI deployment and ensure that these technologies are used for the greater good.
Article
Multiple teams at Meta were hit by layoffs this week. The company confirmed the layoffs in a statement to TechCrunch and noted that the changes were made to reallocate resources. The cuts reportedly impacted teams working on Reality Labs, Instagram, and WhatsApp, though Meta declined to comment on the record about how many employees were affected and what orgs they were part of.
#meta #layoffs #technology
Sharing new research, models, and datasets from Meta FAIR
Meta’s Fundamental AI Research (FAIR) team is focused on achieving advanced machine intelligence (AMI) and using it to power products and innovation for the benefit of everyone. For more than a decade, we’ve been sharing cutting-edge research and collaborating with the global AI community. Our mission to achieve AMI is an extension of this commitment to innovating for the greater good. As Mark Zuckerberg noted in a recent open letter, open source AI “has more potential than any other modern technology to increase human productivity, creativity, and quality of life,” all while accelerating economic growth and advancing groundbreaking medical and scientific research.
#meta #ai #technology
We believe that access to state-of-the-art AI creates opportunities for everyone. That’s why we’re committed to the continued growth and development of an open AI ecosystem.
Meta Spirit LM: An open source language model for seamless speech and text integration
Large language models are frequently used to build text-to-speech pipelines, wherein speech is transcribed by automatic speech recognition (ASR), then synthesized by an LLM to generate text, which is ultimately converted to speech using text-to-speech (TTS). However, this process compromises the expressive aspects of the speech being understood and generated. In an effort to address this limitation, we built Meta Spirit LM, our first open source multimodal language model that freely mixes text and speech.
Meta Spirit LM is trained with a word-level interleaving method on speech and text datasets to enable cross-modality generation. We developed two versions of Spirit LM to display both the generative semantic abilities of text models and the expressive abilities of speech models. Spirit LM Base uses phonetic tokens to model speech, while Spirit LM Expressive uses pitch and style tokens to capture information about tone, such as whether it’s excitement, anger, or surprise, and then generates speech that reflects that tone
Spirit LM lets people generate more natural sounding speech, and it has the ability to learn new tasks across modalities such as automatic speech recognition, text-to-speech, and speech classification. We hope our work will inspire the larger research community to continue to develop speech and text integration.
Meta AI is a robust and diverse platform with numerous capabilities. Here are some of the key features and applications:
Conversational AI:
Answering questions: Providing accurate and up-to-date information.
Generating text: Creating human-like text based on prompts or topics.
Translation: Translating text from one language to another.
Summarization: Summarizing long pieces of text into concise versions.
Content Generation:
Image generation: Creating images based on text prompts.
Text-to-image synthesis: Generating images from text descriptions.
Video generation: Creating short videos based on text prompts.
Language Understanding:
Sentiment analysis: Identifying emotions and sentiment in text.
Entity recognition: Identifying entities like names, locations, and organizations.
Intent detection: Determining user intent behind text inputs.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants:
Customer support: Providing automated support and answers.
Task completion: Assisting with tasks like scheduling and reminders.
Personalized recommendations: Offering tailored suggestions.
Search and Retrieval:
Knowledge graph search: Finding information from vast knowledge databases.
Document search: Retrieving relevant documents.
Accessibility and Inclusivity:
Language accessibility: Supporting multiple languages.
Text-to-speech: Converting text to audio.
Research and Development:
Advancing AI ethics: Exploring responsible AI development.
AI for social good: Applying AI to solve real-world problems.
Integrated Meta Products:
Facebook and Instagram: AI-powered features for content moderation and more.
WhatsApp: AI-driven chatbots and customer support.
Portal: AI-enabled video calling and smart display experiences.
Meta AI Spirit LM is likely referring to the language model technology used to power Meta's AI capabilities
Language models like Spirit LM enable Meta AI to understand and respond to natural language inputs, generating helpful and informative answers. Spirit LM is a specific model developed by Meta to power various AI applications, including chatbots, virtual assistants, and content generation tools.
#meta #llm #ai #technology
Vector database
#ai #technology #database
Vector Representation
In a vector database, each piece of data is represented as a vector of numbers, where each number corresponds to a specific feature or attribute of the data. The dimensions of the vector depend on the specific features being used to represent the data.
For example, in a text database, the vector might have dimensions corresponding to the frequency of each word in the vocabulary, the part of speech (noun, verb, adjective, etc.) of each word, and the sentiment (positive, negative, neutral) of each word. The resulting vector might look something like this:
[0.2, 0.1, 0.05, 0.01, 0.8, 0.3, 0.1, 0.2, 0.1, 0.05]This vector represents the text document, with each number corresponding to the frequency of a specific word or feature.
Similarity Search
The goal of similarity search is to find the most similar vectors to a given query vector, which is the vector representing the data the user is searching for. There are several algorithms that can be used for similarity search, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Inner Product Space (IPS)
The inner product space algorithm calculates the dOT product of the query vector and each vector in the database to find the most similar vectors. The dot product is a measure of the similarity between two vectors, and it can be calculated using the following formula:
dot product = sum(a_i * b_i)where
a_iandb_iare thei-th elements of the two vectors.The inner product space algorithm works by calculating the dot product of the query vector and each vector in the database, and then sorting the results by the dot product. The most similar vectors are the ones with the highest dot product.
Cosine Similarity
The cosine similarity algorithm calculates the cosine of the angle between the query vector and each vector in the database to find the most similar vectors. The cosine similarity is a measure of the angle between two vectors, and it can be calculated using the following formula:
cosine similarity = dot product / (|a| * |b|)where
|a|and|b|are the magnitudes of the two vectors.The cosine similarity algorithm works by calculating the dot product of the query vector and each vector in the database, and then normalizing the result by the magnitudes of the vectors. The most similar vectors are the ones with the highest cosine similarity.
Annular Distance
The annular distance algorithm calculates the distance between the query vector and each vector in the database, using the annular distance metric. The annular distance is a measure of the distance between two vectors, and it can be calculated using the following formula:
annular distance = sqrt(||a - b||^2 + ||a||^2 * ||b||^2)where
||a - b||is the Euclidean distance between the two vectors, and||a||and||b||are the magnitudes of the two vectors.The annular distance algorithm works by calculating the Euclidean distance between the query vector and each vector in the database, and then adding the product of the magnitudes of the vectors. The most similar vectors are the ones with the smallest annular distance.
Clustering
Clustering is a technique for grouping similar vectors together into clusters. There are several clustering algorithms that can be used for this purpose, including:
Applications
Vector databases have many applications, including:
Popular Vector Database Libraries
Some popular vector database libraries include:
These libraries provide a range of features and algorithms for similarity search and clustering, and can be used in a variety of applications.
Technology
Combating water scarcity: invention turns salty water into drinkable water using only sunlight
Is this a revolution in the seawater desalination process? Engineers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), in the United States, have created an innovative technique that transforms salt water into drinkable water using only solar energy.
#newsonleo #technology #energy
It is a prototype solar-powered desalination system that does not require extra batteries and can provide drinking water at low cost. see more details below.
Engineers have built a desalination system (removing salt from seawater and filtering it to produce drinking water) that works using only sunlight, eliminating the need for batteries to store energy or extra power sources.
And how does the invention work? it adapts to sunlight. Solar panels capture light to generate energy for the system. As sunlight increases during the day, the rate of desalination increases. If the light varies, such as the passage of a large cloud, cloudy days or simply dusk, the system reduces the speed at which it produces drinking water.
Salt water is pumped through a membrane that filters out salts. There, the electrodialysis method uses an electric field to extract salt ions from water as it is pumped through other membranes.
The system prototype was tested in groundwater wells in a community in the state of New Mexico, in the United States, for six months, and under different climatic conditions and types of water.
Tests showed that the system was able to harness around 94% of the solar energy generated by solar panels, managing to produce up to 5,000 liters of drinking water per day, enough to supply around 3,000 people.
The researchers' goal is to use this system to desalinate brackish groundwater, a salty source found in underground reservoirs. This is important given that freshwater reserves are overstretched due to scarcity around the world.
And the researchers are also planning to create a company in the coming months to commercialize the new technology. The expectation is that this innovation can be widely adopted, revolutionizing access to drinking water in regions where scarcity is a permanent problem.
China
New high-efficiency solar cell created by Chinese promises to change the future of clean energy
An international team led by scientists from the Institute of Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a new type of high-efficiency solar cell.
#newsonleo #energy #technology #china
The perovskite-organic tandem solar cell can achieve a photoelectric conversion of 26.4%, the highest efficiency for such solar cells to date, according to Li Yongfang, an academician and researcher at the institute.
Perovskite solar cells and organic solar cells represent the next generation of solar cells. Compared to currently widely used crystalline silicon solar cells, they offer advantages such as ease of manufacturing, light weight and the ability to be applied in flexible devices.
These features present significant application prospects in areas such as portable power, building-integrated photovoltaics, and indoor photovoltaics.
The new cell uses broadband perovskite materials to absorb short-wavelength sunlight and the narrow-band organic active layer to absorb long-wavelength sunlight in the near-infrared, Li said.
He added that this combination significantly expands the usable solar spectrum and effectively increases the device's power conversion efficiency.
AI
Mastering the use of artificial intelligence yields an increase of up to 40% in salary
Having your salary adjusted well above inflation is a universal desire, but a privilege for few. And there is a group that tends to benefit from increases of up to 40%, according to a study by the University of Oxford, in England, with the Center for Social Data Science at the University of Copenhagen, in Denmark.
#newsonleo #ai #technology
They are professionals specialized in technological areas and with mastery of skills related to Artificial Intelligence (AI). The study is international, but it applies to the Brazilian reality, including the Espírito Santo market.
Machine learning is the leading skill, with a potential salary increase of 40%, followed by mastery of TensorFlow — an open source library that can be used for machine learning in various tasks —, with 38%; by deep learning, with 27%; and natural language processing (19%).
AI specialist and professor at Faesa, Howard Cruz Roatti explains that this knowledge is useful for bringing innovation and digital transformation to companies.
Machine learning and its applicability contributes, he says, to optimizing processes, increasing efficiency and creating new products. While the Google TensorFlow service domain allows developers to build, train, and deploy neural network models to solve complex problems.
Deep learning uses artificial neural networks “capable of learning complex patterns from large volumes of data”. Finally, Natural Language Processing allows machines to understand, process and generate human language.
Professionals with such skills are sought after especially when combined with data science and algorithms, says the study.
Professionals who want to work with AI need to seek knowledge in data analysis, business management, products and even sales, according to the selection manager for the tech & digital talent division at Gi Group Holding, Henrique Almeida dos Santos. “It is important to understand how a business works and, from that, map how AI can add more value.”
Fabiano Correia Lima, 50, from São Paulo, lived in Greater Vitória for many years, but decided to return to his hometown to study. Graduated in marketing, he specialized in information technology, information security, software engineering, artificial intelligence, ESG and corporate sustainability, in addition to having a master's degree in big data and business intelligence.
He is currently a specialist in Artificial Intelligence (AI) for a large company in São Paulo. He detailed that, with the combination of technical knowledge and behavioral skills, he achieved a 57% salary increase, comparing before and after specializing in AI. “It’s a composition that defines the salary.” In addition, he also has his own company, with clients in Brazil and abroad.
A total of 16 million Brazilian professionals may have to change careers by 2030, due to the advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digitalization, according to a study by the McKinsey Global Institute, according to information from the newspaper O Globo.
AI
Como a inteligência artificial vai mudar o trabalho do professor?
Ledo engano se você acredita que utilizar inteligência artificial (IA) em sala de aula se resume ao ChatGPT. As possibilidades que a inteligência artificial oferece estão em todos os níveis da educação, desde dar mais eficiência para os professores até auxiliar na compreensão dos alunos e ajudar no desenvolvimento de habilidades socioemocionais.
#newsonleo #technology #ai #education #hivebr #pt
Esse movimento já está em curso em instituições de todo o País. Uma pesquisa do Instituto Semesp, realizada com 444 professores da educação básica em março de 2024, mostra que 74,8% dos docentes enxergam a tecnologia e a IA como aliadas no ensino. No entanto, enquanto a tecnologia acelera o acesso à informação, os professores também percebem que ela traz diversos desafios como a dispersão dos alunos.
Curiosamente, apesar do reconhecimento de seus benefícios, apenas 39,2% dos professores afirmam utilizar essas ferramentas com regularidade em sala de aula. Esse dado evidencia que há uma distância entre o potencial da tecnologia e sua implementação cotidiana.
Carlota Boto, diretora da Faculdade de Educação da USP (Universidade de São Paulo), acredita que essa lacuna se deve à complexidade do uso da IA, que vai além de ser uma simples ferramenta técnica. Para ela, a IA tem o poder de redefinir o modo como o conhecimento é acessado e compartilhado. “A inteligência artificial pode ser uma aliada valiosa no preparo das atividades em sala de aula, mas, para que isso ocorra de forma eficaz, é preciso que o professor tenha domínio tanto da ferramenta quanto do conteúdo a ser trabalhado.”
Essa transformação, para ela, exige que os docentes reavaliem as práticas pedagógicas, desafiando tradições e abraçando a inovação. “A primeira questão a ser pensada é o repertório: o que estamos ensinando e como isso se conecta com o mundo em transformação? É importante respeitar as tradições pedagógicas, mas também integrar novos conteúdos que dialoguem com as demandas atuais.”
Na era da IA generativa, o impacto dessa tecnologia é notável na produção de conteúdo. Anderson Soares, coordenador do primeiro bacharelado em Inteligência Artificial da Universidade Federal de Goiás (UFG), observa que “a geração de conteúdo sempre foi algo muito artesanal, mas a IA generativa permite criar músicas, textos e materiais de forma automática”. “Isso abre caminho para que os alunos atuem mais no campo criativo e menos nas tarefas manuais.”
Para Soares, essa nova realidade oferece oportunidades que promovem ações cooperativas e colaborativas, essenciais para o desenvolvimento das competências do futuro. No entanto, o avanço tecnológico também traz um desafio significativo: como trabalhar as habilidades socioemocionais em um ambiente altamente tecnológico?
Para Guilherme Cintra, diretor de inovação e tecnologia da Fundação Lemann, a resposta está na criatividade e na capacidade do professor de criar um ambiente de troca real entre os alunos. “A nossa capacidade de criar e manter relações verdadeiras será o que nos distinguirá das máquinas”, afirma, destacando que o professor precisa ser mais do que um transmissor de conhecimento, atuando como facilitador de interações humanas e reflexões profundas.
Além disso, o sistema educacional como um todo precisa se adaptar para apoiar os professores nessa transformação. “Não podemos esperar que os professores assumam sozinhos a responsabilidade de toda essa mudança”, diz Cintra. Repensar a formação dos docentes, o currículo e a gestão escolar é essencial para que a tecnologia seja usada de forma eficaz, sem sobrecarregar os educadores.
Para o especialista Anderson Soares, embora a tecnologia possa otimizar o aprendizado e personalizar o ensino, o desenvolvimento de habilidades humanas fundamentais como empatia, trabalho em equipe e criatividade ainda depende da capacidade do educador de criar relações significativas. “A educação tem um papel essencial para nos mostrar como tecnologia não vai resolver nenhum problema por nós, mas que a resolução ainda compete ao ser humano, ainda compete a nossas habilidades socioemocionais.”
Lucas Chao, especialista em IA e educador no Colégio Santa Cruz, demonstra como a tecnologia pode ser uma poderosa aliada no processo de ensino. Ele ministra uma eletiva de inteligência artificial no ensino médio da escola em São Paulo, que aborda desde a história até as aplicações mais avançadas da tecnologia, incluindo programação em Python e criação de conteúdo com IA generativa. “O curso vai além do ensino técnico; ele desafia os alunos a refletir criticamente sobre as implicações éticas da IA.”
Paralelamente, no ensino fundamental 2, Chao lidera uma oficina chamada CodingLab, focada em letramento digital e desenvolvimento de jogos, onde introduz conceitos de IA de maneira prática e crítica. Ele enfatiza a importância de “pensar sobre” a IA, questionando os resultados e visões gerados por ferramentas como ChatGPT e Gemini. Lucas investiga se as representações produzidas por essas ferramentas carregam preconceitos ou vieses.
Mas, afinal, a IA pode substituir o papel do professor? Segundo Guilherme Cintra, diretor de inovação e tecnologia da Fundação Lemann, a interação humana continua sendo fundamental para um aprendizado eficaz. “Usar uma ferramenta por si só, sem um contexto de troca com humanos, em que exista uma relação no centro do processo, não basta”, afirma.
Existem diversas ferramentas de IA que podem potencializar o papel dos professores em suas atividades. A PeerTeach, por exemplo, conecta alunos para colaboração, personalizando o aprendizado. Já a Letrus corrige redações, liberando tempo para que os professores se dediquem a atividades mais estratégicas, como identificar as necessidades individuais de cada aluno. “A inteligência artificial, quando bem usada, centraliza o processo na relação humana e permite a adaptação para diferentes contextos. Isso é não substituir o professor”, diz ele.
Inteligência Artificial
IA generativa leva CIO para adolescência
A implementação de projetos de IA generativa parece estar levando muitos CIOs para um mundo similar ao do sexo na adolescência: só se fala sobre o assunto e todo mundo acha que deve experimentar. Por outro lado, falta experiência prática e existe também uma certa dose de medo.
#newsonleo #ai #technology #hivebr #pt
https://img.inleo.io/DQmX8mUiyQc4jMNsu5ZkTRoqAKUZaza4GWu1P8iVVzHcAGr/1729116728_Depositphotos_22386149_S(1).jpg
É o que aponta (em outras palavras, é verdade) uma pesquisa sobre adoção de GenAI feita pela Salesforce com 150 CIOs ao redor do mundo, todos eles de empresas com mais de 1 mil funcionários.
Apropriadamente batizada de “The CIO Dilemma”, a pesquisa mostra CIOs convencidos do potencial (84% acreditam que ela vai ser tão significativa para os negócios quanto a Internet) e do perigo da tecnologia (67% disseram que estão tomando um approach mais cauteloso com IA do que outras tecnologias).
Ainda há muita insegurança sobre o nível de conhecimento sobre o tema: 61% dos pesquisados afirmaram que sentem que deveriam saber mais sobre IA do que eles realmente sabem.
A origem da insegurança são temores sobre segurança, apontados por 57% dos pesquisados, seguidos por falta de informação confiável, apontado por 52%.
Incapacidade de identificar casos de uso, treinamento de profissionais e falta de retorno para o investimento também foram citados por cerca de 30% dos entrevistados.
Os CIOs também estão pressionados: 68% pensam que os “stakeholders” têm expectativas não razoáveis sobre o tempo de implementação da tecnologia.
No geral, os CIOs descrevem uma confusão entre três perfis diferentes dentro das organizações: quem usa IA, quem quer IA e quem está pronto para IA.
A área mais entusiasmada com IA, no geral, seria o marketing, enquanto a que tem mais casos de uso é o customer service. No entanto, quem estaria pronto mesmo para a tecnologia seria o RH. Marketing e customer service aparecem só em quinto e quarto lugares, respectivamente, no ranking de “readiness”.
Por enquanto, os CIOs ainda estão destinando quatro vezes mais orçamento para projetos voltados a dados do que para IA, porém a maior parte (66%) está confiante de que terá retorno nos investimentos em inteligência artificial.
“A IA generativa é uma das tecnologias mais transformadoras deste século. Esta pesquisa dá uma ideia dos fundamentos nos quais CIOs de todo o mundo, indústrias e geografias estão se apoiando para a implementação de tecnologias de IA verdadeiramente transformacionais”, afirma Juan Perez, CIO da Salesforce.
A pesquisa foi aplicada entre 23 e 30 de julho de 2024 e produziu respostas em 18 países e 17 indústrias. Pela pouca quantidade de gestores ouvidos, a empresa não apresentou um recorte por país ou continente/região.