Hello My Leo Warriors,
I hope all of you are well and Completing your Zealy task everyday.
I am also did the same but now I missed some quests because of Job Issues. By the way I am 11K+ XP On the quest. Don't forget to tell your XP on the quest.
Ok, On today's blog I am going to discuss about Ethereum Virtual Machine or EVM that runs on Ethereum blockchain.

I Know about this because On Lockdown period My Brother started to mining Ethereum and on that time we have curiosity to know the works of the GPU and why the mining happens, something like that..
At that time I knew about the Gas fees, Gpu's works, And others stuffs. So let's jump into the topic but before that I have to tell you something regard Ethereum Virtual Machine.
Actually Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about digital transactions and decentralized systems. Among the various blockchain platforms, Ethereum has emerged as a prominent player, thanks to its innovative feature called the Ethereum Virtual Machine or EVM. In this blog, we will explore what the EVM is and how it contributes to the functionality of the Ethereum blockchain, But-
Let's Understanding the EVM First :
The EVM, short for Ethereum Virtual Machine, is not a blockchain in itself but rather a virtual machine or a computer program that runs on the Ethereum blockchain. It acts as a runtime environment for executing smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with predefined rules written in programming languages like Solidity or Vyper. This are Programming languages Like Java.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications :
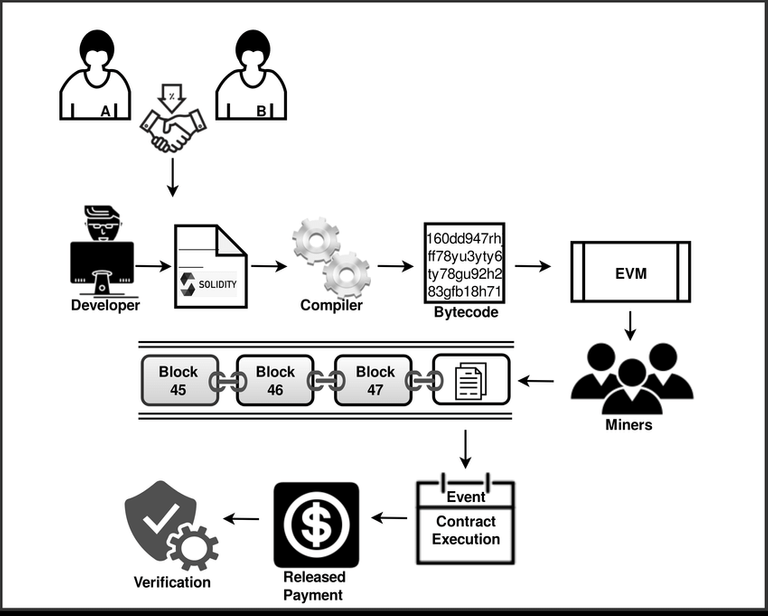
Smart contracts are at the heart of the Ethereum blockchain and are the building blocks of decentralized applications or dApps. They are programmable contracts that automatically execute when certain conditions are met. Smart contracts can represent digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies, or facilitate complex functionalities like decentralized finance or DeFi protocols, supply chain management, and more.

How the EVM Works In Blockchain :
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a crucial component of the Ethereum blockchain that enables the execution of smart contracts. Let's dive into how the EVM works:
Compilation and Deployment :
Smart contracts are written in programming languages like Solidity or Vyper. These contracts are compiled into bytecode, a low-level representation that the EVM can understand. The bytecode is then deployed onto the Ethereum blockchain, where it becomes part of the immutable ledger.EVM as a Runtime Environment :
The EVM acts as a virtual machine or a computer program that runs on every node of the Ethereum network. When a transaction involving a smart contract is initiated, the EVM comes into play. It reads the bytecode of the contract and executes the instructions step by step.Deterministic Execution :
The EVM follows a deterministic execution model, which means that given the same inputs, the output will always be the same. This deterministic nature ensures that the execution of smart contracts is reliable and predictable across all nodes of the Ethereum network.Gas and Gas Fees :
To prevent misuse of computational resources and ensure the security of the network, the EVM introduces the concept of gas. Gas is a unit of computation that represents the computational effort required to execute a specific operation within a smart contract. Each operation in a contract consumes a certain amount of gas. For example, arithmetic operations consume less gas compared to complex loops or database interactions.Gas Fees and Miners :
Users must pay gas fees to cover the computational resources utilized during the execution of a smart contract. Gas fees incentivize miners, who validate and add transactions to the blockchain, to include the transaction in a block. Miners prioritize transactions with higher gas fees, ensuring that the network remains efficient and responsive.Gas Limit :
Each Ethereum block has a gas limit, which determines the maximum amount of gas that can be consumed within the block. If a transaction requires more gas than the block's gas limit, it will be rejected. This gas limit prevents infinite loops or resource-intensive computations from disrupting the network's operation.Out-of-Gas Situations :
If a smart contract execution runs out of gas before completing, the contract execution is reverted, and any state changes made up to that point are undone. This ensures that users are not charged for unfinished or failed computations.
NOTE ::- Through incorporating these mechanisms, the EVM ensures the secure and efficient execution of smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. It provides a robust and deterministic runtime environment, facilitating the development of decentralized applications and programmable digital assets.
- Gas and Security :
To prevent misuse of computational resources and ensure the security of the network, the EVM introduces the concept of gas. Gas is a unit of computation that represents the computational effort required to execute a specific operation within a smart contract. Users must pay gas fees to cover the computational resources utilized and incentivize miners to include their transactions in the blockchain. Gas fees also discourage the execution of inefficient or malicious code, making the Ethereum network more secure.

Benefits and Significance :
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and the Ethereum blockchain offer several benefits and have significant significance in the world of blockchain technology. Let's explore some of these benefits and significance:
Decentralized Applications (dApps):
The EVM enables the creation of decentralized applications (dApps). These applications operate on the Ethereum blockchain, utilizing smart contracts to automate processes, enforce rules, and facilitate trustless interactions. dApps can provide transparent, secure, and censorship-resistant solutions in various domains such as finance, gaming, supply chain management, governance, and more.Programmable Digital Assets:
The EVM allows for the creation of programmable digital assets through smart contracts. These assets, such as cryptocurrencies or tokens, can have predefined rules and functionalities embedded within them. This programmability enables the development of new financial instruments, decentralized exchanges, and tokenized representations of real-world assets, fostering innovation and expanding possibilities within the blockchain ecosystem.Transparency and Immutability:
The Ethereum blockchain, with the EVM as its backbone, provides transparency and immutability. Once a smart contract is deployed on the blockchain, it becomes part of an immutable ledger that is accessible to all participants. This transparency ensures that the execution of smart contracts can be audited and verified by anyone, promoting trust and accountability.Security and Trust lessness:
The EVM enhances security and trustlessness by enforcing the execution of smart contracts in a deterministic manner. The deterministic nature of the EVM ensures that smart contracts produce consistent and predictable results across all nodes of the network. Additionally, the decentralized nature of the Ethereum blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of single points of failure or manipulation.Innovation and Interoperability:
The EVM's support for smart contracts and its Turing-complete nature foster innovation and allow developers to create complex applications and execute a wide range of computations on the blockchain. Furthermore, the Ethereum blockchain's compatibility with various programming languages and development frameworks promotes interoperability and makes it easier for developers to build on top of the platform.Community and Ecosystem:
The Ethereum ecosystem has a vibrant and active community of developers, entrepreneurs, and enthusiasts. This community contributes to the development and improvement of the EVM and the Ethereum blockchain through discussions, collaborations, and the creation of tools, libraries, and frameworks. The collective efforts of this community have propelled Ethereum's growth and adoption, making it one of the most widely used blockchain platforms.

GOVERNANCE OF EVM BLOCKCHAIN COMMUNITY ::-
The governance of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) blockchain refers to the decision-making processes and mechanisms that determine the rules, protocols, and changes to the EVM and the Ethereum blockchain. Ethereum, as a decentralized platform, has an open and community-driven governance model. Let's explore the governance aspects of the EVM blockchain:
Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) :
The Ethereum community uses Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) as a means of suggesting and discussing changes to the Ethereum protocol, including the EVM. EIPs can be submitted by anyone, and the community provides feedback, debates, and collaborates on proposed changes. EIPs cover a wide range of topics, such as protocol upgrades, standards, and optimizations.Core Development Teams:
The development of the Ethereum protocol and the EVM is led by multiple core development teams. These teams, including the Ethereum Foundation and other independent groups, collaborate on implementing proposed changes, improving security, and enhancing the EVM's functionalities. The core development teams work closely with the Ethereum community and consider community feedback during the decision-making process.Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) Lifecycle:
When an EIP is proposed, it goes through a lifecycle that involves community discussion, review, and eventual implementation. The EIP authors, core development teams, and community members engage in discussions on forums, social media, and developer conferences. If there is broad community support and technical consensus, the proposed EIP can be implemented and activated through a network-wide upgrade known as a hard fork.

USAGES OF EVM IN BLOCKCHAIN ::-
I will provide you just a few simplified examples of the usages and applications of the EVM blockchain. So that you can understand it better. But before jump into points at first we have to know that The flexibility and programmability of the EVM allow for a wide range of innovative solutions across various industries and domains.
Cryptocurrencies and Tokens:
One of the most common use cases of the EVM blockchain is the creation and management of cryptocurrencies and tokens. By leveraging smart contracts on the EVM, individuals and organizations can issue their own digital currencies or tokens, enabling various functionalities such as transfers, payments, and rewards within decentralized applications (dApps).
Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
The EVM blockchain has been a game-changer in the realm of decentralized finance (DeFi). DeFi applications built on the EVM allow users to access financial services such as lending, borrowing, yield farming, decentralized exchanges, and stablecoins. These services are often provided by smart contracts that automate the processes, removing the need for intermediaries like banks.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs):
NFTs have gained significant attention in recent times, and many NFT platforms are built on the EVM blockchain. NFTs are unique digital assets that can represent ownership of digital or physical items, such as art, collectibles, in-game items, or real estate. The EVM allows for the creation, trading, and ownership verification of NFTs, providing a secure and transparent environment for these digital assets.
Supply Chain Management:
The EVM blockchain can be utilized for supply chain management, providing transparency and traceability in the movement of goods and products. By recording and verifying transactions on the blockchain, supply chain participants can ensure the authenticity, provenance, and accountability of products, reducing fraud, counterfeiting, and improving overall efficiency.Identity and Authentication:
The EVM blockchain can be used to establish digital identities and provide secure authentication. Instead of relying on centralized systems or third-party authorities, individuals can have ownership and control over their digital identities by utilizing the EVM blockchain. This can enhance privacy, reduce identity theft, and enable secure access to various services.Voting & Works:
The EVM blockchain can facilitate decentralized governance and voting mechanisms. Smart contracts on the EVM can be used to create decentralized autonomous organizations or DAOs where decision-making processes are governed by token holders. This allows for transparent and decentralized governance, enabling stakeholders to participate and vote on proposals and initiatives.Gaming and Virtual Worlds:
The EVM blockchain is utilized in gaming and virtual worlds, offering players true ownership of in-game assets. By tokenizing game items or characters on the EVM blockchain, players can buy, sell, and trade these assets securely and transparently. This fosters an ecosystem where players have actual ownership and control over their virtual possessions.

That's all for the day Guyz, I hope you enjoyed my blog.
You Guyz are awesome ☺️
Stay safe Be Cool 😎

Posted Using LeoFinance Alpha