What is system thinking?
System can be defined as collection of various components/parts.
Which are inter-connected with each other in order to achieve
some objective. All of these components affect each other in a
system. The study of these systems comes under a branch known
as system thinking. It involves studying the relationships and
interactions among the components at a broader perspective. This
makes system thinkers different from component thinkers. Which
only see a specific event in the system. There are numerous
examples of systems around us. Like solar system, banking
system, educational system, ecosystem, business system etc.
How it works
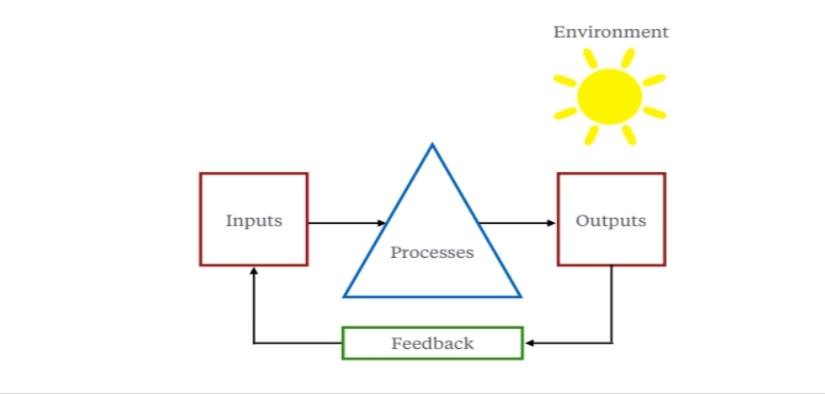
The working of every system can be explained with above figure. In every system we need inputs, which we put into a system. These inputs are then processed to produce something. This leads us to outputs. These three constitute the primary working of system. Apart from these three, Environment and Feedback also play an important role in system working. Feedback is simply when output directly affects the input. Let’s take an example of a student. What he/she studies during the course can be taken as an input. How he/she understands can be taken as a process. The output is the performance he/she shows in examination. The environment part constitutes of what kind company he/she has, what are his/her home conditions etc. At last, feedback involves evaluating yourself on the basis of output.
Tools of System Thinking
1. Interconnectedness
Good system thinkers always believe that things are
interconnected. In other words, everything needs something
else. We as humans need air, water and food for survival.
2. Circularity
This means things don’t happen in linear fashion. The
involvement of feedback loop makes things happen in circular
way.
3. Emergence
Emergence can be described as a natural phenomenon. Which
happen when things interact with each other. We can also set
some simple rules and let emergence happen. Good system
thinkers prefer emergence over silos. Where we force things
the way we want them to happen.
4. Whole
We know in a system, parts are interconnected. So it’s good
practice to study system as a whole, rather than a part.
5. Synthesis
Synthesis means to see interconnectedness and to manage
system as whole. It is different to analysis, where system is
break into parts.
6. Relationship
Relationship means that different parts of the system are
interconnected and related to each other. This is opposite to
isolation, where each part of the system is said to be isolated. It doesn’t affect the other parts of system.