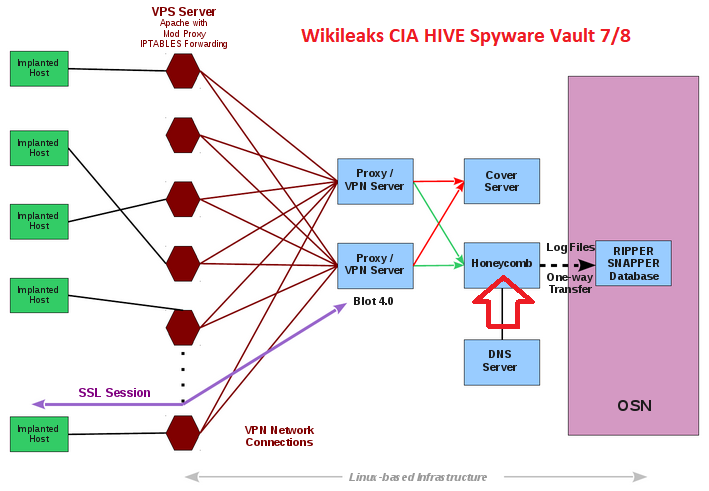
Each cover domain resolves to an IP address that is located at a commercial VPS (Virtual Private Server) provider. The public-facing server forwards all incoming traffic via a VPN to a 'Blot' server that handles actual connection requests from clients. It is setup for optional SSL client authentication: if a client sends a valid client certificate (only implants can do that), the connection is forwarded to the 'Honeycomb' toolserver that communicates with the implant; if a valid certificate is missing (which is the case if someone tries to open the cover domain website by accident), the traffic is forwarded to a cover server that delivers an unsuspicious looking website.
The Honeycomb toolserver receives exfiltrated information from the implant; an operator can also task the implant to execute jobs on the target computer, so the toolserver acts as a C2 (command and control) server for the implant.
Similar functionality (though limited to Windows) is provided by the RickBobby project.
See the classified user and developer guides for HIVE.
hahaha
