
Source
Polar melting refers to the process of melting and retreat of ice sheets in the Earth's polar regions, i.e. at the North and South Poles.
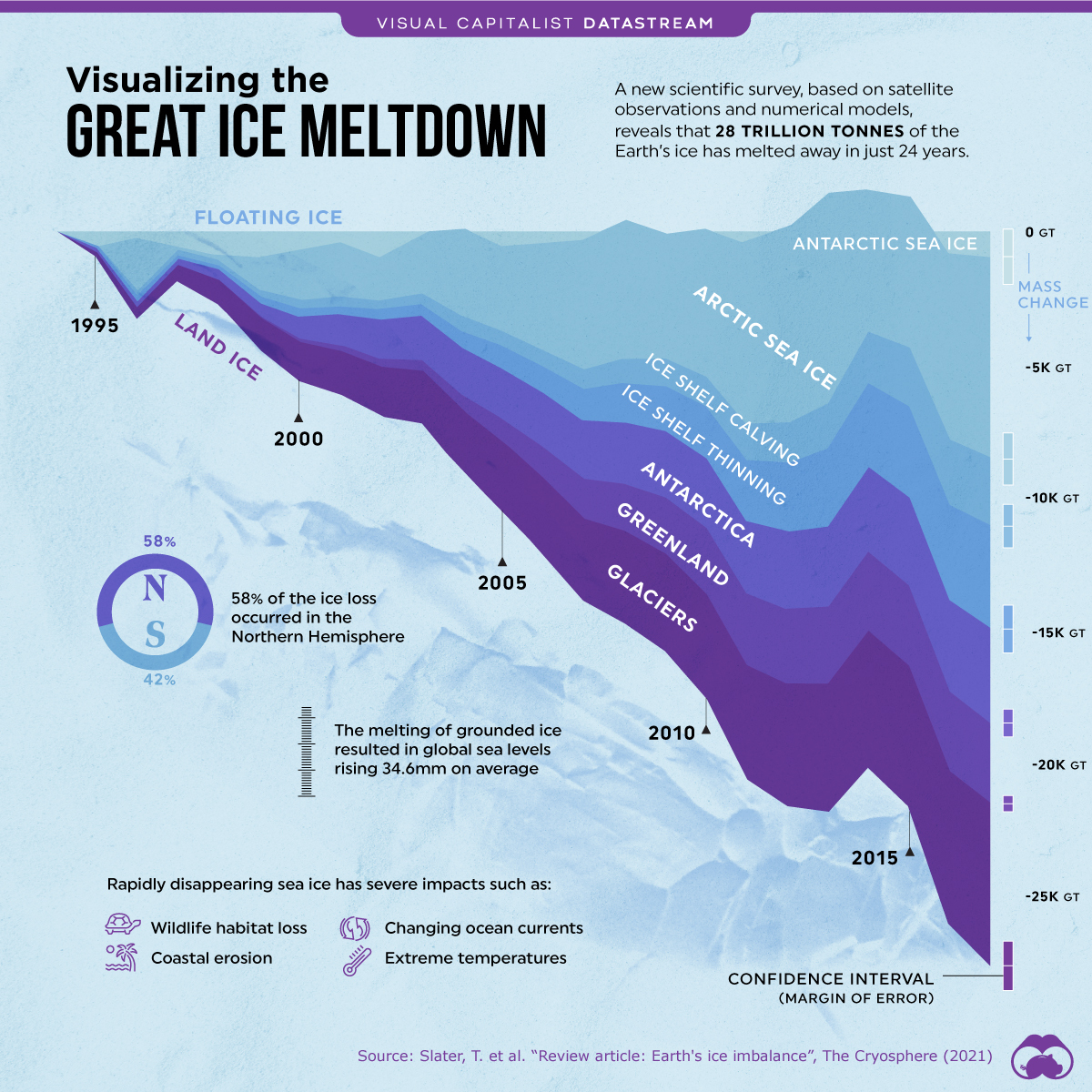
This phenomenon has received much attention due to its implications for climate change and its potential effects on sea levels.
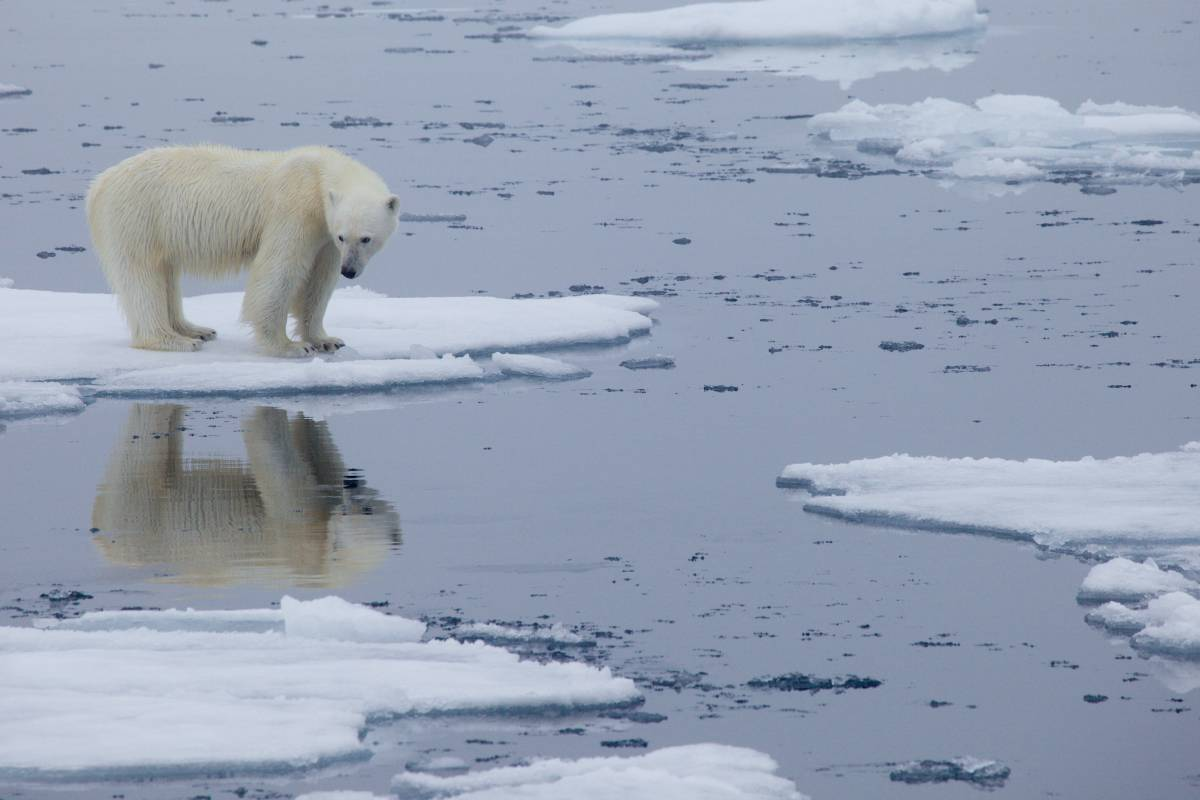
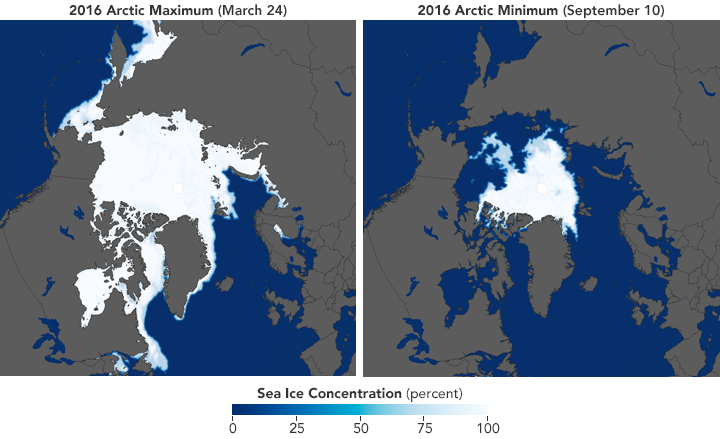
At the North Pole, melting occurs mainly in the Arctic Ocean, where the Arctic ice cap is located, composed mainly of sea ice that forms and melts each year.
In recent decades, a significant decrease in the extent and thickness of Arctic sea ice has been observed, mainly due to rising global temperatures.

Source
Melting at the South Pole is mainly concentrated on the Antarctic ice sheet, which is the world's largest frozen freshwater reservoir.
Antarctica is home to huge glaciers and ice sheets that extend over land and float on the surrounding ocean.
In some areas of West Antarctica and the Antarctic Peninsula, significant glacial retreat and thinning of the ice sheets have been observed, contributing to sea level rise.
The melting of ice at the poles is mainly due to global warming caused by human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation.
Source
 :
Increased greenhouse gas emissions have led to an increase in the Earth's average temperature, which in turn has accelerated the melting of polar ice.
The consequences of melting ice at the poles are worrying. In addition to contributing to sea level rise, the retreat of sea ice and ice sheets can have adverse effects on Arctic and Antarctic ecosystems, as well as on biodiversity and the global climate.
Congratulations @danielpardo! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 800 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP