The early history of the automobile can be divided into a number of eras, based on the prevalent means of propulsion. Later periods were defined by trends in exterior styling, size, and utility preferences.
In 1808 François Isaac de Rivaz designed the first car powered by an internal combustion engine fueled by hydrogen.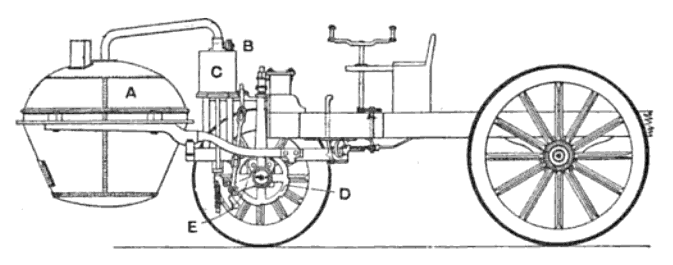
In 1870 Siegfried Marcus built the first gasoline powered combustion engine, which he placed on a pushcart, building four progressively sophisticated combustion-engine cars over a 10-to-15-year span that influenced later cars. Marcus created the two-cycle combustion engine. The car's second incarnation in 1880 introduced a four-cycle, gasoline-powered engine, an ingenious carburetor design and magneto ignition. He created an additional two models further refining his design with steering, a clutch and brakes.
The four-stroke petrol (gasoline) internal combustion engine that still constitutes the most prevalent form of modern automotive propulsion was patented by Nikolaus Otto. The similar four-stroke diesel engine was invented by Rudolf Diesel. The hydrogen fuel cell, one of the technologies hailed as a replacement for gasoline as an energy source for cars, was discovered in principle by Christian Friedrich Schönbein in 1838. The battery electric car owes its beginnings to Ányos Jedlik, one of the inventors of the electric motor, and Gaston Planté, who invented the lead-acid battery in 1859.
In 1885, Karl Benz developed a petrol or gasoline powered automobile. This is also considered to be the first "production" vehicle as Benz made several other identical copies. The automobile was powered by a single[citation needed] cylinder four-stroke engine.
After producing and selling the Model A in 1903, Ford Motor Company's Model T became the first mass-produced automobile in 1908, focusing on affordability for the average consumer. By 1927 Ford produced over 15,000,000 Model T automobiles and only then developed the Model A.
At the turn of the 20th century electrically powered automobiles were a popular method of automobile propulsion, but their common use did not last long, and they diminished to a niche market until the turn of the 21st century.
source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_the_automobile
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_the_automobile
su copy-paste čia nėra kas veikt. Tik susilauksi kad cheetah uždubasins greit už tokius darbus.