Insulin
Insulin is the hormone responsible for the regulation of sugar in the body, and the hormone is produced in specialized cells in the pancreas, called these cells as beta, although the lack of the body causes the body's inability to use the sugar obtained from different foods, Glucose in the blood, and in this article we will show you the mechanism of action of insulin
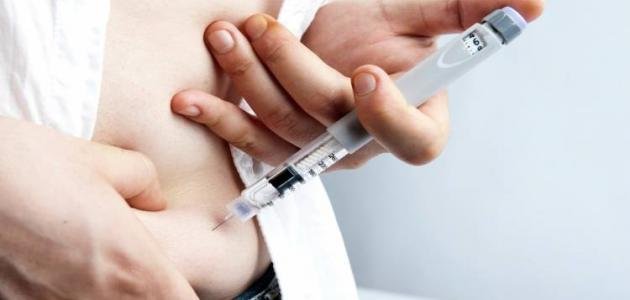
Insulin production
Beta cells in the pancreas produce insulin, which secrete it daily at 3050 units at the healthy adult
. How insulin works when you eat
Insulin starts to rise after eating about 8-10 minutes, and increases to a high level after half an hour to an hour only a quarter of the food, and returns to normal after 90120 minutes of eating, and glucose is one of the most stimuli that Helps produce insulin, and its production may be affected by many different neurotransmitter and hormonal factors
Insulin secretion
The pancreas secrete insulin in two phases
Early stage
Which is when the level of glucose is high; insulin is excreted to a large extent to the level of glucose, which explains the incidence of low sugar in some people who have performed a hysterectomy or part of the small intestine, where they increase the proportion of insulin with no The presence of sufficient space for absorption, leading to a disproportion between the low level of glucose, and the high level of insulin, and thus gradually decrease
Late stage
Insulin starts at this stage rising exponentially, when the body is getting glucose from outside the body such as food, and this happens for more than four hours, and it can occur at high glucose due to internal effects in the body, and this occurs for more than 24 An hour, which explains the high sugar in some people without diabetes, when the proliferation of foods containing sugars, carbohydrates
Insulin exit
Of a beta cell. Insulin comes out of the cell when a large amount of glucose is present in it. At the height of ATP, this process is called the energy process within the cell
Insulin binding with receptors
The receptors are the link between the inner medium of the cell and its outer center. After insulin is released from the cell, it begins to search for these receptors to host. These receptors are located on the surfaces of the cells spread throughout the body
Glucose Transfer Glucose is transported throughout the body to be converted to energy for use, via the feast of distributed vectors in the body called (GLUT)
Carrier 1
This carrier is present in all tissues of the human body where it transfers the basic requirement.
Blood 2
This carrier is the carrier of glucose inside the beta cells, working under high glucose to secrete more insulin.
Carrier 3
In all tissues, it is the primary carrier within the nerve tissue.
Blood 4
This is found in the motor muscle and fatty tissue.
Carrier 5
This carrier is found in the brushes of human digestive cells, liver, and sperm. Carrier 6:
This is found in the liver and some other tissues
Carrier 7
These vectors exist in the digestive tract and kidneys to re-absorb glucose. Carotid 1 Found in the intestines and renal tubes Carotid 2 Found in renal tubules
--------------------------------------------
I am at war for 15 days and I am fighting to solve this problem
https://steemit.com/life/@mars9/i-am-at-war-for-15-days-and-i-am-fighting-to-solve-this-problem
Injecting 10iu of fast acting insulin after weight training is great for muscle building and recovery, just don't forget to have 30 grams of fast acting carbs to go with it. Don't want to go hypo g
Thanks my friend for this information
too easy, anytime
Does emotion affect to in pancreas health?
Like deppression, and loneliness
Sadness and happiness affect the level of sugar in the body
I'm sick of type I diabetes so I try as far as possible to get away from grief but I can not
h hope to solve your problem
اتمنى ذللك
good infornation i vote you
شكرا مها ع المساعدة
Great work dear friend @ mars9, thank you very much for sharing