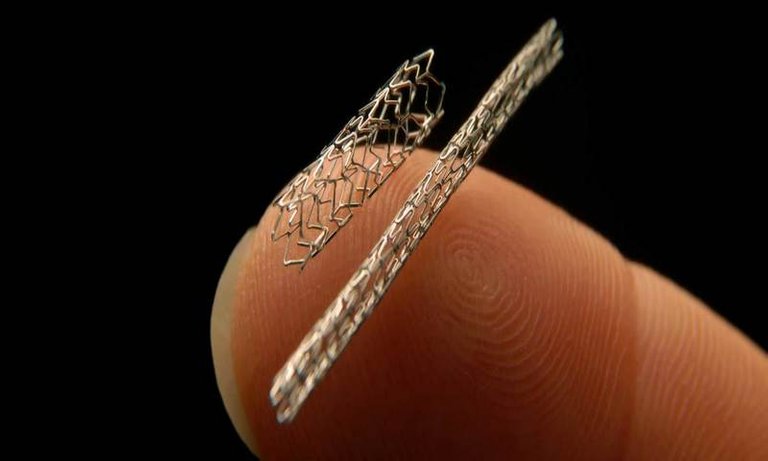
When you've been clinically determined to have a blocked artery inside your heart, there are a good possibility your doctor suggested angioplasty. Which process entails first cleaning the congestion and after that propping the artery open up with a little cylindrical device known as stent.
Near to a million stents are usually injected in people within the U.S. yearly to spread out up obstructed heart blood vessels, based on the latest proof available. However experts possess reputed for more than 10 years that angioplasty generally saves lives only when carried out soon after a heart attack.
HISTORY
Angioplasty, that 1st became acquireable from the 1980s, acquired steam right after its usefulness as an unexpected emergency therapy for heart strikes became obvious.

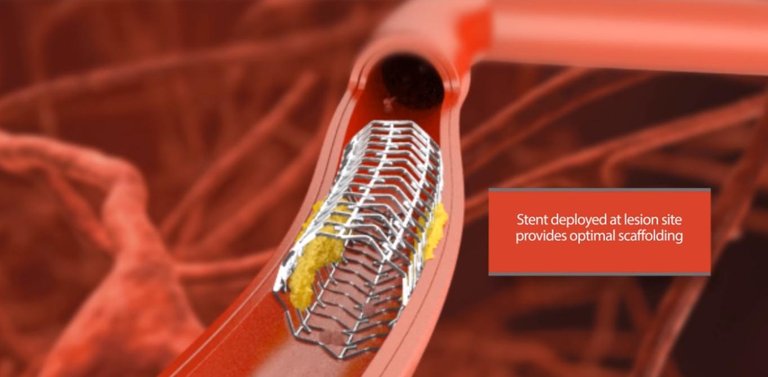
In angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), the physician inflates a skinny balloon inside the narrowed artery in order to grind deposits, leaving behind a stent in position to keep the actual vessel open up.

When carried out inside hours of a myocardial infarction to clear a obstructed or almost obstructed artery, it's very clear that angioplasty might be lifesaving.
WHEN YOU NEED IT OR NOT?
David Brown, M.D., a cardiologist and professor of medicine at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis stated in a statement:
"Thirty years ago, doctors made the assumption that since [angioplasty] could help with a heart attack, it would help with other blockages due to coronary-artery disease”
But a crucial medical test of 2,287 individuals with stable heart problems, released in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2007, discovered that will possessing a stent incorporated did not slow up the possibility of death, a cardiac arrest, or some other significant cardio activities when put into a patient’s medication treatment. Following research had comparable results.
Although the quantity of stents has dropped considerably since that research was released, a 2015 study by Yale University experts in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that 2.Seven million angioplasties conducted over a five-year period, 13% of nonemergency stents had been still regarded as unacceptable.


One description for the ongoing use is that this procedure-which is actually comparatively fast and easy-is seen as an moneymaker regarding doctors and hospitals, says Brown, who have revealed the excessive use of the treatment.
However in nonemergency circumstances, lifestyle changes-plus medicines to manage high blood pressure, lower cholesterol, and stop blood clots-are at least as efficient and generally more secure. A December 2016 evaluation in JAMA Internal Medicine identified that strategy might slow up the number of angioplasties by 80%.

An additional current research, first published on the internet in November 2017 in the Lancet, elevated queries regarding whether or not stents ought to be utilized so frequently (or at all) to deal with chest pain. In sufferers with clinically handled angina and serious narrowing of the arterial blood vessels, this particular small study-which still must be duplicated by larger studies-found which angioplasty was not a more efficient than a sham process at minimizing associated with angina.