在GUSD初览中已经初步看过GUSD合约的代码和实现,全是文字理解起来比较困难,下面来从结构和部署图来分析下。
GUSD合约关系
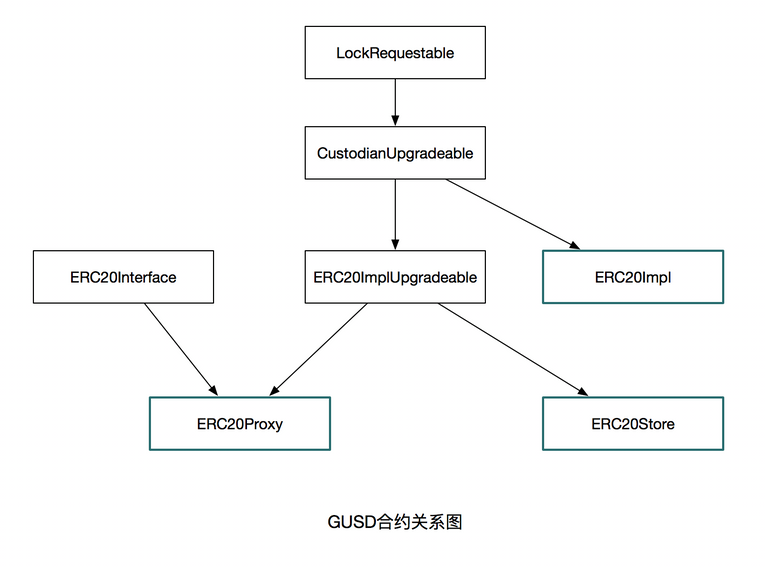
ERC20Proxy通过继承ERC20ImplUpgradeable,可以调用ERC20Impl合约。
ERC20Impl里有两个合约对象,一个是ERC20Proxy,一个是ERC20Store,ERC20Proxy只是传递一些事件,如:
erc20Proxy.emitApproval(_sender, _spender, _value);
而ERC20Store是真正的数据存储。
ERC20Proxy和ERC20Impl是互相引用,主要是ERC20Proxy调用ERC20Impl,而ERC20Impl只是事件通知时会调用ERC20Proxy。
GUSD合约部署

Custodian只用在以下几个函数用来判断:
function confirmCustodianChange(bytes32 _lockId) public onlyCustodian {
custodian = getCustodianChangeReq(_lockId);
delete custodianChangeReqs[_lockId];
emit CustodianChangeConfirmed(_lockId, custodian);
}
function confirmImplChange(bytes32 _lockId) public onlyCustodian {
erc20Impl = getImplChangeReq(_lockId);
delete implChangeReqs[_lockId];
emit ImplChangeConfirmed(_lockId, address(erc20Impl));
}
function confirmPrint(bytes32 _lockId) public onlyCustodian {
PendingPrint storage print = pendingPrintMap[_lockId];
// reject ‘null’ results from the map lookup
// this can only be the case if an unknown `_lockId` is received
address receiver = print.receiver;
require (receiver != address(0));
uint256 value = print.value;
delete pendingPrintMap[_lockId];
uint256 supply = erc20Store.totalSupply();
uint256 newSupply = supply + value;
if (newSupply >= supply) {
erc20Store.setTotalSupply(newSupply);
erc20Store.addBalance(receiver, value);
emit PrintingConfirmed(_lockId, receiver, value);
erc20Proxy.emitTransfer(address(0), receiver, value);
}
}
简单说就是确认Custodian地址变化、确认ERC20Impl变化、确认token增发。
可以看出ERC20Proxy是不能升级(真正的ERC20合约发布地址,肯定是不能随便改),能够升级或者需要升级的就是ERC20Impl合约,而ERC20Impl中又引用了ERC20Store,所以这两者都是可变化的。
结论
GUSD合约关系和部署已经比较清晰了,通过Custodian(这个也是合约,实现了2/N的签名机制,有空再分析)进行中心化控制,可更新合约,修改发行量等,设计还是比较巧妙,值得学习。
Hello! Your post has been resteemed and upvoted by @ilovecoding because we love coding! Keep up good work! Consider upvoting this comment to support the @ilovecoding and increase your future rewards! ^_^ Steem On!

Reply !stop to disable the comment. Thanks!