
British Columbia experiences at least an earthquake every day, nevertheless, only a little number if these earthquakes are being brought to notice and some of these quakes results into colossal damages.
British Columbia has witnessed several amount of earthquakes in the past and scientific analysis now show that more Earthquakes will emmerge in the future.
We humans are being laid at a high level of risk due to the dangers attached to these geoligical processes that takes place in the earth crust of British Columbia, BC.
Plates in the surface of the earth sometimes shift to produce earthquake and with the help of the science of geology, we can now discern among various grounds and be able to know the types of ground that can be affected by earthquakes.
The paramount step in making sure your own safety is guaranteed is to understand the answers to the following questions:
WHAT CAUSES EARTHQUAKES?
A sudden release of an energy that occur is oweing to the shaking motion of an earthquake. What am i trying to pinpoint here?
We witness earthquakes whenever stress, building up within rocks of the earth's crust, is being released in a jolt. Rocks crack and slip past each other which in turn results into the vibration of the ground.
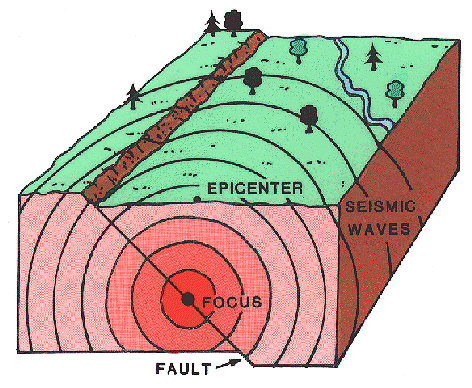
Relationship between the focus of an earthquake and the epicentre
Know this; Cracks along which rocks slips are referred to as FAULTS
Its either these faults break through the ground surface or pierce deep within the earth. On this same fault we are talking about, we call the area in which the slip first occur, FOCUS. Yeah! We call it Focus. Ans also, the position that is directly above the focus and above the ground surface is referred to as the EPICENTRE. see the image above.
Earthquakes rarely occur at the surface of the earth but at some reasonable amount of depth below the ground even to as deep as 720km. Therefore, Based on the depth of the focus, Earthquakes can be grouped into the following:
Shallow- when the depth is less than 60km,
Intermediate- when the depth is between 60 and 300km,
Deep- when the depth is above 300km.
HOW BIG ARE EARTHQUAKES?
The size of an earthquake can be measured in two ways. The intensity measures the fierceness of the earthquake while the magnitude measures the release of energy as a result of the earthquake.
In terms of Intensity, we have:
- instrumental- not felt by people except with the help of seismographs.
- feeble- felt only by a few persons at rest especially those occupying the upper floor of a building or structure.
- moderate- felt indoors by many persons
- strong- felt by all, many persons got frightened and run outdoors, some heavy furniture could shift position.
- very strong- general alarm, people run outside for safety.
- disastrous- ground cracks so badly, many number of buildings destroyed.
catastrophic- complete destruction of properties, ground rises and falls in waves and objects thrown into the air.
In terms of Magnitude, we have:
Let A= Magnitude and
Let B= Number of earthquake per year globally.
If A is > 8.0,
B is 0.1-0.2
If A is 7.4-8.0,
B is 4
If A is 7.0-7.3,
B is 15
If A is 4.9-5.4,
B is 1400
If A is 3.5-4.2,
B is 30000
If A is 2.0-3.4,
B is 800000.
WHERE DO EARTHQUAKES OCCUR?
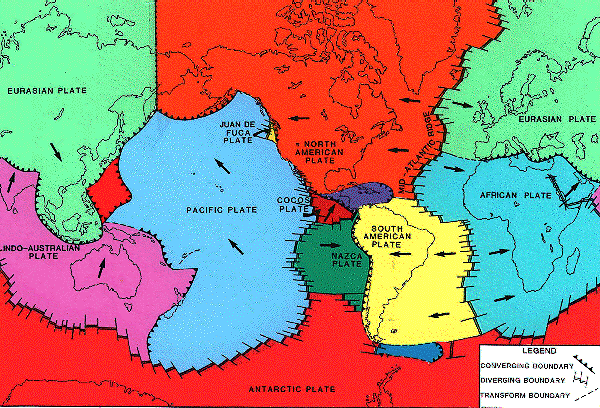
Earthquakes occur most often on, or near, the edges of plates where stress is concentrated the most.
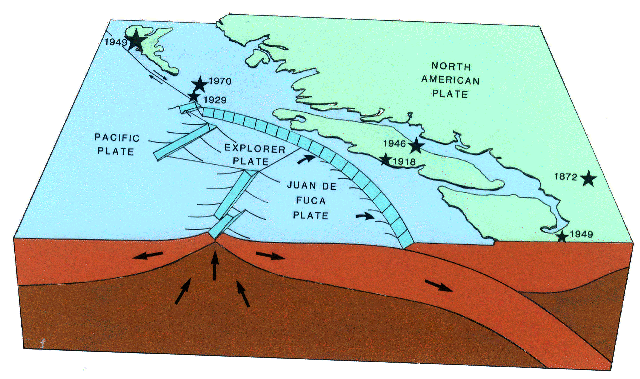
Just off the west coast, four plates meet and interact making offshore B.C. the most active earthquake zone in Canada.
In the north, there is a major transform fault boundary amidst the Pacific and the North American plates called the Queen Charlotte fault. This fault was the site, in 1949, of Canada's largest earthquake.
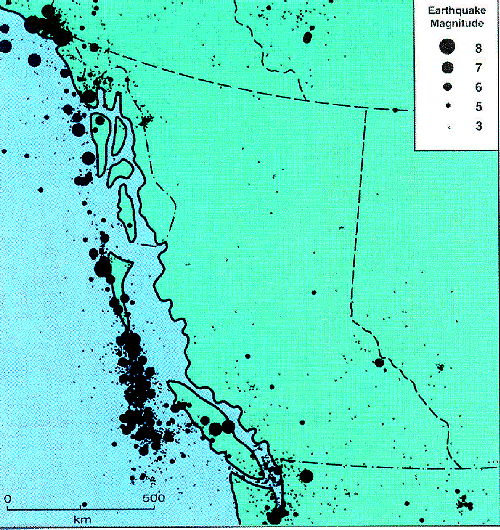
Earthquake Patterns
The location of several earthquakes that occured in B.C. are shown pictorially below, most of these earthquakes are not really noticed by people.. See the image below for proper explanation:
Along the Canadian west coast, Earthquakes large enough to cause these earthquakes do occur at about every 10 years. In the past lets say 100 years ago, several number of major earthquakes have occured in the B.C. or along its coast.
WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF EARTHQUAKES?
- Strong ground shaking,
- Ground failure, and
- Tsunami.
The intensity as we've seen earlier depends on sevaral factors which are:
- The magnitude of the quake
- Distance of the focus
- Types of soil on the site.
The 2 Largest Earthquakes in the past:
In 1964, the earthquake in Alaska has a magnitude of 9.2 which results into Tsunami damage in vancouver island.
In 1949, There was an earthquake in Queen Charlotte Island with a magnitude of 8.1 and it happens to be the largest earthquake in Canada, one of the world's great quake.
HOW CAN GEOLOGY BE USED TO MINIMIZE RISK?
The resulting damage from an earthquake is influenced by these three (3) important geological processes:
AMPLIFICATION -- The severity of ground shaking is often caused by the type and depth of the soil affected.
LIQUEFACTION -- These shakings as a result of an earthquake can cause the change in form of a sediment such as, sand and mud, into a fluid mass.
LANDSLIDES -- This happens in mountainous slopes and its one of the major causes of damage emanating from an earthquake.
Earthquakes are an unavoidable phenomenous natural disaster but their destructive power can be minimized by Geological Studies,, Proper Planning,, and A well informed people.
I hope you have learnt something tangible today as a result of this research..
Thanks for your time


Awesome explain Earthquakes thanks.
You received a 10.0% upvote since you are not yet a member of geopolis and wrote in the category of "geology".
To read more about us and what we do, click here.
https://steemit.com/geopolis/@geopolis/geopolis-the-community-for-global-sciences-update-4
Wow!! This is a great article @gabeman, keep up the great wok.
thanks @menoski