A Profile of Main Chain and Side Chain
Main Chain
A main chain refers to an independent blockchain network that is officially put into operation. Let’s put it this way: the main chain itself is generally the equivalent of data storage of a blockchain. Typical examples include main chains of Bitcoin, Ethereum and the upcoming EOS.
Side Chain
Above all, a side chain protocol is essentially a cross-chain solution, which enables data transfer between individual blockchains. The concept of side chain was initially introduced to allow circulation of Bitcoin and other digital assets among multiple blockchains.
In layman’s terms, side chains are paths that connect different blockchains in order to extend the system. Although the side chain keeps independent of the main chain, the two ledgers are actually interoperable to ensure effective interaction between them.

‘Fork’ is one of the terms frequently mentioned with the side chain. What’s that then?
Let’s take Bitcoin as an example. Generally, Bitcoin forks generate to form different branch chains in case of divergences, such as circumstances when the Bitcoin network is under malicious attack, the miner does not upgrade the software on time or developers hold different ideas about the development of Bitcoin network. As you can see, forks and side chains are so not alike in all ways.
Why Side Chain Technology is Great?
So many functionalities impossible on the main chain could be supported and improved on side chains. By building side chains, we can easily create smart contract stakes, futures and other derivatives. While a blockchain network has only one main chain, it is possible to build tens of thousands of side chains to fulfill various functions. They are the key that has opened a door of possibilities for the world of blockchain.
Side chains make the main chain safer. This is because side chains allow protocol upgrade in a different way, or they could play the role of the fire wall, which protects the main chain from damage when a single side chain is trapped in a disaster.
A bunch of platforms, including RSK, MimbleWimble, and Bitcoin Hivemind are working vigorously on the development of side chain technology, and the arena is getting crowded as more players step in.
Gaia Parachain — A Unique Side-chain Technology by GaiaWorld
Side chain technology provides developers with a new application mode of parachain. Although parachains are created using the same coding system and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithm as the main chain, every one of them is basically an independent blockchain as it forms a network of nodes on its own, and has relatively standalone code and data system. That’s why parachains do not put burdens on the main chain in operation and quite the contrary, they prevent data over-expansion.
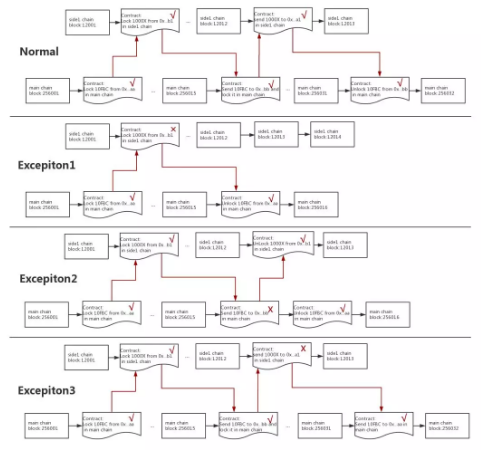
In the system of Gaia Parachain, the main chain and side chains mutually benefit from each other: the main chain provides fundamental functions for side chain operation, such as writing database, network communication and encryption; whereas the side chains supplement more nodes to the main chain to keep the system growing, and in turn support the main chain and make it more secure if they could drawn enough nodes. The main chain and side chain transmit messages and transfer values through the value exchange channel between them.
Gaia Parachain is just streets ahead of many other rival options today in terms of technical feasibility and scalability. It aims at the root of scalability problem and is a better solution to mitigation of chain jams.