
Fast-food is a masterful marketing scheme.
Americans are obsessed with fast-food. It is cheap, fast, easy and tastes good. McDonalds revolutionized fast food by cutting costs at every corner. They put workers in charge of one task, boosting efficiency and building a systematic machine from farm to table. Everything was intentional designed, and they sparked a new wave of food production. One that reaps profit at the cost of human lives.
If a consumer isn't satisfied with a product, they will voice their concern by choosing an alternative product. But, in the case of food production, customers have been inundated with propaganda which has kept them under a veil of ignorance.
And, it's not just fast-food. Big companies like Monsanto want you to think that they are sustainable and ethical. The food industry is an incredibly well marketed machine. They have convinced an entire nation that they put the customer first. Yet, they oppose GMO labeling, mislead people about where there food comes from, neglect safe practices which leads to foodborne illnesses, target marginalized communities, lobby to keep consumers in the dark, mistreat animals, treat their workers poorly, and much more.
That said, there has been a strong push for organic and non-GMO foods over the past decade. This has definitely made an impact, but we still have a ways to go before we have a transparent, profitable, sustainable and healthy food system.
How can Blockchain fix the food industry?
If you're not familiar with the Blockchain or only have a vague idea about what it is, here are a few resources I recommend, ordered by your level of expertise:
- BEGINNER [2:19 min] General introduction to the Blockchain
- INTERMEDIATE [5:59 min] A broad technical overview of the Blockchain
- ADVANCED [26:20 min] A fairly comprehensive description
Recommended reading: 'How Blockchain technology could transform the food industry' and 'How can blockchain help helpless farmers?'
Prefer infographics? Check out my infographic compilation here.
Back to the food industry. Here are some ways Blockchain can fundamentally change the way we grow, produce and consume food.
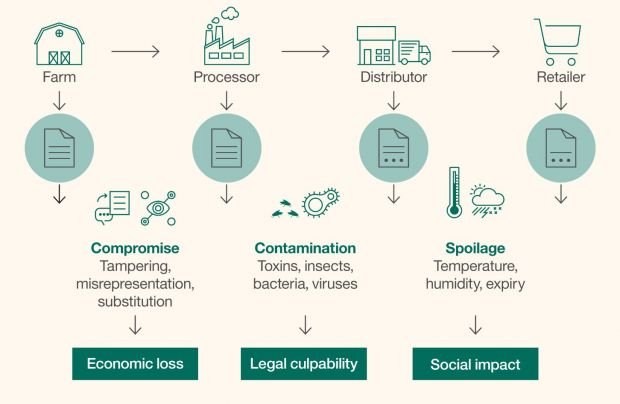
Food safety and traceability
Blockchain can improve overall transparency of the food supply chain to the benefit of both consumers and producers. If a food disaster were to strike, Blockchain technology would enable nearly every consumer to instantaneously track the origins of their food. Producers would be able to reduce the time it takes them to stop the spread of an illness, 2.2 seconds in Walmart's case. Also, reducing the time it takes for food to travel from point A to B, decreases the chance of an outbreak.
Consumers generally don't know where there food is coming from. Imagine if that changed. Blockchain makes that possible.
Preventing fraud
Blockchain is decentralized making it more difficult to tamper with. Misrepresenting, mislabeling, substituting or tampering with any food product at any point along the farm–to–table food supply–chain is considered food fraud.Compliance data is stored in centralized servers making them prone to manipulation. Blockchain secures this information but it also facilitates communication and data-sharing between actors in the food chain. Food fraud is subtle but more common than you probably though.
Equitable and fast payment
Blockchain will ensure that farmers, and every other participant in the food supply chain, get paid more quickly. Farmers face price coercion and retroactive payments, both of which would be limited by using a Blockchain. Middlemen do not always play to the farmer's benefit.The Blockchain can be empowering for farmers, especially ones that rely on marketing boards. In some countries, the problem is severe; middlemen will steal produce, leaving farmers with very little. Cryptocurrencies can play a role in facilitating faster and trusted transactions.
Reducing food wasted
More than a 1/3 of all food farmed is wasted costing the food industry upwards of one trillion dollars every year. The Blockchain can help identify bottlenecks that are contributing to spoilage. Ultimately, when a system is transparent and autonomous, it can be examined much more closely.
Disclaimer
Keep in mind that, in most cases, Blockchain needs to be adopted by a large body of people before it benefits a system. That said, when a company like Walmart develops their own Blockchain, we are sure to see the impact.
Case studies:
Further learning:
https://gro-intelligence.com/insights/blockchain-in-agriculture
https://www.foodlogistics.com/technology/article/12382466/blockchain-next-on-food-supply-chain-menu
https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/nl/Documents/consumer-business/deloitte-nl-cb-blockchain-in-the-food-chain.pdf
https://www.sklkommentus.se/globalassets/kommentus/bilder/publication-eng-blockchain-for-food-traceability-and-control-2017.pdf

There is a new blockchain technology for food traceability: OLIVACOIN
https://steemit.com/blockchain/@phdismael/re-dcaroa-re-juanfb-la-trazabilidad-basada-en-blockchain-cambia-la-forma-en-que-documentamos-la-calidad-20181123t133100391z