What does “European Added Value” (EAV) means to the European Commission (EC)? It is EC’s basic guiding principle behind proposing legislation, budgeting, implementing and managing the business of the EU since 2014.

European Commission introduced the concept of the European added value (EAV) when it released its EU budget proposal for 2014 to 2020. According to the EC, the added value "is best defined as the value resulting from an EU intervention which is additional to the value that would have been otherwise created by member states alone".
The assumption is that in certain areas where, for example, economies of scale come into play,
"a euro spent at the EU level brings more benefits than if spent at the national or regional level."
Since its introduction, EAV has become an important communication tool to prove to the EU citizens that EU funds are well spent and that they offer a better deal compared to national spending. As a precondition for the legitimacy of the EU budget, EAV helps to create transparency about the benefits of EU cooperation in areas in which the EU should act by legislating, policy-making or financing. The added value can consist of greater effectiveness, or complementarity, improved coordination, or enhanced legal certainty.
An investment is considered value-added when it has relevance and significance for the EU as a whole and not just for the region or country concerned.
Transnational cooperation helps to reduce regional disparities and increases cohesion in specific territories, building trust across borders and fosters European integration for a more competitive Europe. EU funding is decisive in making macro-regional strategies work, resulting in new knowledge, shared experiences and enhanced capacities that enable regions and cities to make better use of limited resources, and jointly tackle challenges that go beyond borders.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) & European Added Value
Poverty, gender equality and the remaining 15 SDGs are not just issues of each country but are European issues because all the European countries share the same challenges and should share also common solutions. EU, already a world leader in sustainability, prioritizes SDGs in all of the European Commission's 10 priorities.
Horizon Europe: The €100 Billion EAV Funding
Here's how EU has been pumping up its EAV spending for innovations since 1984 culminating into the next €100+ Billion plan to run from 2021 to 2027.
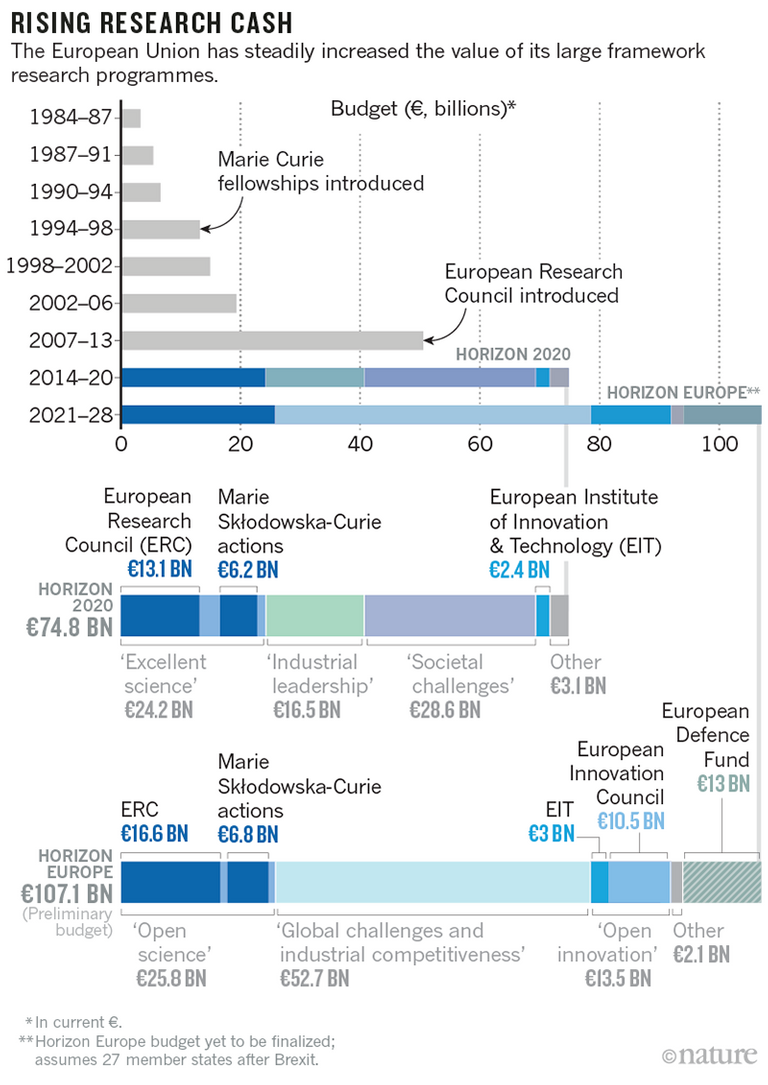
European Scientists Will Spend €100 Billion
The European Added Value Influencers
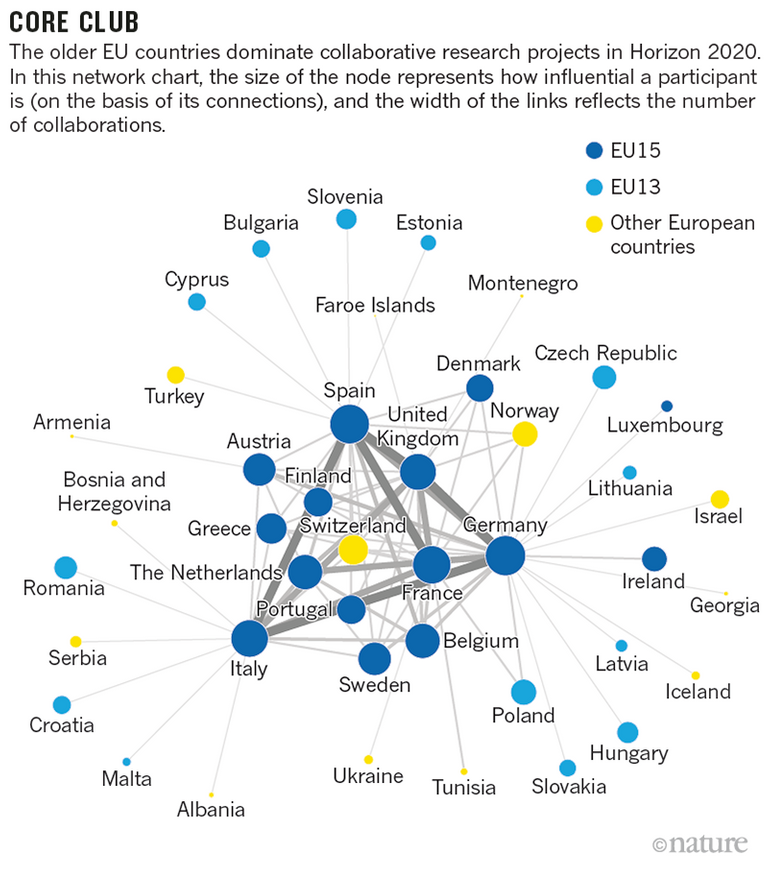
The EU's much sought after multi-year research programmes support academic and commercial research across its 28 member states and other countries that pay to join in (see 'Core club').
Source: European Commission: From Horizon 2020 to Horizon Europe
Thus EAV is the guiding principle behind all EU funding initiatives including the current Horizon 2020 program and the Horizon Europe to follow Horizon 2020.
This article was simultaneously published in Medium
I understand all Horizon 2020 proposals have to be collaborative projects, like 3 or more entities from at least 3 different European countries. Is that true?
As far as my knowledge is concerned that's mostly true. But I know at least one exception, which is SME - Instrument Phase I. I should rather say it was, because from this month the SME-I Inst is closed. It is being replaced by SME-2b SME Instrument (grant only and blended finance).
Quite familiar with Horizon 2020. Also saw the "Added Value" clause in the Horizon 2020 proposals, but didn't know "European Added Value" had an explicit technical meaning. Thanks for the info. Very helpful. :)
You are welcome dear :)
The Horizon 2020 funding is quite generous, but extremely competitive. Horizon Europe will be even more attractive.
You bet it wil be. :)
Oh so now I know why my Horizon 2020 proposal got rejected.