Hi everyone, 😊
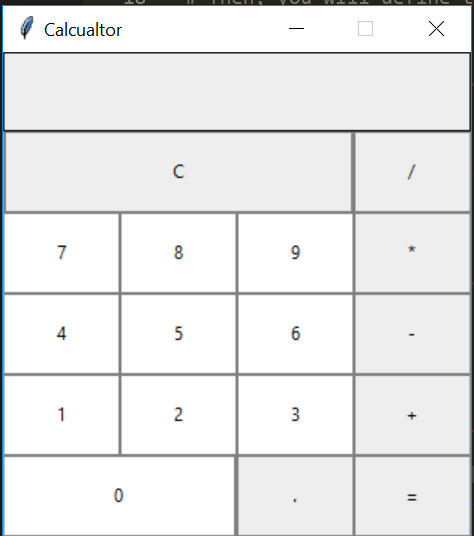
today we shall be using writing codes using python language to create a calculator,VScode is the IDE that will be used to do this,the calculator will have python builtin functions like multiplication,addition,subtraction and division,you can also use decimal point to solve a maths problem/task on this program,it is efficient and reliable, please find below the corresponding codes.
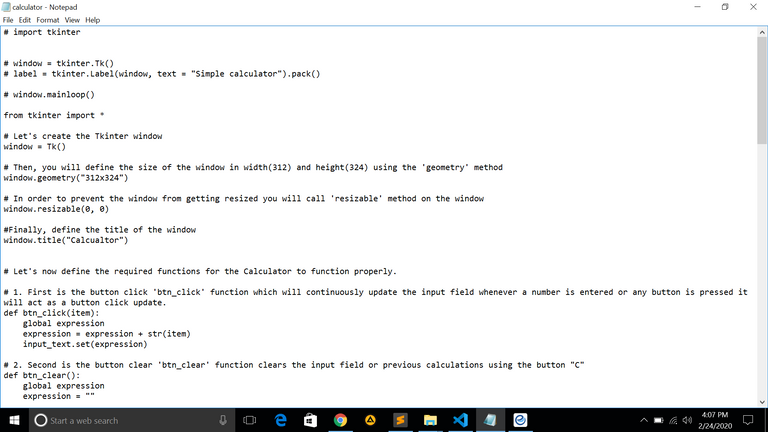
**# import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
label = tkinter.Label(window, text = "Simple calculator").pack()
window.mainloop()
from tkinter import *
firstly, create the Tkinter window
window = Tk()
{Then, you will define the size of the window in width(312) and height(324) using the 'geometry' method}
window.geometry("312x324")
{In order to prevent the window from getting a different siz,we will call 're-sizable' method on the window}
window.resizable(0, 0)
{Thirdly we will define the title of the window by naming it "calculator"}
window.title("Calcualtor")
{furthermore, we proceed defining the required functions for the Calculator to function properly}
** {1. First is the button click 'btn_click' function which will continuously updated the input field whenever an integer is entered or any button is pressed it will act as a button click update}**
def btn_click(item):
global expression
expression = expression + str(item)
input_text.set(expression)
{2. Secondly the button clear 'btn_clear' function clears the input field or previous calculations using the button "C"}
def btn_clear():
global expression
expression = ""
input_text.set("")
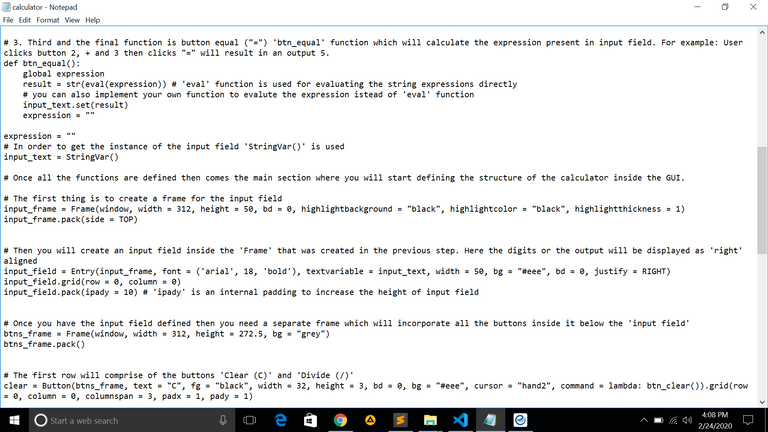
{3. Third and the final function is button equal ("=") 'btn_equal' function which will calculate the expression present in input field. For example: User clicks button 2, + and 3 then clicks "=" will result in an output 5}
def btn_equal():
global expression
result = str(eval(expression)) # 'eval' function is used for evaluating the string expressions directly
# you can also implement your own function to evalute the expression istead of 'eval' function
input_text.set(result)
expression = ""
expression = ""
In order to get the instance of the input field 'StringVar()' is used
input_text = StringVar()
** then when all the functions are defined then comes the main section where you will start defining the structure of the calculator inside the GUI**.
{The first thing is to create a frame for the input field}
input_frame = Frame(window, width = 312, height = 50, bd = 0, highlightbackground = "black", highlightcolor = "black", highlightthickness = 1)
input_frame.pack(side = TOP)
Then you will create an input field inside the 'Frame' that was created in the previous step. Here the digits or the output will be displayed as 'right' aligned
input_field = Entry(input_frame, font = ('arial', 18, 'bold'), textvariable = input_text, width = 50, bg = "#eee", bd = 0, justify = RIGHT)
input_field.grid(row = 0, column = 0)
input_field.pack(ipady = 10) # 'ipady' is an internal padding to increase the height of input field
{Once you have the input field defined then you need a separate frame which will incorporate all the buttons inside it below the 'input field'}
btns_frame = Frame(window, width = 312, height = 272.5, bg = "grey")
btns_frame.pack()
The first row will comprise of the buttons 'Clear (C)' and 'Divide (/)'
clear = Button(btns_frame, text = "C", fg = "black", width = 32, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#eee", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_clear()).grid(row = 0, column = 0, columnspan = 3, padx = 1, pady = 1)
divide = Button(btns_frame, text = "/", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#eee", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click("/")).grid(row = 0, column = 3, padx = 1, pady = 1)
The second row will comprise of the buttons '7', '8', '9' and 'Multiply ()'*
seven = Button(btns_frame, text = "7", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#fff", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(7)).grid(row = 1, column = 0, padx = 1, pady = 1)
eight = Button(btns_frame, text = "8", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#fff", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(8)).grid(row = 1, column = 1, padx = 1, pady = 1)
nine = Button(btns_frame, text = "9", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#fff", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(9)).grid(row = 1, column = 2, padx = 1, pady = 1)
multiply = Button(btns_frame, text = "", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#eee", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click("")).grid(row = 1, column = 3, padx = 1, pady = 1)
**
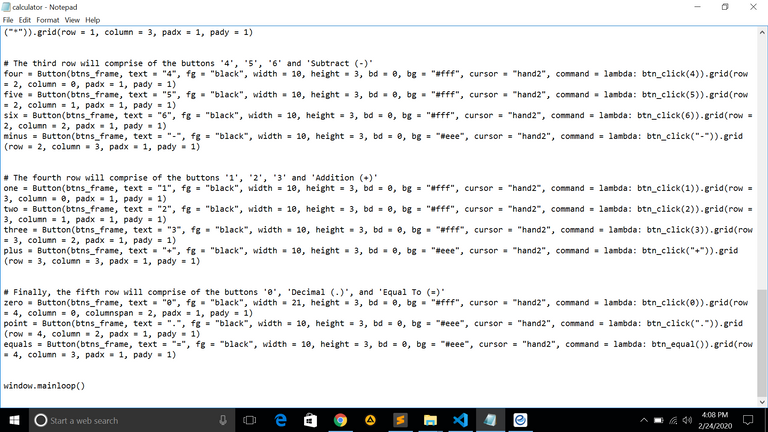
The third row will comprise of the buttons '4', '5', '6' and 'Subtract (-)**'
four = Button(btns_frame, text = "4", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#fff", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(4)).grid(row = 2, column = 0, padx = 1, pady = 1)
five = Button(btns_frame, text = "5", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#fff", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(5)).grid(row = 2, column = 1, padx = 1, pady = 1)
six = Button(btns_frame, text = "6", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#fff", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(6)).grid(row = 2, column = 2, padx = 1, pady = 1)
minus = Button(btns_frame, text = "-", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#eee", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click("-")).grid(row = 2, column = 3, padx = 1, pady = 1)
The fourth row will comprise of the buttons '1', '2', '3' and 'Addition (+)'
one = Button(btns_frame, text = "1", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#fff", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(1)).grid(row = 3, column = 0, padx = 1, pady = 1)
two = Button(btns_frame, text = "2", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#fff", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(2)).grid(row = 3, column = 1, padx = 1, pady = 1)
three = Button(btns_frame, text = "3", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#fff", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(3)).grid(row = 3, column = 2, padx = 1, pady = 1)
plus = Button(btns_frame, text = "+", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#eee", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click("+")).grid(row = 3, column = 3, padx = 1, pady = 1)
Finally, the fifth row will comprise of the buttons '0', 'Decimal (.)', and 'Equal To (=)'
zero = Button(btns_frame, text = "0", fg = "black", width = 21, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#fff", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(0)).grid(row = 4, column = 0, columnspan = 2, padx = 1, pady = 1)
point = Button(btns_frame, text = ".", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#eee", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_click(".")).grid(row = 4, column = 2, padx = 1, pady = 1)
equals = Button(btns_frame, text = "=", fg = "black", width = 10, height = 3, bd = 0, bg = "#eee", cursor = "hand2", command = lambda: btn_equal()).grid(row = 4, column = 3, padx = 1, pady = 1)
window.mainloop()
**

Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/gui-tkinter-python