What Is It?
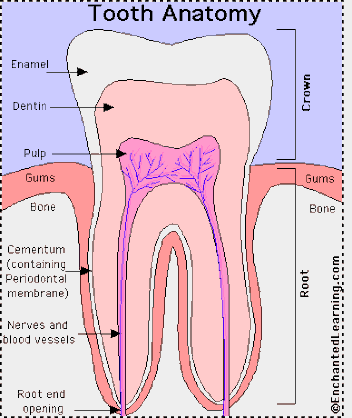
Dental caries is the scientific term for tooth decay.It is caused by specific types of bacteria that produce acid which destroys the tooth's outermost layer called Enamel and the layer under it called Dentin.
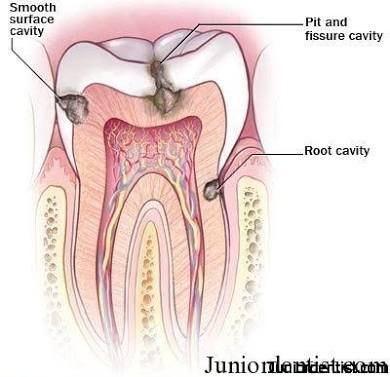
Many different types of bacteria normally live in the human mouth. They build up sticky film on the surface of the teeth called Plaque. This plaque also contains saliva, bits of food and other natural substances which gets accumulated in certain places. These include:
Cracks, pits or grooves in the back teeth and in
Between teeth
Around non polished dental fillings or bridgework
Near the gum
These bacteria turn sugar and carbohydrates (starches) in the foods that we eat into acids. This acids dissolves the minerals in the hard enamel. The enamel dissolves and develops pits. These pits are too small to see at first. But they get larger over time and become cavities.
Acid also seep through pores in the enamel. This causes decay in the softer dentin layer, the main body of the tooth. As the dentin and enamel break down, a cavity is created.
If the decay is not removed, bacteria will continue to grow and produce more acid that eventually will get into the tooth's inner layer called Pulp which is made up of sensory nerve fibers.
Tooth roots exposed by receding gums also can develop decay. The root's outer layer, cementum, is not as thick as enamel. Acids from plaque bacteria can dissolve it rapidly.
Symptoms
Early caries may not have any symptoms. Later, when the decay has pass through the enamel, the teeth may be sensitive to sweet, hot & sour foods or drinks which with passage of time results in sensation to all of the above objects along with exposure of pulp leading to sensitivity to hot objects and drinks.
Diagnosis
A dentist will look for caries at each office visit. The dentist will look at each teeth and may probe them with a tool called an explorer to look for pits or areas of damage. The problem with these methods is that they often do not catch cavities when they are just forming. Occasionally, if too much force is used, an explorer can puncture the enamel. This could allow the cavity-causing bacteria to spread to healthy teeth.
Your dentist will take X-rays of your teeth, and also if a problem is suspected. The X-rays scan shows newly forming decay, particularly between teeth. They also show the more advanced decay, including whether decay has reached the pulp and whether the tooth requires a root canal treatment.
Newer devices also can help to detect tooth decay. They are useful in some situations, and they do not spread decay. The one most commonly used in dental offices is a liquid dye or stain. Your dentist brushes the nontoxic dye over your teeth, then rinses it off with water. It rinses away cleanly from healthy areas but sticks in between the decayed areas.
Some dentists also use high-tech devices such as lasers to detect cavities. Under many conditions, these devices can detect very early tooth decay, which can actually be reversed.
Treatment
Caries is a process. If detected in early stages, tooth decay can be stopped or it can even be reversed. Fluorides and other prevention methods also help a tooth in early stages of decay to repair itself (remineralisation). White spots is the last stage of early caries.
Once caries gets worse and there is loss of enamel, only the dentist can repair the tooth. Then the standard treatment for a cavity is filling the tooth. If a drill is used, the dentist will numb (anesthetise) the area. If a laser is used, a anesthesia shot is not usually required. The decayed material in the cavity is removed and the cavity is filled.
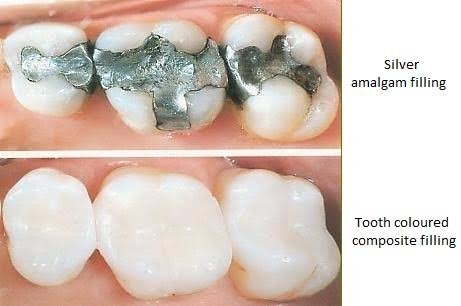
Many fillings are made of dental amalgam or composite resin.Dental Amalgam(Silver Filling) material made from silver, mercury, copper or other metals.The Silver filling is the best material of choice for Molars and Premolars because of it’s strength Composite resin offers a better appearance because it is tooth-colored. Newer resins are very durable.They are best material of choice for filling of Incisors and Canines due to its colour masking nature.
If a cavity is large or if the remaining tooth may not be able to support enough filling material to repair it. In this case, the dentist will remove the decay and cover the tooth with a ceramic inlay, onlay or artificial crown. These may be made in the office or in a lab.
Sometimes bacteria may infect the pulp inside the tooth even if the part of the tooth you can see remains relatively intact. In this case, the tooth will need Root Canal Treatment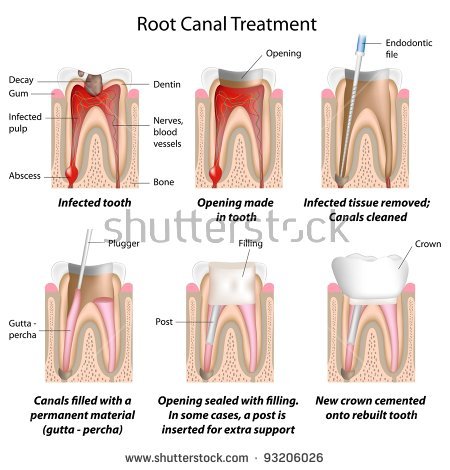
 . A general dentist or an endodontist will remove the pulp and replace it with an inert material. In most cases, the tooth will need a crown.
. A general dentist or an endodontist will remove the pulp and replace it with an inert material. In most cases, the tooth will need a crown.
✅ @inderjot001, I gave you an upvote on your post! Please give me a follow and I will give you a follow in return and possible future votes!
Thank you in advance!
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://www.colgate.com/en-us/oral-health/conditions/cavities/dental-caries-cavities